Conversational commerce leverages chat interfaces and messaging apps to enable personalized, real-time customer interactions and transactions. Voice commerce utilizes voice recognition technology through smart assistants and devices to facilitate hands-free shopping experiences. Explore the distinctions and benefits of both to optimize your retail strategy.
Why it is important
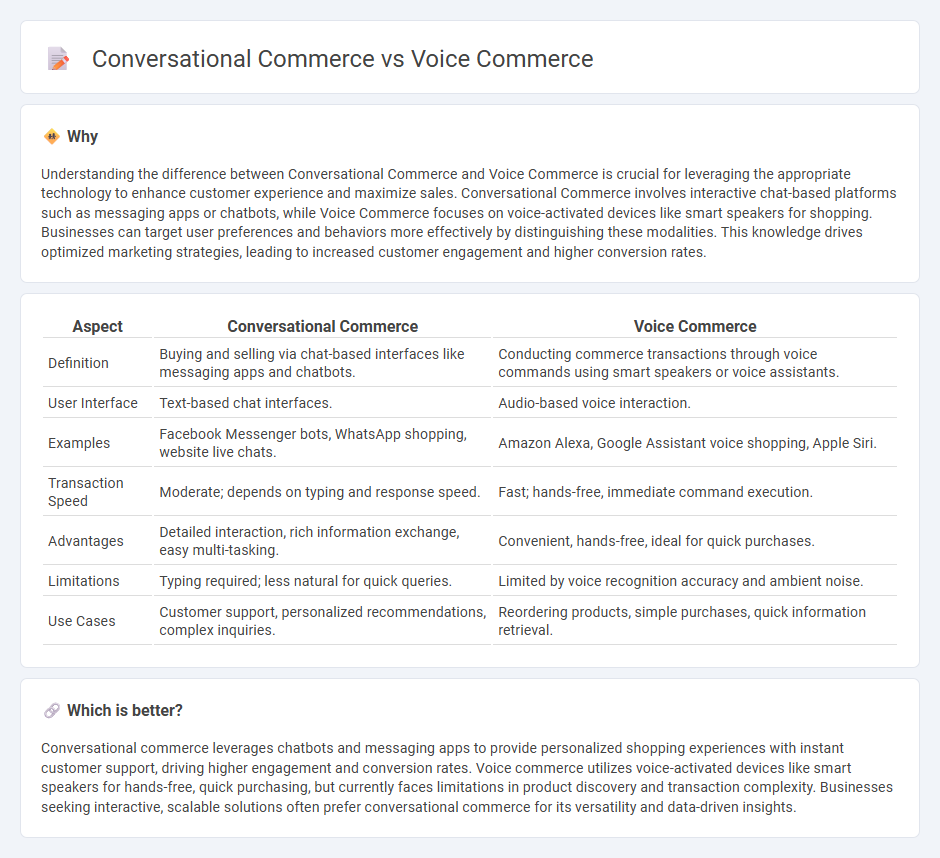
Understanding the difference between Conversational Commerce and Voice Commerce is crucial for leveraging the appropriate technology to enhance customer experience and maximize sales. Conversational Commerce involves interactive chat-based platforms such as messaging apps or chatbots, while Voice Commerce focuses on voice-activated devices like smart speakers for shopping. Businesses can target user preferences and behaviors more effectively by distinguishing these modalities. This knowledge drives optimized marketing strategies, leading to increased customer engagement and higher conversion rates.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Conversational Commerce | Voice Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying and selling via chat-based interfaces like messaging apps and chatbots. | Conducting commerce transactions through voice commands using smart speakers or voice assistants. |
| User Interface | Text-based chat interfaces. | Audio-based voice interaction. |
| Examples | Facebook Messenger bots, WhatsApp shopping, website live chats. | Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant voice shopping, Apple Siri. |
| Transaction Speed | Moderate; depends on typing and response speed. | Fast; hands-free, immediate command execution. |
| Advantages | Detailed interaction, rich information exchange, easy multi-tasking. | Convenient, hands-free, ideal for quick purchases. |
| Limitations | Typing required; less natural for quick queries. | Limited by voice recognition accuracy and ambient noise. |
| Use Cases | Customer support, personalized recommendations, complex inquiries. | Reordering products, simple purchases, quick information retrieval. |
Which is better?
Conversational commerce leverages chatbots and messaging apps to provide personalized shopping experiences with instant customer support, driving higher engagement and conversion rates. Voice commerce utilizes voice-activated devices like smart speakers for hands-free, quick purchasing, but currently faces limitations in product discovery and transaction complexity. Businesses seeking interactive, scalable solutions often prefer conversational commerce for its versatility and data-driven insights.
Connection
Conversational commerce integrates chatbots and messaging apps to enable personalized shopping experiences through natural language interactions, while voice commerce uses voice-activated devices like smart speakers for hands-free purchasing. Both leverage artificial intelligence and natural language processing technologies to streamline customer engagement and simplify transactions. This synergy enhances user convenience and drives increased online sales by providing seamless, intuitive communication channels.
Key Terms
Voice Assistants
Voice commerce leverages voice assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant to facilitate hands-free shopping experiences through voice commands, enabling users to search, order, and pay without using screens. Conversational commerce extends beyond voice to include chatbots and messaging apps, offering interactive dialogues that guide customers through product discovery and support. Explore how voice assistants revolutionize shopping by blending convenience and AI-driven personalization.
Chatbots
Voice commerce leverages voice-activated devices like smart speakers to facilitate seamless shopping experiences through spoken commands, enhancing convenience and speed. Conversational commerce employs chatbots to engage customers in real-time text-based interactions, offering personalized product recommendations and support that boost user satisfaction. Explore how integrating voice and chatbot technologies can revolutionize your e-commerce strategy.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Voice commerce utilizes Natural Language Processing (NLP) to enable consumers to make purchases through voice commands on devices like smart speakers and smartphones. Conversational commerce extends NLP capabilities by integrating chatbots and virtual assistants in messaging platforms, facilitating interactive dialogues that guide users through product discovery, recommendations, and transactions. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how NLP drives these commerce innovations and reshapes the online shopping experience.
Source and External Links
Voice Commerce: Definition, How it Works, and Benefits - Voice commerce, also known as v-commerce, enables consumers to make purchases and manage orders using voice commands through smart speakers or virtual assistants like Alexa and Google Assistant, offering a seamless, hands-free shopping experience rapidly growing in popularity and expected to reach over $55 billion by 2026.
What Is Voice Commerce? - Voice commerce allows consumers to search for and purchase products online using voice commands, reducing reliance on keyboards and screens, and benefits from advances in AI that improve natural language understanding and shopper trust in virtual assistants like Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri.
Overview of Voice Commerce - Voice commerce is an electronic commerce method where users execute purchases using voice commands through devices such as smart speakers and virtual assistants, offering a new way to shop online without keyboards or screens by linking payment methods like credit cards or PayPal to these devices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com