Outside-in benchmarking evaluates a company's performance by comparing it with external organizations, focusing on industry trends and competitor strategies for comprehensive market insights. Best-in-class benchmarking targets top-performing peers within the same sector to identify superior processes and practices driving excellence. Discover how these benchmarking approaches can transform your consulting strategy.
Why it is important
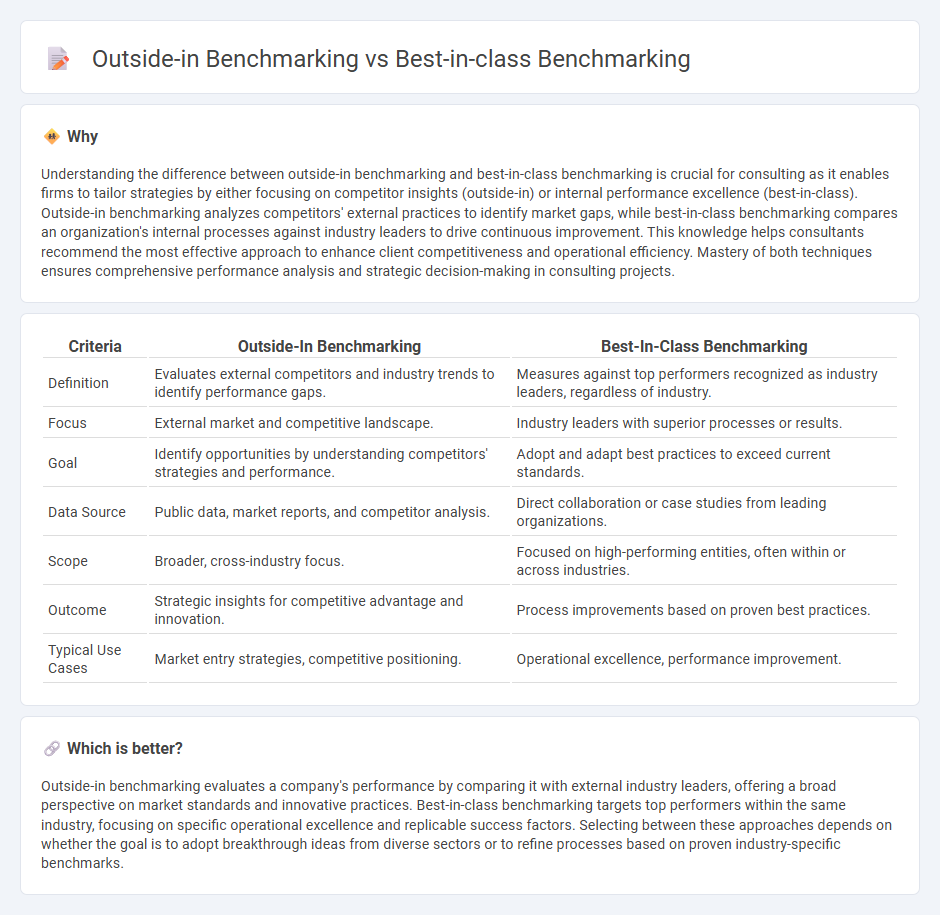
Understanding the difference between outside-in benchmarking and best-in-class benchmarking is crucial for consulting as it enables firms to tailor strategies by either focusing on competitor insights (outside-in) or internal performance excellence (best-in-class). Outside-in benchmarking analyzes competitors' external practices to identify market gaps, while best-in-class benchmarking compares an organization's internal processes against industry leaders to drive continuous improvement. This knowledge helps consultants recommend the most effective approach to enhance client competitiveness and operational efficiency. Mastery of both techniques ensures comprehensive performance analysis and strategic decision-making in consulting projects.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Outside-In Benchmarking | Best-In-Class Benchmarking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluates external competitors and industry trends to identify performance gaps. | Measures against top performers recognized as industry leaders, regardless of industry. |
| Focus | External market and competitive landscape. | Industry leaders with superior processes or results. |
| Goal | Identify opportunities by understanding competitors' strategies and performance. | Adopt and adapt best practices to exceed current standards. |
| Data Source | Public data, market reports, and competitor analysis. | Direct collaboration or case studies from leading organizations. |
| Scope | Broader, cross-industry focus. | Focused on high-performing entities, often within or across industries. |
| Outcome | Strategic insights for competitive advantage and innovation. | Process improvements based on proven best practices. |
| Typical Use Cases | Market entry strategies, competitive positioning. | Operational excellence, performance improvement. |
Which is better?
Outside-in benchmarking evaluates a company's performance by comparing it with external industry leaders, offering a broad perspective on market standards and innovative practices. Best-in-class benchmarking targets top performers within the same industry, focusing on specific operational excellence and replicable success factors. Selecting between these approaches depends on whether the goal is to adopt breakthrough ideas from diverse sectors or to refine processes based on proven industry-specific benchmarks.
Connection
Outside-in benchmarking leverages insights from external industry leaders to evaluate organizational performance, while best-in-class benchmarking identifies top-performing companies exemplifying superior practices. Both methods focus on comparing an organization's processes and outcomes against those of leading competitors to uncover gaps and opportunities for improvement. This connection enables consultants to drive strategic enhancements by integrating external perspectives with proven industry standards.
Key Terms
Performance Metrics
Best-in-class benchmarking concentrates on comparing internal performance metrics against industry leaders to identify gaps and opportunities for operational improvements. Outside-in benchmarking extends this approach by integrating external customer feedback and market trends to offer a holistic view of performance in real-world contexts. Explore in-depth analyses to understand how each benchmarking method can transform your performance evaluation strategies.
Industry Standards
Best-in-class benchmarking evaluates performance by comparing metrics against top-performing companies within the same industry, emphasizing adherence to established industry standards and operational excellence. Outside-in benchmarking examines external market factors, customer expectations, and competitor strategies beyond direct industry peers to identify innovative practices and unmet needs. Explore how leveraging both approaches can refine your strategic insights and drive superior competitive performance.
External Comparison
Best-in-class benchmarking involves comparing an organization's internal processes and performance against industry leaders to identify gaps and improvement opportunities. Outside-in benchmarking emphasizes examining competitors and market trends externally to drive innovation and customer-centric strategies. Explore more to understand how external comparison can transform business outcomes and strategic positioning.
Source and External Links
Compare and Conquer: 12 Types of Benchmarking for ... - Best-in-class benchmarking involves analyzing the leading competitor or company that excels at specific functions to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement by comparing processes and performance metrics against industry leaders.
Benchmarking - Best-in-class benchmarking, also called best practice benchmarking, studies leading firms' processes and results, allowing organizations to adopt superior practices for performance enhancement, often as a continuous improvement process.
Benchmarking: Achieving the Best in Class - Best-in-class benchmarking focuses outside the organization's industry, targeting innovative practices from top performers in specific functions to model and improve one's own processes and performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com