Advisory sprints focus on rapid, iterative problem-solving sessions that align strategy and execution within a condensed timeframe, delivering actionable insights and tailored recommendations. In contrast, audits provide comprehensive evaluations of processes or systems, identifying risks and compliance gaps through detailed analysis and thorough documentation. Explore the benefits and use cases of advisory sprints versus audits to determine the best fit for your consulting needs.
Why it is important
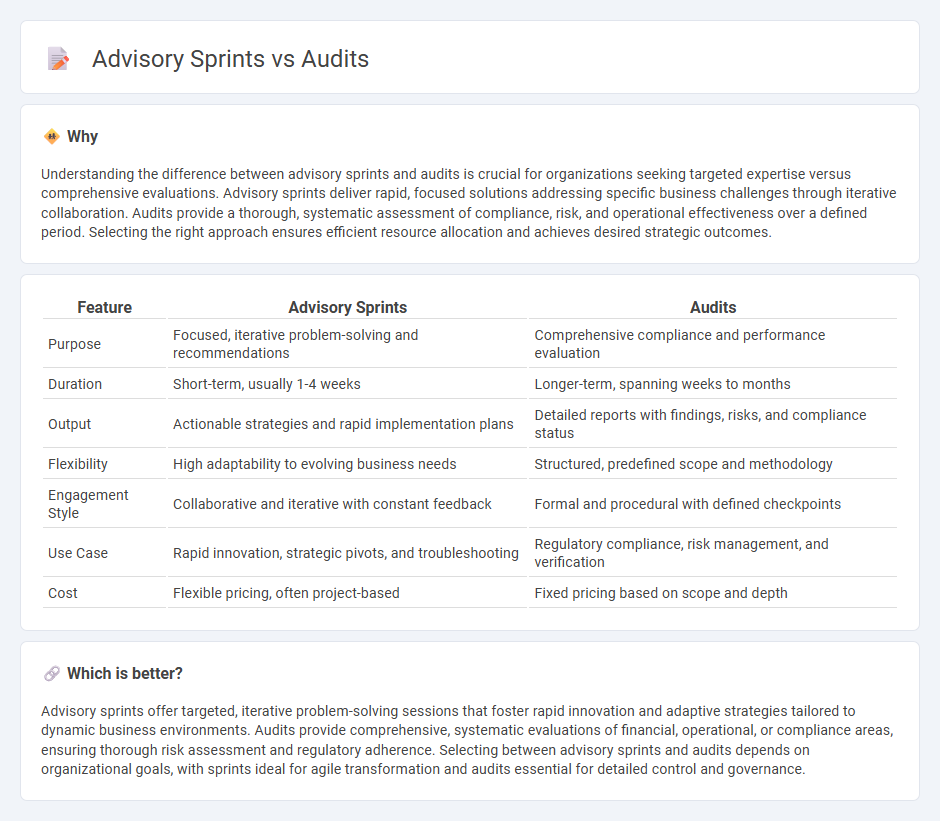
Understanding the difference between advisory sprints and audits is crucial for organizations seeking targeted expertise versus comprehensive evaluations. Advisory sprints deliver rapid, focused solutions addressing specific business challenges through iterative collaboration. Audits provide a thorough, systematic assessment of compliance, risk, and operational effectiveness over a defined period. Selecting the right approach ensures efficient resource allocation and achieves desired strategic outcomes.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Advisory Sprints | Audits |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Focused, iterative problem-solving and recommendations | Comprehensive compliance and performance evaluation |
| Duration | Short-term, usually 1-4 weeks | Longer-term, spanning weeks to months |
| Output | Actionable strategies and rapid implementation plans | Detailed reports with findings, risks, and compliance status |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to evolving business needs | Structured, predefined scope and methodology |
| Engagement Style | Collaborative and iterative with constant feedback | Formal and procedural with defined checkpoints |
| Use Case | Rapid innovation, strategic pivots, and troubleshooting | Regulatory compliance, risk management, and verification |
| Cost | Flexible pricing, often project-based | Fixed pricing based on scope and depth |
Which is better?
Advisory sprints offer targeted, iterative problem-solving sessions that foster rapid innovation and adaptive strategies tailored to dynamic business environments. Audits provide comprehensive, systematic evaluations of financial, operational, or compliance areas, ensuring thorough risk assessment and regulatory adherence. Selecting between advisory sprints and audits depends on organizational goals, with sprints ideal for agile transformation and audits essential for detailed control and governance.
Connection
Advisory sprints and audits are interconnected through their focus on targeted, iterative evaluation and improvement within consulting projects. Advisory sprints involve short, focused cycles of analysis and strategy development that align with audit findings to pinpoint risks and opportunities. The integration of audits ensures data-driven insights drive each sprint, enhancing decision-making and operational efficiency.
Key Terms
Compliance
Compliance audits systematically assess an organization's adherence to regulatory standards, identifying gaps and ensuring risk mitigation through detailed documentation and corrective actions. Advisory sprints offer iterative, expert-driven guidance to integrate compliance best practices into business processes, fostering proactive improvements and continuous alignment with evolving regulations. Explore how combining audits and advisory sprints can optimize your compliance strategy for sustained regulatory success.
Recommendations
Audits provide a thorough evaluation of current processes, identifying gaps and risks to ensure compliance and performance standards are met. Advisory sprints focus on delivering actionable recommendations and strategic guidance tailored to improve specific business outcomes rapidly. Explore how each approach can optimize your organizational efficiency and decision-making by learning more.
Rapid Assessment
Rapid assessment in audits centers on systematically evaluating an organization's compliance, controls, and risk exposure within a compressed timeframe to identify critical issues quickly. Advisory sprints prioritize iterative collaboration, delivering tailored recommendations and actionable insights that facilitate swift strategic improvements. Discover how combining audit precision with advisory agility can optimize your organization's risk management and decision-making processes.
Source and External Links
Audit - Overview, How It Works, Stages and Levels - An audit is a thorough examination of a company's financial statements conducted to provide stakeholders with confidence in the accuracy and compliance of the company's financial reporting, often resulting in an auditor's opinion on the financial position.
What is an audit? - PwC Middle East - An audit is an independent examination of an organization's financial report to form an opinion on whether the information accurately reflects the financial position at a given date, following established auditing standards.
What is an Audit? - Types of Audits & Auditing Certification - ASQ - Auditing involves on-site verification of processes or systems to ensure compliance, with types including first-party (internal), second-party (customer-performed), and third-party (independent) audits, serving different assurance and certification purposes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com