Circular supply chains prioritize the continuous reuse and recycling of materials to minimize waste and extend product life cycles, focusing on a closed-loop system. Sustainable supply chains emphasize environmental, social, and economic responsibility throughout the entire supply process, aiming to reduce overall ecological impact while supporting ethical labor practices. Explore the differences and benefits of each model to optimize your business strategy.
Why it is important
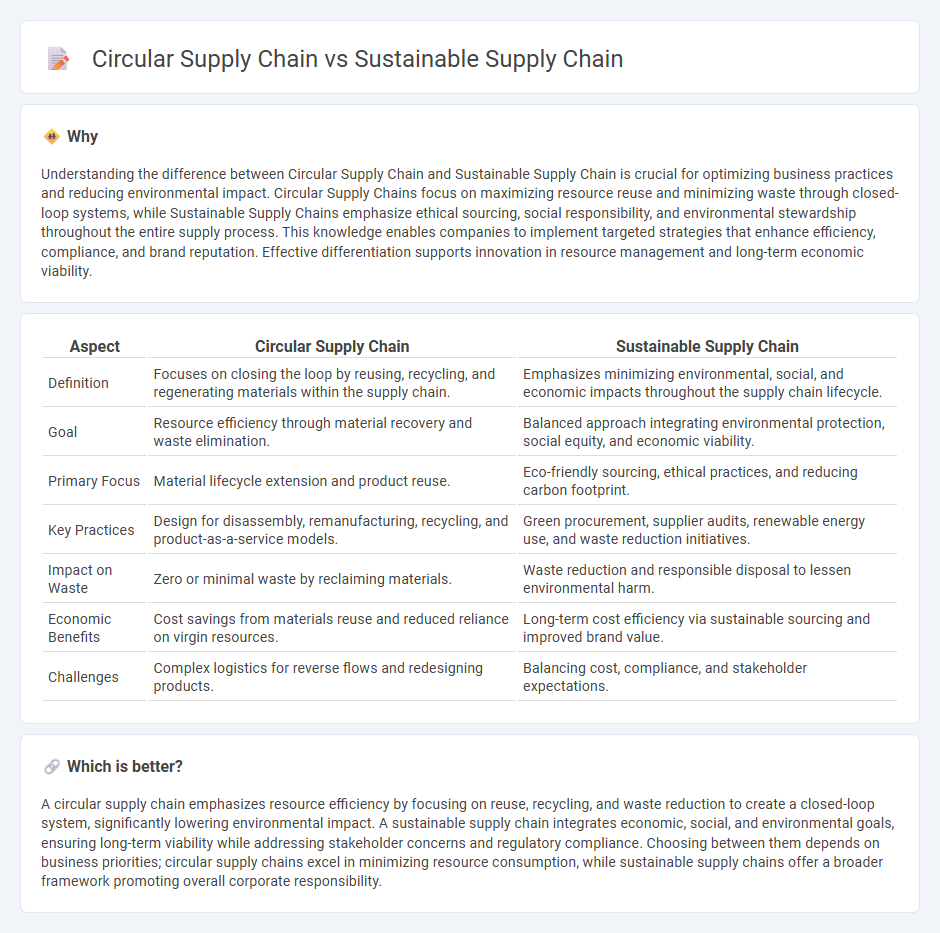
Understanding the difference between Circular Supply Chain and Sustainable Supply Chain is crucial for optimizing business practices and reducing environmental impact. Circular Supply Chains focus on maximizing resource reuse and minimizing waste through closed-loop systems, while Sustainable Supply Chains emphasize ethical sourcing, social responsibility, and environmental stewardship throughout the entire supply process. This knowledge enables companies to implement targeted strategies that enhance efficiency, compliance, and brand reputation. Effective differentiation supports innovation in resource management and long-term economic viability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Supply Chain | Sustainable Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on closing the loop by reusing, recycling, and regenerating materials within the supply chain. | Emphasizes minimizing environmental, social, and economic impacts throughout the supply chain lifecycle. |
| Goal | Resource efficiency through material recovery and waste elimination. | Balanced approach integrating environmental protection, social equity, and economic viability. |
| Primary Focus | Material lifecycle extension and product reuse. | Eco-friendly sourcing, ethical practices, and reducing carbon footprint. |
| Key Practices | Design for disassembly, remanufacturing, recycling, and product-as-a-service models. | Green procurement, supplier audits, renewable energy use, and waste reduction initiatives. |
| Impact on Waste | Zero or minimal waste by reclaiming materials. | Waste reduction and responsible disposal to lessen environmental harm. |
| Economic Benefits | Cost savings from materials reuse and reduced reliance on virgin resources. | Long-term cost efficiency via sustainable sourcing and improved brand value. |
| Challenges | Complex logistics for reverse flows and redesigning products. | Balancing cost, compliance, and stakeholder expectations. |
Which is better?
A circular supply chain emphasizes resource efficiency by focusing on reuse, recycling, and waste reduction to create a closed-loop system, significantly lowering environmental impact. A sustainable supply chain integrates economic, social, and environmental goals, ensuring long-term viability while addressing stakeholder concerns and regulatory compliance. Choosing between them depends on business priorities; circular supply chains excel in minimizing resource consumption, while sustainable supply chains offer a broader framework promoting overall corporate responsibility.
Connection
Circular supply chains integrate resource recovery and waste minimization, directly supporting the principles of sustainable supply chains focused on reducing environmental impact and promoting long-term ecological balance. Both approaches emphasize closed-loop systems, material reutilization, and reduced carbon footprints, fostering resource efficiency and resilience in global commerce. Implementing circular supply chains enhances sustainability metrics by minimizing resource extraction and waste generation throughout the supply network.
Key Terms
Resource Efficiency
Sustainable supply chains prioritize minimizing environmental impact by optimizing resource use, reducing waste, and lowering carbon emissions throughout the production and distribution processes. Circular supply chains emphasize resource efficiency by designing products for reuse, refurbishment, and recycling, creating a closed-loop system that extends product life cycles and minimizes raw material extraction. Explore the differences and benefits of both approaches to enhance your supply chain's resource efficiency strategies.
Waste Minimization
Sustainable supply chains emphasize reducing environmental impact through efficient resource use, energy conservation, and waste minimization to create long-term value. Circular supply chains specifically prioritize the regeneration of resources by designing products and processes for reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling to eliminate waste entirely. Explore expert insights to understand how these strategies transform waste management in modern logistics.
Product Lifecycle
A sustainable supply chain emphasizes reducing environmental impact through resource efficiency and ethical sourcing across every stage of the product lifecycle, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. A circular supply chain focuses on extending the product lifecycle by integrating processes like recycling, refurbishing, and reusing materials, aiming to achieve a closed-loop system that minimizes waste. Discover more about how these supply chain strategies transform product lifecycle management for a greener future.
Source and External Links
What Is Sustainable Supply Chain Management? - IBM - Sustainable supply chain management integrates environmental, social, and financial considerations throughout sourcing, production, and distribution to reduce negative impacts and increase efficiency and resilience in business operations.
What Is Supply Chain Sustainability and Why Is It Important? - NetSuite - Supply chain sustainability includes efforts to minimize environmental and human impacts with innovations like circular economy, eco-friendly transportation, and AI-driven analytics to optimize decisions balancing economic and environmental goals.
Supply chain sustainability: what is it and why is it important? - Sedex - A sustainable supply chain uses both environmentally and socially sustainable practices at every stage to protect people and the environment, emphasizing that social standards like fair labor are as crucial as environmental ones.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com