Regenerative business models focus on restoring and revitalizing natural ecosystems while creating long-term economic value, surpassing traditional Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) which often centers on mitigating harm. By integrating circular economy principles and stakeholder engagement, regenerative approaches drive innovation and resilience in businesses. Explore how consulting can guide organizations in transitioning from CSR to regenerative strategies for sustainable growth.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between regenerative business models and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is crucial for driving sustainable impact in consulting. Regenerative business models focus on restoring and enhancing natural and social systems, creating long-term value, whereas CSR often emphasizes compliance and philanthropy without fundamentally altering business operations. Consultants must distinguish these approaches to guide clients in adopting strategies that foster resilience, innovation, and systemic change. This knowledge enables the design of transformative solutions that align profitability with planetary and societal well-being.
Comparison Table
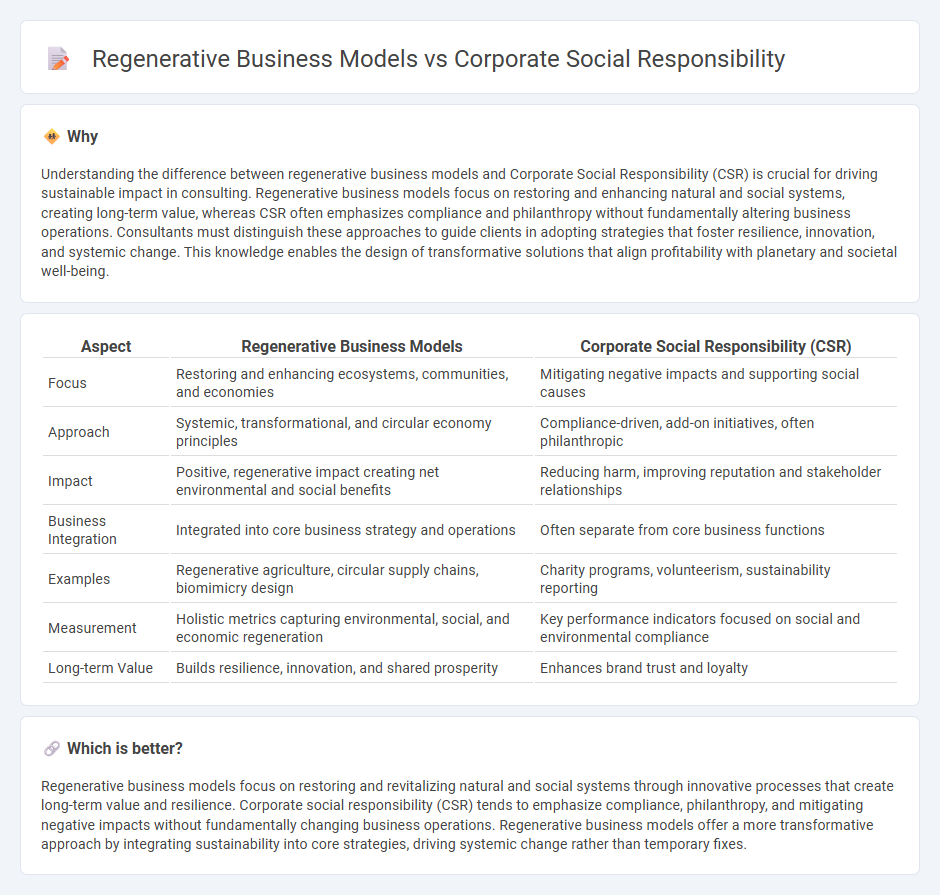
| Aspect | Regenerative Business Models | Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Restoring and enhancing ecosystems, communities, and economies | Mitigating negative impacts and supporting social causes |
| Approach | Systemic, transformational, and circular economy principles | Compliance-driven, add-on initiatives, often philanthropic |
| Impact | Positive, regenerative impact creating net environmental and social benefits | Reducing harm, improving reputation and stakeholder relationships |
| Business Integration | Integrated into core business strategy and operations | Often separate from core business functions |
| Examples | Regenerative agriculture, circular supply chains, biomimicry design | Charity programs, volunteerism, sustainability reporting |
| Measurement | Holistic metrics capturing environmental, social, and economic regeneration | Key performance indicators focused on social and environmental compliance |
| Long-term Value | Builds resilience, innovation, and shared prosperity | Enhances brand trust and loyalty |
Which is better?
Regenerative business models focus on restoring and revitalizing natural and social systems through innovative processes that create long-term value and resilience. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) tends to emphasize compliance, philanthropy, and mitigating negative impacts without fundamentally changing business operations. Regenerative business models offer a more transformative approach by integrating sustainability into core strategies, driving systemic change rather than temporary fixes.
Connection
Regenerative business models prioritize restoring ecological systems while creating long-term value, deeply integrating Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) principles to address environmental and social impacts. CSR initiatives support regenerative approaches by encouraging sustainable practices, ethical governance, and community engagement that drive positive change beyond profit maximization. The synergy between these frameworks fosters resilient businesses that contribute to planetary health and stakeholder well-being simultaneously.
Key Terms
Sustainability
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) emphasizes companies' efforts to minimize environmental harm and contribute positively to society, whereas regenerative business models go beyond sustainability by actively restoring and enhancing ecosystems through their operations. Regenerative businesses integrate circular economy principles, renewable energy adoption, and social equity to create systems that are both economically viable and environmentally restorative. Explore how shifting from CSR to regenerative practices can transform sustainability strategies for lasting impact.
Stakeholder engagement
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) emphasizes ethical practices and community support, often focusing on minimizing negative impacts on stakeholders. Regenerative business models go further by actively restoring and enhancing social, environmental, and economic systems through deep stakeholder collaboration and innovation. Explore how shifting from CSR to regenerative approaches can transform stakeholder engagement and drive sustainable value creation.
Value creation
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) emphasizes ethical practices and community engagement to enhance brand reputation and stakeholder trust. Regenerative business models prioritize restoring environmental and social systems, aiming for long-term value creation beyond profit by integrating circular economy principles. Explore how shifting from CSR to regenerative strategies can drive sustainable value generation across industries.
Source and External Links
What is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)? Guide & Examples - Corporate social responsibility (CSR) involves a company's voluntary efforts to improve society through initiatives such as charitable donations, environmental sustainability, diverse hiring, and community engagement, aiming to give positive social value beyond profit.
Corporate social responsibility - Wikipedia - CSR is a form of private business self-regulation that contributes to societal goals via philanthropy, ethical business practices, and increasingly mandatory standards, moving from voluntary corporate ethics to regulated impacts on communities.
What Is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)? - CSR ensures a company's daily operations are ethical and beneficial to society, with examples from companies like Google, LEGO, and Starbucks showing commitments to sustainability, ethical sourcing, and community support.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com