Peer-to-peer payments enable direct money transfers between individuals via mobile apps, offering convenience and speed without intermediaries. Point-of-sale (POS) systems facilitate in-store transactions by processing payments through card readers and integrated software, enhancing business operations and customer experience. Explore the key differences and advantages of peer-to-peer payments compared to POS solutions to optimize your transaction methods.
Why it is important
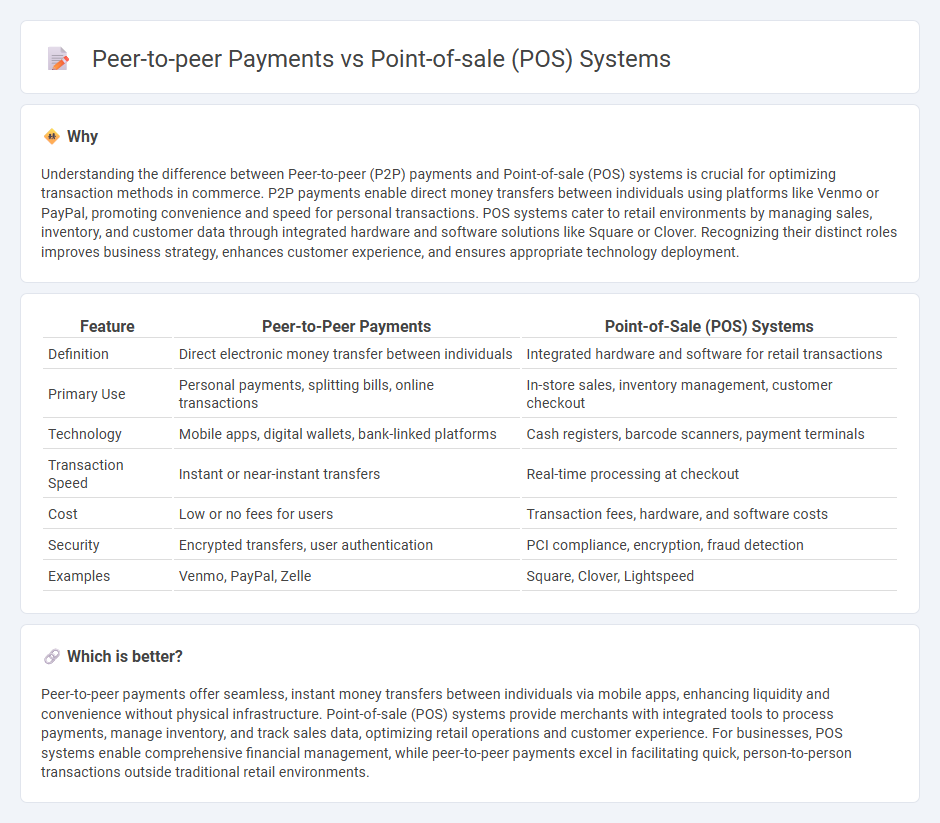
Understanding the difference between Peer-to-peer (P2P) payments and Point-of-sale (POS) systems is crucial for optimizing transaction methods in commerce. P2P payments enable direct money transfers between individuals using platforms like Venmo or PayPal, promoting convenience and speed for personal transactions. POS systems cater to retail environments by managing sales, inventory, and customer data through integrated hardware and software solutions like Square or Clover. Recognizing their distinct roles improves business strategy, enhances customer experience, and ensures appropriate technology deployment.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Peer-to-Peer Payments | Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct electronic money transfer between individuals | Integrated hardware and software for retail transactions |
| Primary Use | Personal payments, splitting bills, online transactions | In-store sales, inventory management, customer checkout |
| Technology | Mobile apps, digital wallets, bank-linked platforms | Cash registers, barcode scanners, payment terminals |
| Transaction Speed | Instant or near-instant transfers | Real-time processing at checkout |
| Cost | Low or no fees for users | Transaction fees, hardware, and software costs |
| Security | Encrypted transfers, user authentication | PCI compliance, encryption, fraud detection |
| Examples | Venmo, PayPal, Zelle | Square, Clover, Lightspeed |
Which is better?
Peer-to-peer payments offer seamless, instant money transfers between individuals via mobile apps, enhancing liquidity and convenience without physical infrastructure. Point-of-sale (POS) systems provide merchants with integrated tools to process payments, manage inventory, and track sales data, optimizing retail operations and customer experience. For businesses, POS systems enable comprehensive financial management, while peer-to-peer payments excel in facilitating quick, person-to-person transactions outside traditional retail environments.
Connection
Peer-to-peer payments and Point-of-sale (POS) systems are interconnected through seamless transaction processing that enhances consumer convenience and merchant efficiency in commerce. Peer-to-peer payment platforms integrate with POS systems to enable instant, contactless payments, reducing the reliance on cash or card swipes. This integration supports faster checkout experiences and broadens payment options, driving digital commerce adoption and improving sales conversion rates.
Key Terms
Transaction Processing
Point-of-sale (POS) systems streamline transaction processing by integrating hardware and software to instantly capture sales data, manage inventory, and process payments securely through various methods like credit cards and mobile wallets. Peer-to-peer payments facilitate direct money transfers between individuals via digital platforms or apps, bypassing traditional financial intermediaries, which expedites personal transactions but may lack comprehensive sales tracking features. Explore the detailed differences in transaction processing to choose the most efficient payment solution for your business or personal needs.
Payment Networks
Point-of-sale (POS) systems utilize established payment networks like Visa, Mastercard, and American Express to facilitate secure and efficient transaction processing at retail locations. In contrast, peer-to-peer payments often rely on digital wallets and mobile platforms such as PayPal, Venmo, or Zelle, which use underlying payment networks but emphasize person-to-person fund transfers without physical card presence. Explore the differences in payment network integration and security protocols to better understand their impact on transaction speed and reliability.
User Authentication
Point-of-sale (POS) systems primarily utilize multi-factor user authentication methods such as biometric verification, PIN codes, and RFID cards to ensure secure transactions at physical retail locations. Peer-to-peer payment platforms emphasize seamless user authentication through smartphone biometrics, two-factor authentication (2FA), and encrypted digital wallets to facilitate fast and secure money transfers. Explore the latest advancements in authentication technologies for both POS and peer-to-peer payments to enhance transaction security.
Source and External Links
What is a POS System? Overview, Meaning & Best Practices - A POS system integrates hardware like terminals, card readers, receipt printers, and barcode scanners with software for sales reporting, inventory management, and customer relationship management to streamline transactions and provide business insights.
Point-of-sale (POS) systems explained: A guide for businesses - Stripe - POS systems combine hardware and software to process sales, manage payments, update inventory in real time, generate receipts, collect customer data, and integrate with other business tools like CRM and accounting software.
What Is a Point-of-Sale (POS) System and How Does It Work? - A POS system is a combination of hardware, software, and services that records purchases, accepts payments, issues receipts, and tracks data to help businesses manage sales both in-person and online.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com