Digital twin simulation leverages real-time data and virtual modeling to optimize system performance, reduce costs, and predict outcomes with high accuracy. Design Thinking emphasizes user-centric innovation through iterative problem-solving and creative collaboration, fostering solutions that align with customer needs. Explore how integrating digital twin simulation with Design Thinking can revolutionize your consulting strategy.
Why it is important
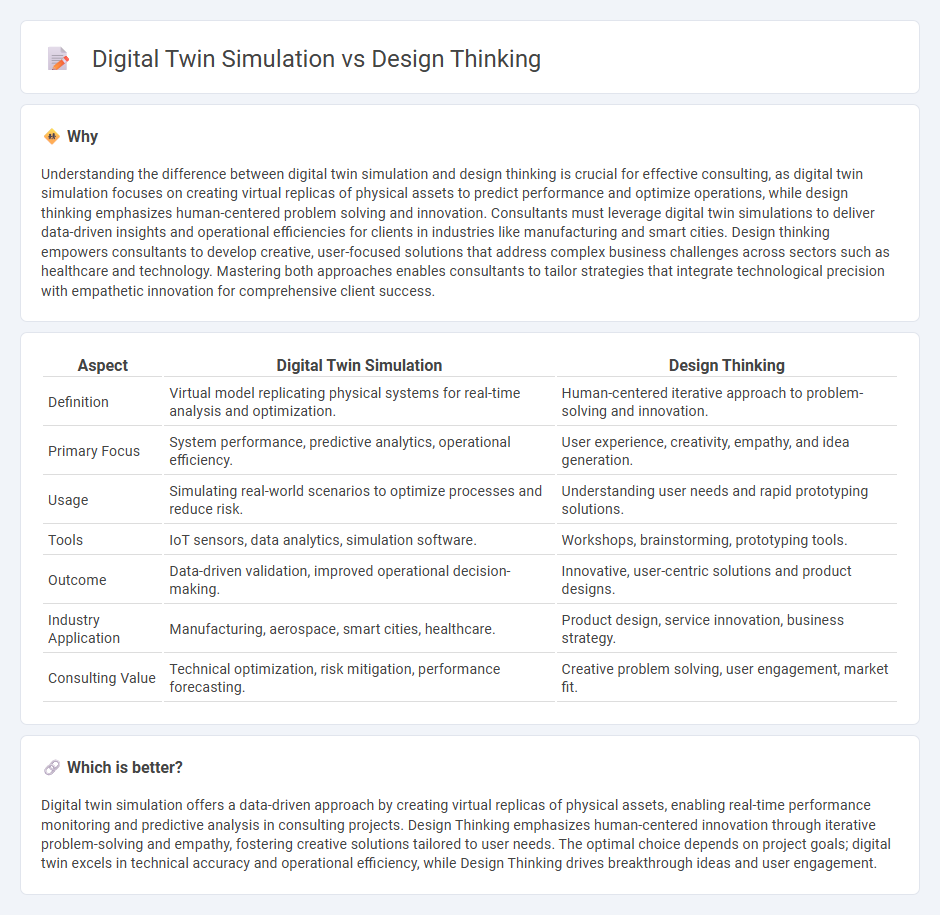
Understanding the difference between digital twin simulation and design thinking is crucial for effective consulting, as digital twin simulation focuses on creating virtual replicas of physical assets to predict performance and optimize operations, while design thinking emphasizes human-centered problem solving and innovation. Consultants must leverage digital twin simulations to deliver data-driven insights and operational efficiencies for clients in industries like manufacturing and smart cities. Design thinking empowers consultants to develop creative, user-focused solutions that address complex business challenges across sectors such as healthcare and technology. Mastering both approaches enables consultants to tailor strategies that integrate technological precision with empathetic innovation for comprehensive client success.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Digital Twin Simulation | Design Thinking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual model replicating physical systems for real-time analysis and optimization. | Human-centered iterative approach to problem-solving and innovation. |
| Primary Focus | System performance, predictive analytics, operational efficiency. | User experience, creativity, empathy, and idea generation. |
| Usage | Simulating real-world scenarios to optimize processes and reduce risk. | Understanding user needs and rapid prototyping solutions. |
| Tools | IoT sensors, data analytics, simulation software. | Workshops, brainstorming, prototyping tools. |
| Outcome | Data-driven validation, improved operational decision-making. | Innovative, user-centric solutions and product designs. |
| Industry Application | Manufacturing, aerospace, smart cities, healthcare. | Product design, service innovation, business strategy. |
| Consulting Value | Technical optimization, risk mitigation, performance forecasting. | Creative problem solving, user engagement, market fit. |
Which is better?
Digital twin simulation offers a data-driven approach by creating virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling real-time performance monitoring and predictive analysis in consulting projects. Design Thinking emphasizes human-centered innovation through iterative problem-solving and empathy, fostering creative solutions tailored to user needs. The optimal choice depends on project goals; digital twin excels in technical accuracy and operational efficiency, while Design Thinking drives breakthrough ideas and user engagement.
Connection
Digital twin simulation and Design Thinking are connected through their shared focus on iterative problem-solving and innovation. Digital twin simulation enables real-time, data-driven modeling of physical systems, allowing designers to prototype and test ideas virtually. This complements Design Thinking's user-centered approach by providing actionable insights that enhance empathy, ideation, and solution validation in consulting projects.
Key Terms
Empathy Mapping
Empathy Mapping in Design Thinking emphasizes understanding user needs and experiences to create human-centered solutions. Digital twin simulation enhances this process by providing real-time data and virtual replicas of physical systems, enabling precise analysis of user interactions and behaviors. Explore how integrating empathy mapping with digital twin technology can revolutionize product design and user experience research.
Virtual Prototyping
Virtual prototyping leverages design thinking to iteratively explore user-centered solutions, while digital twin simulation provides real-time, data-driven virtual replicas for performance testing and optimization. Integrating digital twin simulation within the design thinking framework accelerates product development by enabling dynamic scenario analysis and informed decision-making. Discover how combining these approaches enhances innovation and reduces time-to-market in virtual prototyping.
Iterative Testing
Design Thinking incorporates iterative testing by emphasizing user feedback and rapid prototyping to refine solutions continuously. Digital twin simulation enhances iterative testing through real-time data integration and predictive analytics, enabling virtual experimentation and optimization of physical systems. Explore how combining these approaches accelerates innovation and improves design accuracy.
Source and External Links
What is Design Thinking? -- updated 2025 | IxDF - Design thinking is a non-linear, iterative, human-centered process involving five phases--Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test--that helps teams understand users, challenge assumptions, and create innovative solutions primarily by starting with desirability before feasibility and viability.
Design thinking - Wikipedia - Design thinking is a set of cognitive, strategic, and practical procedures used by designers to solve complex problems, characterized by a designerly way of thinking that has evolved since the 1950s and applies across diverse domains for innovation in products and services.
What is Design Thinking & Why Is It Beneficial? - IDEO U - Design thinking is a human-centered, collaborative approach that balances empathy, creativity, and experimentation to design solutions that are desirable, feasible, viable, and responsible, enabling teams to tackle challenging problems with bold, actionable ideas.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com