Micro fulfillment centers optimize last-mile delivery by using automated systems in compact urban spaces, significantly reducing delivery times compared to traditional warehouses. Traditional warehouses, often large and located on city outskirts, focus on bulk storage and centralized inventory management, resulting in longer shipping distances and increased costs. Explore the advantages of micro fulfillment to understand how it revolutionizes commerce logistics.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between micro fulfillment and traditional warehouses is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency, reducing delivery times, and meeting evolving consumer expectations in commerce. Micro fulfillment centers use automation and proximity to urban areas to enable faster last-mile delivery, unlike traditional warehouses that focus on large-scale storage and bulk distribution. This knowledge empowers businesses to select the right fulfillment strategy to enhance customer satisfaction and lower operational costs. Adopting the appropriate model directly impacts competitiveness in the rapidly changing retail landscape.
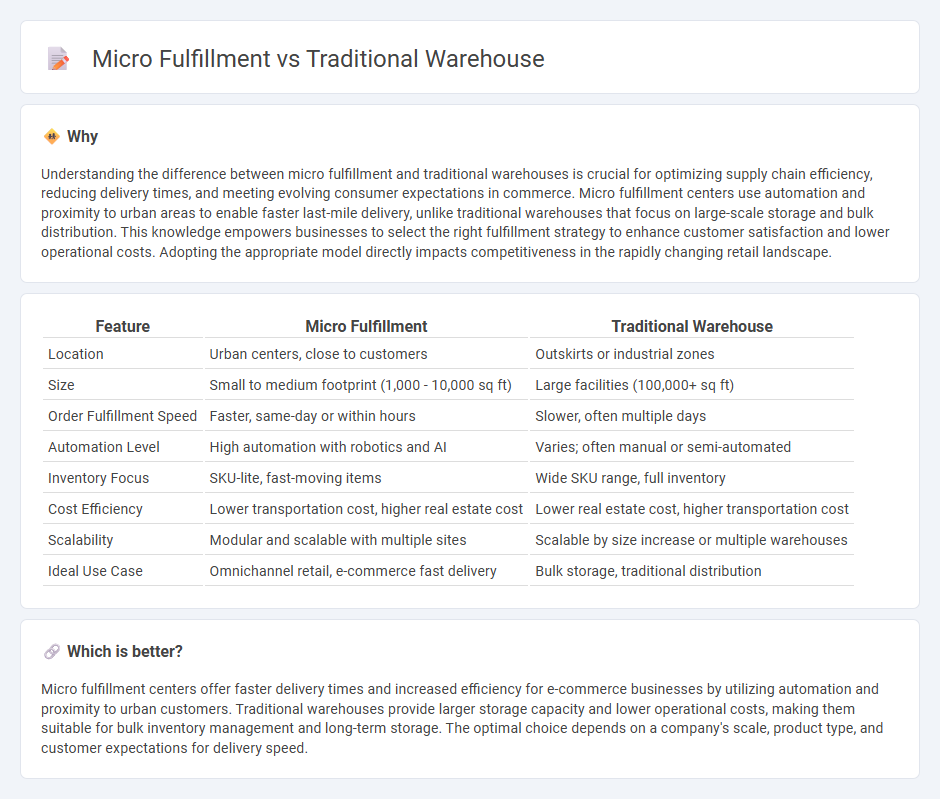
Comparison Table
| Feature | Micro Fulfillment | Traditional Warehouse |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Urban centers, close to customers | Outskirts or industrial zones |
| Size | Small to medium footprint (1,000 - 10,000 sq ft) | Large facilities (100,000+ sq ft) |
| Order Fulfillment Speed | Faster, same-day or within hours | Slower, often multiple days |
| Automation Level | High automation with robotics and AI | Varies; often manual or semi-automated |
| Inventory Focus | SKU-lite, fast-moving items | Wide SKU range, full inventory |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower transportation cost, higher real estate cost | Lower real estate cost, higher transportation cost |
| Scalability | Modular and scalable with multiple sites | Scalable by size increase or multiple warehouses |
| Ideal Use Case | Omnichannel retail, e-commerce fast delivery | Bulk storage, traditional distribution |
Which is better?
Micro fulfillment centers offer faster delivery times and increased efficiency for e-commerce businesses by utilizing automation and proximity to urban customers. Traditional warehouses provide larger storage capacity and lower operational costs, making them suitable for bulk inventory management and long-term storage. The optimal choice depends on a company's scale, product type, and customer expectations for delivery speed.
Connection
Micro fulfillment centers and traditional warehouses intersect as integral components of modern commerce logistics, optimizing inventory management and order fulfillment. Micro fulfillment emphasizes speed and proximity by decentralizing inventory closer to consumers, while traditional warehouses focus on large-scale storage and bulk handling. This connection enhances overall supply chain efficiency, meeting the demands of e-commerce growth and same-day delivery expectations.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Traditional warehouses manage inventory through bulk storage with longer lead times and larger stock levels, often requiring extensive manual handling and slower replenishment cycles. Micro-fulfillment centers leverage automation and proximity to customers to optimize inventory turnover, reduce storage space, and enable real-time tracking, enhancing efficiency in fulfilling e-commerce orders. Explore how different inventory management strategies impact operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Order Processing Speed
Traditional warehouses rely on large-scale inventory storage and manual picking processes, resulting in slower order processing speeds often measured in hours or days. Micro-fulfillment centers use automation and proximity to consumers, enabling rapid order processing typically within minutes or a few hours. Explore the advantages of micro-fulfillment to optimize your supply chain efficiency.
Last-Mile Delivery
Traditional warehouses typically operate on a bulk storage model with slower inventory turnover, causing delays in last-mile delivery due to distance from urban centers. Micro-fulfillment centers are smaller, technology-driven facilities located closer to customers, enabling faster order processing and reduced delivery times. Explore how micro-fulfillment transforms last-mile logistics for improved speed and customer satisfaction.
Source and External Links
What Is Traditional Warehousing- Concept, Benefits & Operation - Traditional warehouse is a permanent building designed for long-term storage where goods are methodically organized on pallets or shelves for efficient space use and easy retrieval, relying on manual or simple barcode inventory management and centralized logistics for transportation coordination.
Smart Warehouse vs. Traditional Warehouse - Portable Intelligence - Traditional warehouses are characterized by manual labor-intensive operations, rigid layouts, and often lack real-time inventory visibility, leading to potential errors and inefficiencies in inventory management and order fulfillment.
Flexible Warehousing Vs Traditional Warehousing - Traditional warehousing involves fixed, long-term storage capacity with low cost variability and guaranteed space but lacks scalability and flexibility to adapt to fluctuating inventory or sudden demand spikes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com