Ghost commerce enables sellers to operate without a dedicated storefront by leveraging third-party platforms and invisible supply chains, focusing on efficient product fulfillment and branding flexibility. Marketplace selling involves listing products on established platforms like Amazon, eBay, or Etsy, benefiting from built-in traffic but facing high competition and platform fees. Explore the key differences and advantages between ghost commerce and marketplace selling to optimize your e-commerce strategy.
Why it is important
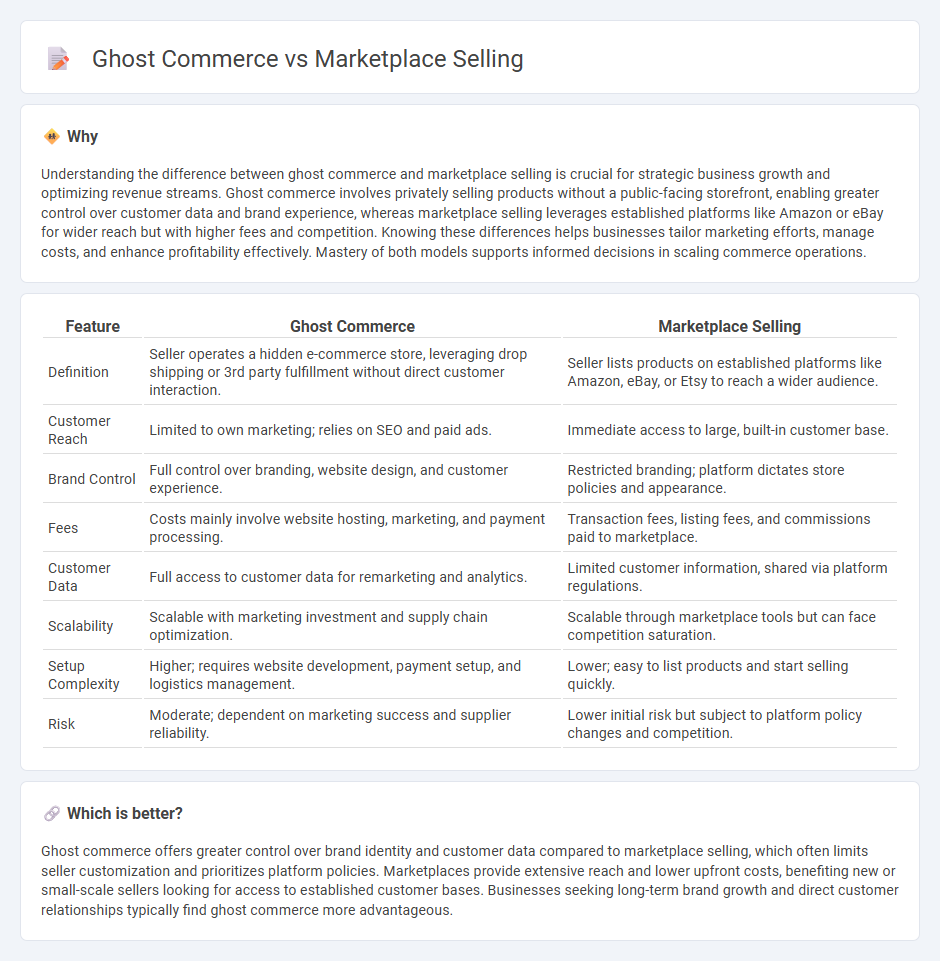
Understanding the difference between ghost commerce and marketplace selling is crucial for strategic business growth and optimizing revenue streams. Ghost commerce involves privately selling products without a public-facing storefront, enabling greater control over customer data and brand experience, whereas marketplace selling leverages established platforms like Amazon or eBay for wider reach but with higher fees and competition. Knowing these differences helps businesses tailor marketing efforts, manage costs, and enhance profitability effectively. Mastery of both models supports informed decisions in scaling commerce operations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Ghost Commerce | Marketplace Selling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seller operates a hidden e-commerce store, leveraging drop shipping or 3rd party fulfillment without direct customer interaction. | Seller lists products on established platforms like Amazon, eBay, or Etsy to reach a wider audience. |
| Customer Reach | Limited to own marketing; relies on SEO and paid ads. | Immediate access to large, built-in customer base. |
| Brand Control | Full control over branding, website design, and customer experience. | Restricted branding; platform dictates store policies and appearance. |
| Fees | Costs mainly involve website hosting, marketing, and payment processing. | Transaction fees, listing fees, and commissions paid to marketplace. |
| Customer Data | Full access to customer data for remarketing and analytics. | Limited customer information, shared via platform regulations. |
| Scalability | Scalable with marketing investment and supply chain optimization. | Scalable through marketplace tools but can face competition saturation. |
| Setup Complexity | Higher; requires website development, payment setup, and logistics management. | Lower; easy to list products and start selling quickly. |
| Risk | Moderate; dependent on marketing success and supplier reliability. | Lower initial risk but subject to platform policy changes and competition. |
Which is better?
Ghost commerce offers greater control over brand identity and customer data compared to marketplace selling, which often limits seller customization and prioritizes platform policies. Marketplaces provide extensive reach and lower upfront costs, benefiting new or small-scale sellers looking for access to established customer bases. Businesses seeking long-term brand growth and direct customer relationships typically find ghost commerce more advantageous.
Connection
Ghost commerce enables sellers to operate without a physical storefront by using digital platforms, seamlessly integrating with marketplace selling models. These marketplaces allow vendors to list products directly online, facilitating inventory management and customer reach through a centralized digital hub. Leveraging ghost commerce techniques optimizes scalability and reduces overhead in marketplace selling environments.
Key Terms
Platform Fees
Marketplace selling typically involves platform fees ranging from 5% to 20% per transaction, impacting overall profitability for sellers. Ghost commerce reduces or eliminates these fees by leveraging direct-to-consumer channels and private label strategies, maximizing margin retention. Explore the cost benefits and strategic choices in platform fees to optimize your e-commerce model.
Inventory Management
Marketplace selling relies on shared inventory systems where multiple sellers list products on a centralized platform, streamlining stock tracking and order fulfillment but limiting direct inventory control. Ghost commerce operates on the principle of maintaining private inventory across multiple sales channels, enabling sellers to optimize stock levels and reduce overstock through sophisticated inventory management tools. Explore detailed strategies to leverage inventory management for both marketplace selling and ghost commerce for maximum efficiency and profitability.
Brand Visibility
Marketplace selling offers significant brand exposure by placing products on popular platforms such as Amazon, eBay, or Etsy, reaching millions of potential customers instantly. Ghost commerce, meanwhile, emphasizes stealth selling through third-party channels without prominently featuring the brand, reducing direct brand visibility but potentially increasing sales volume. Explore the strategic advantages of both models to optimize your brand's presence and sales performance.
Source and External Links
How to Sell on Facebook Marketplace - A step-by-step video guide to listing items on Facebook Marketplace using a desktop, including uploading photos, setting a price, and managing buyer interactions.
22 Selling Websites and Marketplaces for Selling Things - Overview of popular online selling platforms like Facebook Marketplace and Craigslist, focusing on local sales with no listing fees and tips on reaching customers.
13 Places to Sell Stuff Online - Detailed information on various marketplaces including fee structures for sites like Bonanza, and advice on local sales via platforms such as Facebook Marketplace and Nextdoor without seller fees.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com