Cost-to-serve analysis evaluates the total expenses involved in delivering a product or service to customers, emphasizing operational efficiency and profitability. Benchmarking compares these costs and processes against industry leaders to identify performance gaps and improvement opportunities. Explore how integrating both strategies can optimize your business outcomes and drive competitive advantage.
Why it is important
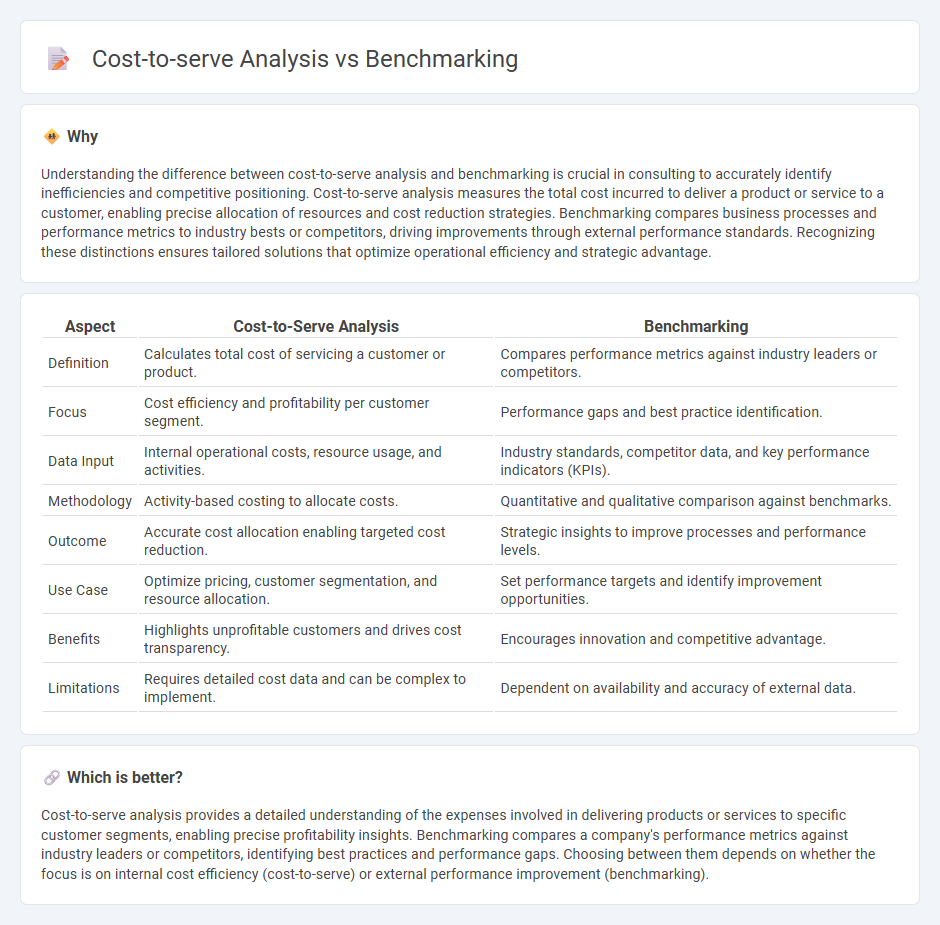
Understanding the difference between cost-to-serve analysis and benchmarking is crucial in consulting to accurately identify inefficiencies and competitive positioning. Cost-to-serve analysis measures the total cost incurred to deliver a product or service to a customer, enabling precise allocation of resources and cost reduction strategies. Benchmarking compares business processes and performance metrics to industry bests or competitors, driving improvements through external performance standards. Recognizing these distinctions ensures tailored solutions that optimize operational efficiency and strategic advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cost-to-Serve Analysis | Benchmarking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Calculates total cost of servicing a customer or product. | Compares performance metrics against industry leaders or competitors. |
| Focus | Cost efficiency and profitability per customer segment. | Performance gaps and best practice identification. |
| Data Input | Internal operational costs, resource usage, and activities. | Industry standards, competitor data, and key performance indicators (KPIs). |
| Methodology | Activity-based costing to allocate costs. | Quantitative and qualitative comparison against benchmarks. |
| Outcome | Accurate cost allocation enabling targeted cost reduction. | Strategic insights to improve processes and performance levels. |
| Use Case | Optimize pricing, customer segmentation, and resource allocation. | Set performance targets and identify improvement opportunities. |
| Benefits | Highlights unprofitable customers and drives cost transparency. | Encourages innovation and competitive advantage. |
| Limitations | Requires detailed cost data and can be complex to implement. | Dependent on availability and accuracy of external data. |
Which is better?
Cost-to-serve analysis provides a detailed understanding of the expenses involved in delivering products or services to specific customer segments, enabling precise profitability insights. Benchmarking compares a company's performance metrics against industry leaders or competitors, identifying best practices and performance gaps. Choosing between them depends on whether the focus is on internal cost efficiency (cost-to-serve) or external performance improvement (benchmarking).
Connection
Cost-to-serve analysis identifies the total expenses involved in delivering products or services to customers, providing a detailed view of cost drivers across the supply chain. Benchmarking compares these cost metrics against industry standards or competitors to reveal efficiency gaps and best practices. Together, they enable consulting firms to recommend targeted strategies for cost reduction and operational improvement.
Key Terms
Performance Metrics
Benchmarking utilizes performance metrics such as Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to compare operational efficiency against industry standards, highlighting areas for improvement. Cost-to-serve analysis breaks down expenses associated with delivering products or services to specific customer segments, providing detailed insights into profitability and resource allocation. Explore our comprehensive guides to deepen your understanding of how these analytics drive strategic decision-making and optimize business performance.
Activity-Based Costing
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) enhances benchmarking and cost-to-serve analysis by accurately assigning costs to activities, providing a detailed understanding of resource consumption and profitability at the process level. Benchmarking leverages ABC data to compare operational efficiency against industry standards, identifying performance gaps and areas for improvement. Explore how integrating Activity-Based Costing can elevate your cost analysis and strategic decision-making processes.
Best Practices
Benchmarking identifies performance gaps by comparing key metrics against industry leaders, ensuring adherence to best practices that drive operational excellence. Cost-to-serve analysis breaks down expenses associated with delivering products or services to customers, enabling businesses to optimize resource allocation and pricing strategies effectively. Explore detailed strategies and tools to enhance your competitive advantage through these essential methodologies.
Source and External Links
Benchmarking - Benchmarking is the practice of comparing business processes and performance metrics to industry bests and best practices, typically measuring quality, time, and cost to improve performance continuously or on a one-time basis.
What is Benchmarking? Technical & Competitive ... - Benchmarking is the process of measuring products, services, and processes against those of leading organizations, involving steps such as defining the subject, studying your own process, identifying partners, collecting data, analyzing gaps, and implementing improvements.
What are the Four Types of Benchmarking? - Key types of benchmarking include performance benchmarking, which gathers quantitative data to identify gaps, and practice benchmarking, which collects qualitative information on how activities are conducted to uncover best practices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com