Dark patterns exploit user psychology to manipulate decisions, often leading to unwanted purchases or data sharing, undermining trust in e-commerce platforms. Ethical design prioritizes transparency, user consent, and fairness, fostering long-term customer loyalty and enhancing brand reputation. Discover how balancing dark patterns and ethical design impacts online commerce success.
Why it is important
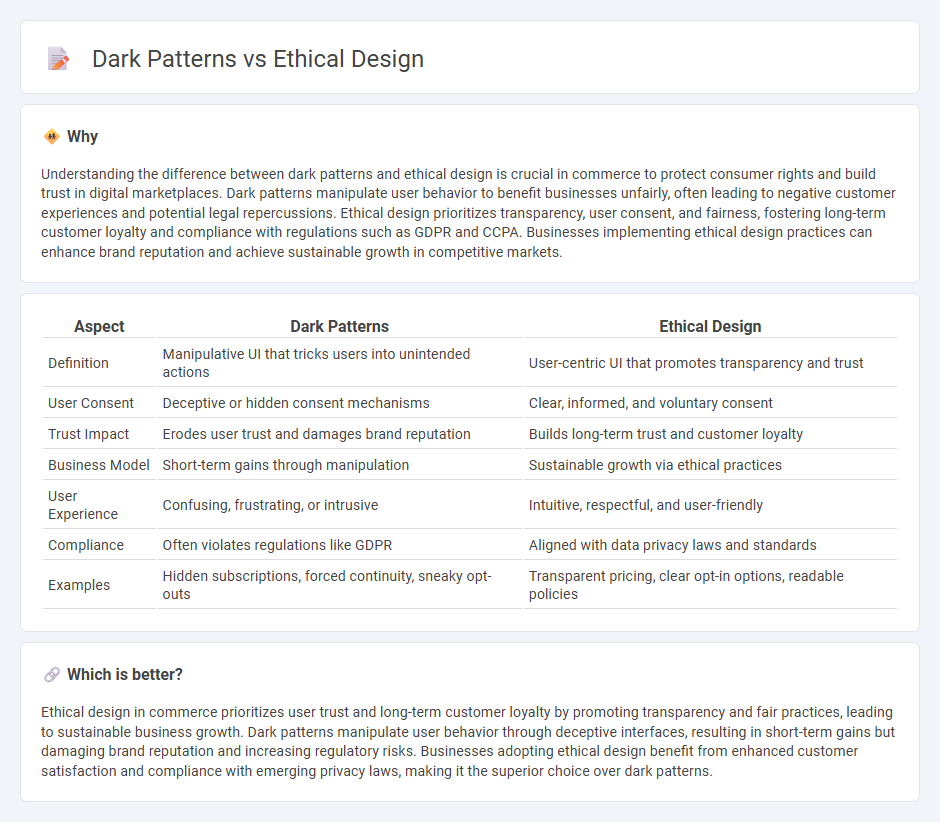
Understanding the difference between dark patterns and ethical design is crucial in commerce to protect consumer rights and build trust in digital marketplaces. Dark patterns manipulate user behavior to benefit businesses unfairly, often leading to negative customer experiences and potential legal repercussions. Ethical design prioritizes transparency, user consent, and fairness, fostering long-term customer loyalty and compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Businesses implementing ethical design practices can enhance brand reputation and achieve sustainable growth in competitive markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Patterns | Ethical Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manipulative UI that tricks users into unintended actions | User-centric UI that promotes transparency and trust |
| User Consent | Deceptive or hidden consent mechanisms | Clear, informed, and voluntary consent |
| Trust Impact | Erodes user trust and damages brand reputation | Builds long-term trust and customer loyalty |
| Business Model | Short-term gains through manipulation | Sustainable growth via ethical practices |
| User Experience | Confusing, frustrating, or intrusive | Intuitive, respectful, and user-friendly |
| Compliance | Often violates regulations like GDPR | Aligned with data privacy laws and standards |
| Examples | Hidden subscriptions, forced continuity, sneaky opt-outs | Transparent pricing, clear opt-in options, readable policies |
Which is better?
Ethical design in commerce prioritizes user trust and long-term customer loyalty by promoting transparency and fair practices, leading to sustainable business growth. Dark patterns manipulate user behavior through deceptive interfaces, resulting in short-term gains but damaging brand reputation and increasing regulatory risks. Businesses adopting ethical design benefit from enhanced customer satisfaction and compliance with emerging privacy laws, making it the superior choice over dark patterns.
Connection
Dark patterns manipulate user behavior through deceptive interface design to increase sales or data collection, undermining consumer trust in commerce. Ethical design prioritizes transparency and user autonomy, fostering long-term customer loyalty and sustainable business growth. Understanding the contrast between dark patterns and ethical design is crucial for developing responsible e-commerce platforms and enhancing user experience.
Key Terms
User Consent
Ethical design prioritizes transparent user consent by clearly outlining data usage and ensuring users have control over their personal information, fostering trust and respect. Dark patterns manipulate user choices by obscuring consent options or using deceptive interfaces to obtain permission, undermining user autonomy and privacy. Explore how adopting ethical design transforms user experiences and safeguards digital rights.
Transparency
Ethical design prioritizes transparency by clearly informing users about data collection, usage, and privacy policies, fostering trust and informed consent. Dark patterns deliberately obscure or manipulate information, leading users to make decisions they might not fully understand, often compromising privacy and autonomy. Explore the key differences between ethical design and dark patterns to enhance user experience and trust.
Manipulation
Ethical design prioritizes user autonomy by fostering transparency and consent, ensuring interfaces guide decisions without deception or coercion. Dark patterns manipulate user behavior through hidden tactics like disguised ads or forced continuity, exploiting cognitive biases for profit. Explore the nuances between ethical design and manipulation to enhance user trust and engagement.
Source and External Links
Ethical design guide: principles, benefits and examples - Ethical design involves creating products and systems that prioritize fairness, transparency, inclusivity, privacy, and sustainability, avoiding manipulative dark patterns and aiming to maximize positive impacts on individuals, society, and the environment.
The principles of ethical design (and how to use them) - 99Designs - Ethical design means aligning design work with moral values and business principles to ensure that products positively affect real people and communities, taking responsibility for its social and cultural impacts.
Ethical Design: What It Is & Why It's Important | Built In - Ethical design resists manipulative dark patterns, respects data privacy, prioritizes accessibility, and involves co-design with users to create human-centered, transparent, and responsible products.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com