Transformation Management Office (TMO) focuses on steering large-scale organizational change initiatives, ensuring alignment with strategic goals and stakeholder engagement. Business Process Improvement Office (BPIO) emphasizes optimizing existing workflows to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve quality through continuous process analysis and refinement. Explore how these offices drive organizational success by visiting our detailed consulting insights.
Why it is important
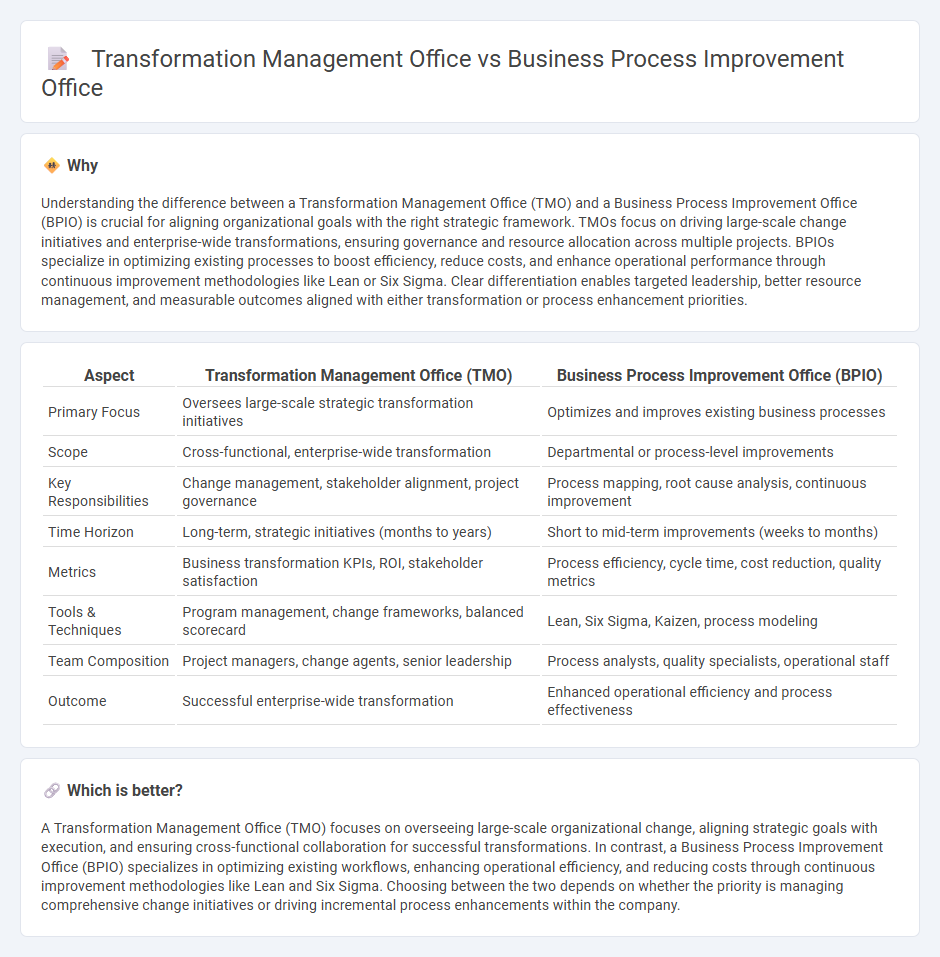
Understanding the difference between a Transformation Management Office (TMO) and a Business Process Improvement Office (BPIO) is crucial for aligning organizational goals with the right strategic framework. TMOs focus on driving large-scale change initiatives and enterprise-wide transformations, ensuring governance and resource allocation across multiple projects. BPIOs specialize in optimizing existing processes to boost efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance operational performance through continuous improvement methodologies like Lean or Six Sigma. Clear differentiation enables targeted leadership, better resource management, and measurable outcomes aligned with either transformation or process enhancement priorities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Transformation Management Office (TMO) | Business Process Improvement Office (BPIO) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Oversees large-scale strategic transformation initiatives | Optimizes and improves existing business processes |
| Scope | Cross-functional, enterprise-wide transformation | Departmental or process-level improvements |
| Key Responsibilities | Change management, stakeholder alignment, project governance | Process mapping, root cause analysis, continuous improvement |
| Time Horizon | Long-term, strategic initiatives (months to years) | Short to mid-term improvements (weeks to months) |
| Metrics | Business transformation KPIs, ROI, stakeholder satisfaction | Process efficiency, cycle time, cost reduction, quality metrics |
| Tools & Techniques | Program management, change frameworks, balanced scorecard | Lean, Six Sigma, Kaizen, process modeling |
| Team Composition | Project managers, change agents, senior leadership | Process analysts, quality specialists, operational staff |
| Outcome | Successful enterprise-wide transformation | Enhanced operational efficiency and process effectiveness |
Which is better?
A Transformation Management Office (TMO) focuses on overseeing large-scale organizational change, aligning strategic goals with execution, and ensuring cross-functional collaboration for successful transformations. In contrast, a Business Process Improvement Office (BPIO) specializes in optimizing existing workflows, enhancing operational efficiency, and reducing costs through continuous improvement methodologies like Lean and Six Sigma. Choosing between the two depends on whether the priority is managing comprehensive change initiatives or driving incremental process enhancements within the company.
Connection
The Transformation Management Office (TMO) aligns strategic initiatives with organizational change by overseeing project execution and performance metrics, ensuring successful transformation outcomes. The Business Process Improvement Office (BPIO) focuses on analyzing and enhancing operational workflows to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve quality. Both offices collaborate to integrate process improvements within transformation projects, driving sustainable change and maximizing business value across the enterprise.
Key Terms
Continuous Improvement
The Business Process Improvement Office (BPIO) specializes in analyzing and optimizing workflows to drive continuous improvement, utilizing methodologies such as Lean and Six Sigma for incremental gains. In contrast, the Transformation Management Office (TMO) oversees large-scale organizational change initiatives, integrating strategic goals with project management to ensure seamless transformation execution. Explore how aligning these offices can accelerate operational excellence and sustain long-term growth.
Change Management
The Business Process Improvement Office (BPIO) focuses on enhancing operational efficiency by analyzing and refining workflows to drive incremental change, while the Transformation Management Office (TMO) oversees strategic, large-scale organizational change initiatives aimed at achieving long-term business goals. Change management within BPIO typically targets process-level adjustments and employee adoption at a departmental scale, whereas in TMO, it involves comprehensive stakeholder engagement, cultural shifts, and aligning transformation efforts across the enterprise. Explore how both offices complement each other in effective change management to maximize organizational agility and success.
Strategic Alignment
The Business Process Improvement Office (BPIO) concentrates on optimizing workflows, increasing operational efficiency, and enhancing process performance to align with strategic business goals. The Transformation Management Office (TMO) oversees large-scale organizational change initiatives, ensuring that transformation efforts are strategically aligned with the company's vision and long-term objectives. Discover how these offices synergize to drive comprehensive strategic alignment and business success.
Source and External Links
Business Process Improvement Office - AITS - The Business Process Improvement Office at University of Illinois coordinates and facilitates process improvement projects such as Kaizen events, process mapping, and trainings to enhance workflows across multiple units since 2011.
Business Process Improvement - Army Financial Management - The Army uses Business Process Improvement methodologies including Business Process Reengineering, Continuous Process Improvement, and Lean Six Sigma to enhance process accuracy, effectiveness, and efficiency within financial management and other domains.
What Is Business Process Improvement? The 6 Types of BPI - Business Process Improvement is a systematic approach to analyze and optimize current processes aimed at boosting productivity, streamlining workflows, reducing costs, and aligning operations with business goals, often through continuous efforts and integration of automation and innovation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com