Corporate venturing involves established companies investing in or partnering with startups to drive innovation and gain strategic advantages, while business incubation focuses on nurturing early-stage startups through mentorship, resources, and support to accelerate their growth. Both approaches aim to stimulate entrepreneurship and market expansion but differ in investment scope, risk levels, and operational integration. Explore further to understand how these models can transform your business growth strategy.
Why it is important
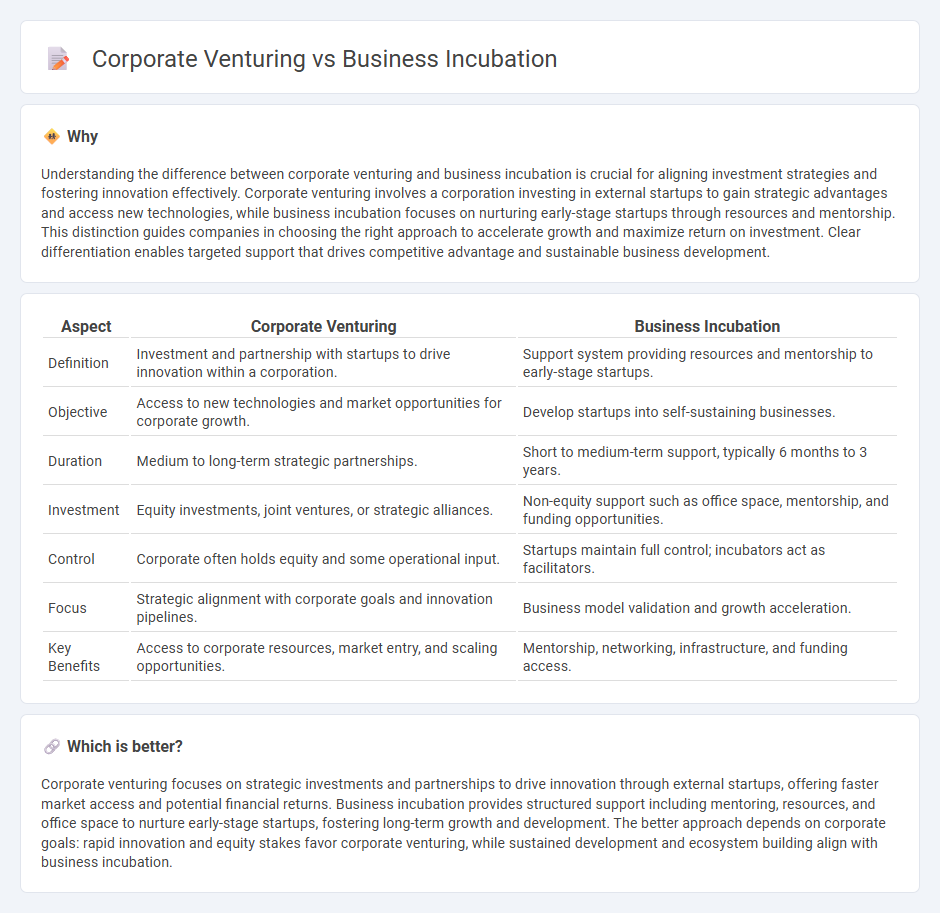
Understanding the difference between corporate venturing and business incubation is crucial for aligning investment strategies and fostering innovation effectively. Corporate venturing involves a corporation investing in external startups to gain strategic advantages and access new technologies, while business incubation focuses on nurturing early-stage startups through resources and mentorship. This distinction guides companies in choosing the right approach to accelerate growth and maximize return on investment. Clear differentiation enables targeted support that drives competitive advantage and sustainable business development.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Corporate Venturing | Business Incubation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment and partnership with startups to drive innovation within a corporation. | Support system providing resources and mentorship to early-stage startups. |
| Objective | Access to new technologies and market opportunities for corporate growth. | Develop startups into self-sustaining businesses. |
| Duration | Medium to long-term strategic partnerships. | Short to medium-term support, typically 6 months to 3 years. |
| Investment | Equity investments, joint ventures, or strategic alliances. | Non-equity support such as office space, mentorship, and funding opportunities. |
| Control | Corporate often holds equity and some operational input. | Startups maintain full control; incubators act as facilitators. |
| Focus | Strategic alignment with corporate goals and innovation pipelines. | Business model validation and growth acceleration. |
| Key Benefits | Access to corporate resources, market entry, and scaling opportunities. | Mentorship, networking, infrastructure, and funding access. |
Which is better?
Corporate venturing focuses on strategic investments and partnerships to drive innovation through external startups, offering faster market access and potential financial returns. Business incubation provides structured support including mentoring, resources, and office space to nurture early-stage startups, fostering long-term growth and development. The better approach depends on corporate goals: rapid innovation and equity stakes favor corporate venturing, while sustained development and ecosystem building align with business incubation.
Connection
Corporate venturing and business incubation are interconnected through their shared focus on fostering innovation and accelerating startup growth within established companies. Corporate venturing provides strategic investments and resources to startups, while business incubation offers structured mentorship, infrastructure, and support services to nurture early-stage ventures. Together, they create a collaborative ecosystem that drives technological advancement and market expansion by combining financial backing with hands-on development guidance.
Key Terms
Startup Acceleration
Business incubation provides startups with essential resources, mentorship, and infrastructure to nurture early-stage companies, focusing primarily on long-term growth and market readiness. Corporate venturing involves established corporations investing in or partnering with startups to accelerate innovation, often aiming for strategic alignment and quicker market entry. Explore the distinct advantages and strategies of startup acceleration in both models for deeper insights.
Strategic Investment
Business incubation involves nurturing early-stage startups by providing resources, mentorship, and workspace to accelerate growth and innovation within a controlled environment. Corporate venturing focuses on strategic investment by leveraging a company's capital to invest in startups that align with its long-term business goals, enhancing competitive advantage through direct equity stakes or partnerships. Discover how strategic investment bridges these approaches to drive innovation and market expansion.
Internal Innovation
Business incubation fosters internal innovation by providing startups with resources, mentorship, and a supportive environment to develop disruptive ideas within a company. Corporate venturing drives internal innovation through strategic investments or partnerships with external startups, enabling access to new technologies and market insights while integrating innovations into the corporate structure. Explore deeper insights on how internal innovation strategies enhance competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Source and External Links
Neighborhood Business Incubators - Provides free or low-cost workspace, mentorship, access to investors, and tailored business development support to help entrepreneurs--especially from underrepresented communities--launch and grow sustainable businesses.
What Is a Business Incubator and How Does It Work? - A specialized program offering reduced-rate workspace, mentorship, training, and networking to help startups plan, develop, and save costs during their early stages.
How a Business Incubator Program Can Help Your Startup - Supports early-stage startups with resources like office space, seed funding, mentoring, and professional services to shape business ideas and strategies over a sustained period.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com