Sustainability benchmarking evaluates a company's overall environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance against industry standards to drive long-term strategic goals. Carbon footprinting specifically measures the total greenhouse gas emissions produced directly or indirectly by an organization, providing a focused metric for climate impact reduction. Explore the differences and benefits of sustainability benchmarking versus carbon footprinting to optimize your consulting strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sustainability benchmarking and carbon footprinting is crucial for effective environmental strategy; sustainability benchmarking evaluates overall environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance against industry standards, while carbon footprinting focuses specifically on measuring greenhouse gas emissions. Accurate sustainability benchmarking helps organizations identify comprehensive improvement areas beyond emissions, ensuring balanced resource allocation and stakeholder engagement. Carbon footprinting provides precise data for setting emission reduction targets and complying with regulatory requirements. Knowing these distinctions enables consultants to tailor solutions that align with clients' strategic goals and sustainability commitments.
Comparison Table
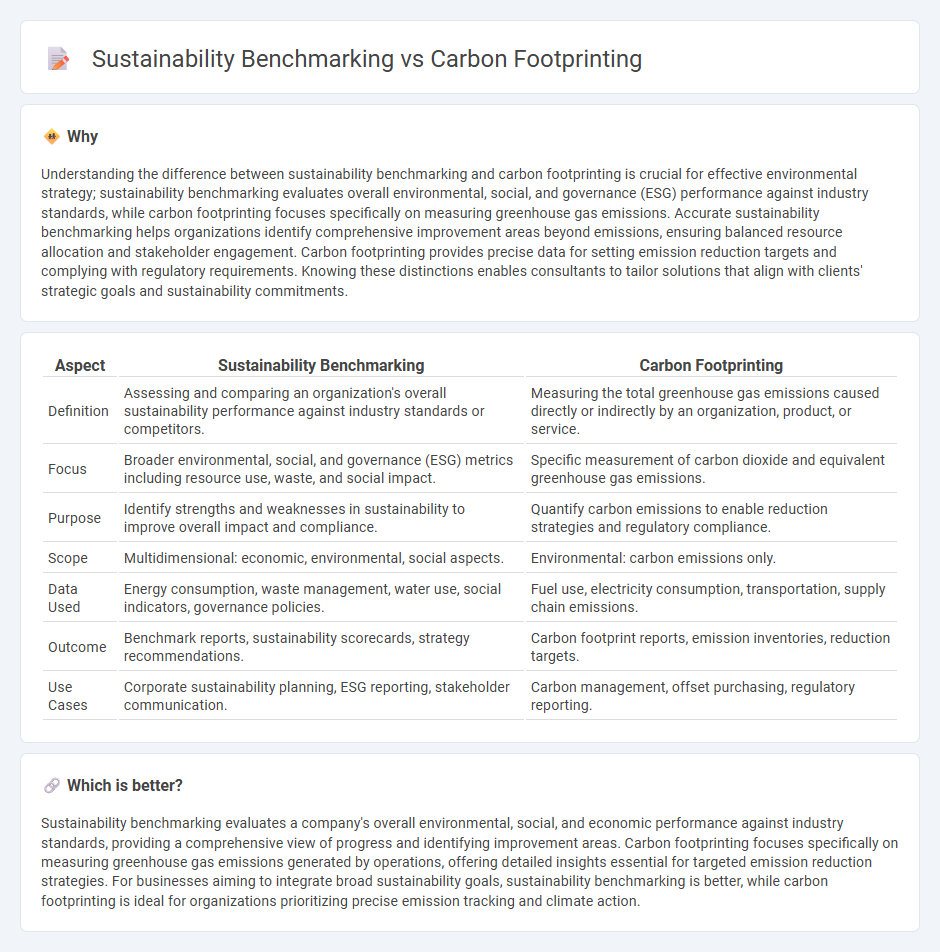
| Aspect | Sustainability Benchmarking | Carbon Footprinting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assessing and comparing an organization's overall sustainability performance against industry standards or competitors. | Measuring the total greenhouse gas emissions caused directly or indirectly by an organization, product, or service. |
| Focus | Broader environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics including resource use, waste, and social impact. | Specific measurement of carbon dioxide and equivalent greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Purpose | Identify strengths and weaknesses in sustainability to improve overall impact and compliance. | Quantify carbon emissions to enable reduction strategies and regulatory compliance. |
| Scope | Multidimensional: economic, environmental, social aspects. | Environmental: carbon emissions only. |
| Data Used | Energy consumption, waste management, water use, social indicators, governance policies. | Fuel use, electricity consumption, transportation, supply chain emissions. |
| Outcome | Benchmark reports, sustainability scorecards, strategy recommendations. | Carbon footprint reports, emission inventories, reduction targets. |
| Use Cases | Corporate sustainability planning, ESG reporting, stakeholder communication. | Carbon management, offset purchasing, regulatory reporting. |
Which is better?
Sustainability benchmarking evaluates a company's overall environmental, social, and economic performance against industry standards, providing a comprehensive view of progress and identifying improvement areas. Carbon footprinting focuses specifically on measuring greenhouse gas emissions generated by operations, offering detailed insights essential for targeted emission reduction strategies. For businesses aiming to integrate broad sustainability goals, sustainability benchmarking is better, while carbon footprinting is ideal for organizations prioritizing precise emission tracking and climate action.
Connection
Sustainability benchmarking involves evaluating an organization's environmental performance against industry standards or best practices, while carbon footprinting quantifies the total greenhouse gas emissions produced by its activities. Carbon footprinting provides essential data that feeds into sustainability benchmarks, enabling companies to measure their impact and identify areas for improvement. Integrating these processes supports more accurate reporting and drives strategic efforts toward reducing environmental impacts.
Key Terms
Emissions Assessment
Emissions assessment plays a critical role in both carbon footprinting and sustainability benchmarking, with carbon footprinting specifically quantifying greenhouse gas emissions from organizational activities to identify key areas for reduction. Sustainability benchmarking evaluates emissions alongside broader environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to measure overall sustainability performance against industry standards or competitors. Explore further to understand how integrating emissions data enhances strategic decision-making for effective sustainability initiatives.
Performance Metrics
Carbon footprinting quantifies greenhouse gas emissions directly linked to organizational activities, providing precise environmental impact data. Sustainability benchmarking evaluates a broader range of performance metrics, including social, economic, and environmental factors, to gauge overall corporate responsibility and long-term viability. Explore comprehensive strategies to integrate both approaches for enhanced operational performance and reporting accuracy.
Reporting Standards
Carbon footprinting quantifies greenhouse gas emissions directly linked to organizational activities, adhering to standards such as the Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHG Protocol) and ISO 14064 for accuracy and comparability. Sustainability benchmarking evaluates a broader spectrum of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics against industry peers, leveraging frameworks like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) to ensure comprehensive disclosure. Explore further to understand how reporting standards shape transparent and accountable sustainability practices.
Source and External Links
Carbon footprint - Wikipedia - A carbon footprint is a calculated value that measures the total greenhouse gases emitted by an activity, product, company, or country, reported in tonnes of CO2-equivalent per unit of comparison, such as per year, per kilometer, or per kilogram, allowing for comparison and mitigation strategies.
Carbon footprinting - Introduction for organizations - Carbon footprinting quantifies the total amount of CO2 and other greenhouse gas emissions for which an individual or organization is responsible, encompassing direct emissions (like fuel combustion) and indirect emissions (like supply chain, employee travel), and is essential for managing, reducing, and reporting emissions.
What is a carbon footprint? - Climeworks - Carbon footprints quantify the amount of global warming gases, primarily CO2, emitted from human activities like transport, energy use, and production, and are often expressed as carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) to compare the impact of different greenhouse gases.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com