Product traceability enables businesses to track the origin and movement of goods throughout the supply chain, ensuring transparency and quality control. Serialization assigns unique identifiers to individual products, facilitating precise tracking and authentication to combat counterfeiting and improve recall efficiency. Explore how integrating product traceability and serialization can enhance supply chain management and customer trust.
Why it is important
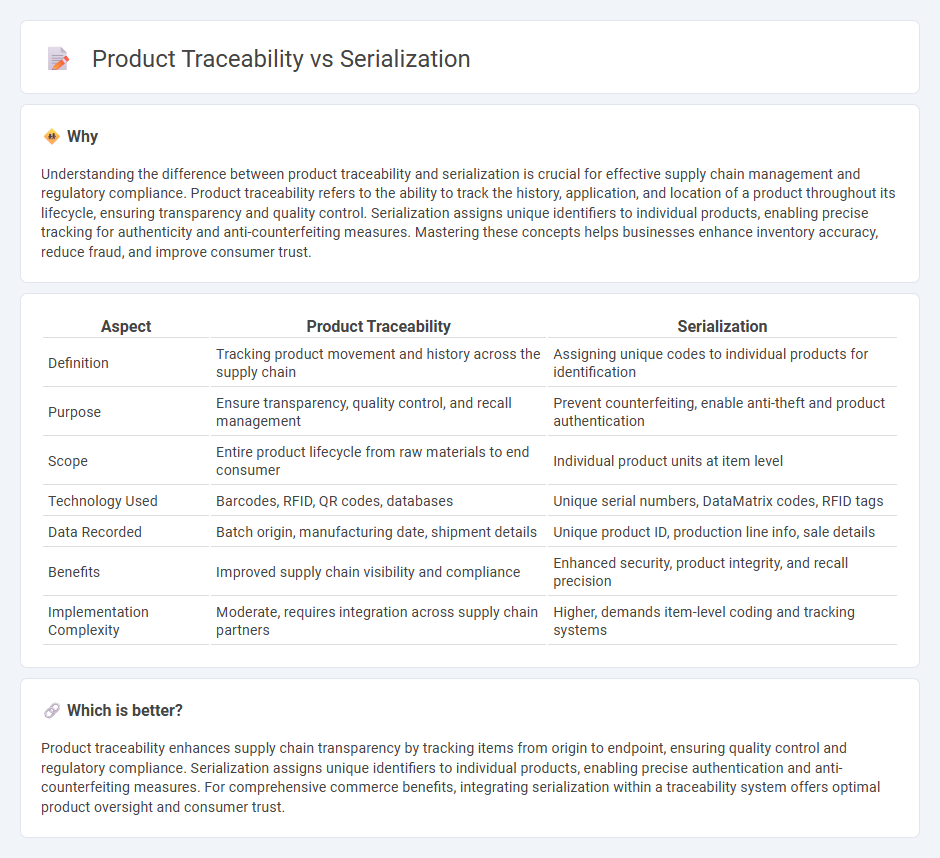
Understanding the difference between product traceability and serialization is crucial for effective supply chain management and regulatory compliance. Product traceability refers to the ability to track the history, application, and location of a product throughout its lifecycle, ensuring transparency and quality control. Serialization assigns unique identifiers to individual products, enabling precise tracking for authenticity and anti-counterfeiting measures. Mastering these concepts helps businesses enhance inventory accuracy, reduce fraud, and improve consumer trust.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Product Traceability | Serialization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tracking product movement and history across the supply chain | Assigning unique codes to individual products for identification |
| Purpose | Ensure transparency, quality control, and recall management | Prevent counterfeiting, enable anti-theft and product authentication |
| Scope | Entire product lifecycle from raw materials to end consumer | Individual product units at item level |
| Technology Used | Barcodes, RFID, QR codes, databases | Unique serial numbers, DataMatrix codes, RFID tags |
| Data Recorded | Batch origin, manufacturing date, shipment details | Unique product ID, production line info, sale details |
| Benefits | Improved supply chain visibility and compliance | Enhanced security, product integrity, and recall precision |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate, requires integration across supply chain partners | Higher, demands item-level coding and tracking systems |
Which is better?
Product traceability enhances supply chain transparency by tracking items from origin to endpoint, ensuring quality control and regulatory compliance. Serialization assigns unique identifiers to individual products, enabling precise authentication and anti-counterfeiting measures. For comprehensive commerce benefits, integrating serialization within a traceability system offers optimal product oversight and consumer trust.
Connection
Product traceability and serialization are interconnected processes essential for supply chain transparency and product authentication. Serialization assigns unique identifiers to individual products, enabling detailed tracking through every stage of distribution and sale. This traceability system enhances recall efficiency, combats counterfeiting, and ensures regulatory compliance in commerce.
Key Terms
Unique Identifier
Serialization involves assigning a unique identifier (UID) to each product unit, enabling precise tracking at the individual item level throughout the supply chain. Product traceability leverages these UIDs to monitor the movement, history, and origin of products, ensuring authenticity and compliance with industry regulations such as the FDA and EU Falsified Medicines Directive. Discover how integrating serialization with product traceability enhances supply chain transparency and combat counterfeiting efforts.
Supply Chain
Serialization enhances supply chain visibility by assigning unique codes to individual products, enabling precise tracking from manufacturing to the end consumer. Product traceability offers a broader perspective, tracing batches or lots through every stage of the supply chain to identify origins and movements. Explore how integrating serialization and traceability can optimize supply chain management and ensure regulatory compliance.
Transparency
Serialization assigns a unique identifier to each product unit, enabling precise tracking and authentication throughout the supply chain. Product traceability encompasses the entire history of a product's lifecycle, ensuring transparency by documenting all stages from raw material sourcing to distribution. Explore how these systems enhance supply chain integrity and regulatory compliance for greater transparency.
Source and External Links
What is serialization and how does it work? - Serialization is the process of converting a data object into a series of bytes that saves the object's state in a form that can be easily transmitted or stored and later reconstructed through deserialization.
Serialization - Wikipedia - Serialization is the process of translating a data structure or object state into a format that can be stored or transmitted and reconstructed later, enabling the creation of a semantically identical clone of the original object.
Serialization - .NET - Serialization converts the state of an object into a form that can be persisted or transported, with multiple technologies like JSON, XML, and binary serialization supporting different needs and level of fidelity for data transfer and storage.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com