Algorithmic auditing involves systematically evaluating algorithms for bias, accuracy, and compliance with regulatory standards, ensuring transparency in automated decision-making processes. Change management focuses on guiding organizations through transitions by aligning people, processes, and technology with strategic goals to minimize disruption and enhance adoption. Explore how integrating algorithmic auditing with change management can drive responsible innovation in your enterprise.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between algorithmic auditing and change management is crucial for consultants to ensure ethical AI deployment and organizational adaptability. Algorithmic auditing focuses on evaluating AI systems for bias, accuracy, and compliance with regulations. Change management involves guiding teams through transitions to new processes or technologies to minimize disruption and maximize adoption. Accurate differentiation optimizes strategic interventions and mitigates risks in tech-driven projects.
Comparison Table
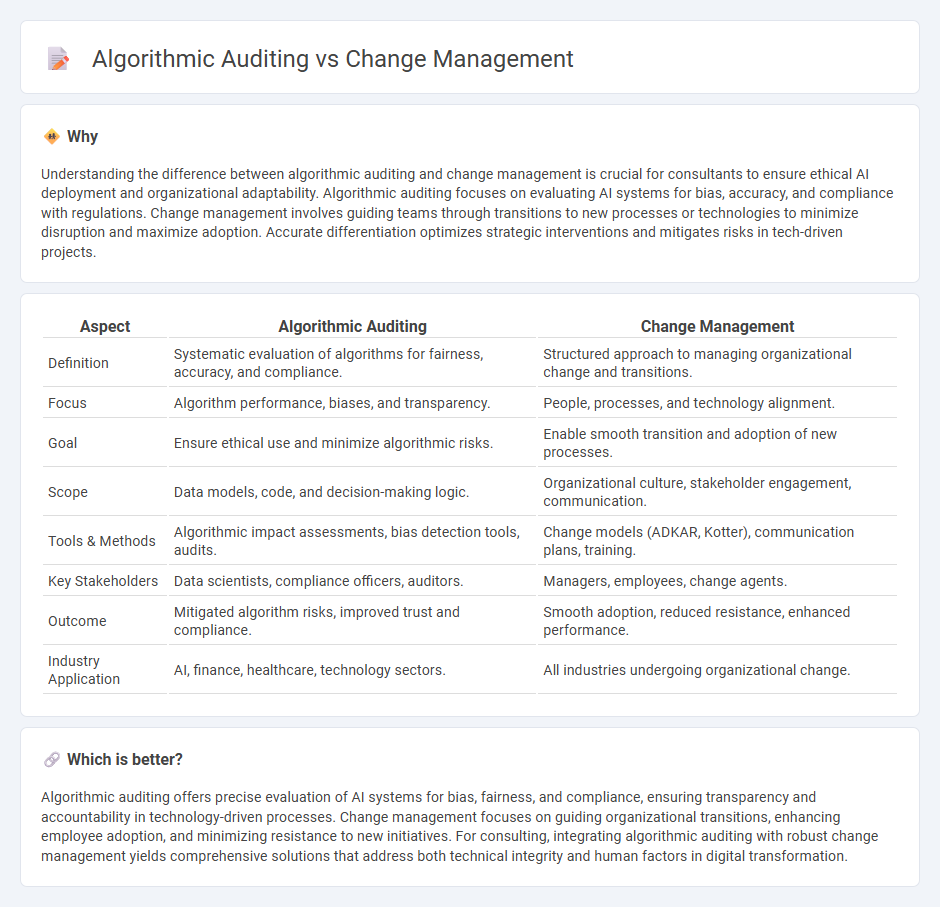
| Aspect | Algorithmic Auditing | Change Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic evaluation of algorithms for fairness, accuracy, and compliance. | Structured approach to managing organizational change and transitions. |
| Focus | Algorithm performance, biases, and transparency. | People, processes, and technology alignment. |
| Goal | Ensure ethical use and minimize algorithmic risks. | Enable smooth transition and adoption of new processes. |
| Scope | Data models, code, and decision-making logic. | Organizational culture, stakeholder engagement, communication. |
| Tools & Methods | Algorithmic impact assessments, bias detection tools, audits. | Change models (ADKAR, Kotter), communication plans, training. |
| Key Stakeholders | Data scientists, compliance officers, auditors. | Managers, employees, change agents. |
| Outcome | Mitigated algorithm risks, improved trust and compliance. | Smooth adoption, reduced resistance, enhanced performance. |
| Industry Application | AI, finance, healthcare, technology sectors. | All industries undergoing organizational change. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic auditing offers precise evaluation of AI systems for bias, fairness, and compliance, ensuring transparency and accountability in technology-driven processes. Change management focuses on guiding organizational transitions, enhancing employee adoption, and minimizing resistance to new initiatives. For consulting, integrating algorithmic auditing with robust change management yields comprehensive solutions that address both technical integrity and human factors in digital transformation.
Connection
Algorithmic auditing identifies biases and inefficiencies in automated systems, providing actionable insights for targeted improvements. Change management leverages these insights to implement structured modifications, ensuring smooth adaptation and stakeholder alignment. This connection enhances algorithm reliability and organizational agility in consulting projects.
Key Terms
**Change Management:**
Change management involves structured approaches to transitioning individuals, teams, and organizations to a desired future state by managing resistance, communication, and training effectively. It emphasizes stakeholder engagement, leadership alignment, and continuous feedback to ensure smooth adoption of new processes or technologies. Explore how strategic change management can drive successful organizational transformation and sustainability.
Stakeholder Engagement
Stakeholder engagement in change management emphasizes active communication, collaboration, and resistance mitigation to ensure successful adoption of organizational changes. In algorithmic auditing, stakeholder engagement focuses on transparency, accountability, and including diverse perspectives to identify biases and ethical concerns in algorithmic systems. Explore deeper insights on how effective stakeholder involvement varies between these critical processes.
Communication Strategy
Effective communication strategy plays a crucial role in change management by ensuring clear messaging, stakeholder engagement, and minimizing resistance during organizational transformations. In contrast, algorithmic auditing demands transparent communication about data use, ethical considerations, and audit outcomes to build trust and accountability in AI systems. Explore deeper insights into how tailored communication approaches enhance both change management and algorithmic auditing success.
Source and External Links
The 10 Best Organizational Change Management Strategies - Change management is a structured approach to transition individuals and organizations to a desired future state by planning, implementing, and reinforcing changes, minimizing resistance, maximizing engagement, and aligning everyone with new organizational directions for competitive adaptability and resilience.
What is Change Management? Definition & Process - Change management involves creating clear vision and objectives, providing training and support, addressing resistance, and monitoring progress to ensure sustainable adoption of organizational changes and alignment of all stakeholders with the change goals.
What is Change Management? - Change management is a method used by organizations to communicate and implement change by supporting people and processes through a structured approach that includes engaging employees as change agents and tailoring strategies to different levels of employee experience and change impact.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com