Peer-to-peer (P2P) payments enable direct money transfers between individuals through mobile apps or online platforms, enhancing convenience and speed for personal transactions. Electronic funds transfer (EFT) encompasses a broader range of digital payment systems, including direct deposits, wire transfers, and automated clearing house (ACH) transactions used by businesses and financial institutions. Explore the key differences and use cases of P2P payments and EFT to optimize your commerce strategy.
Why it is important
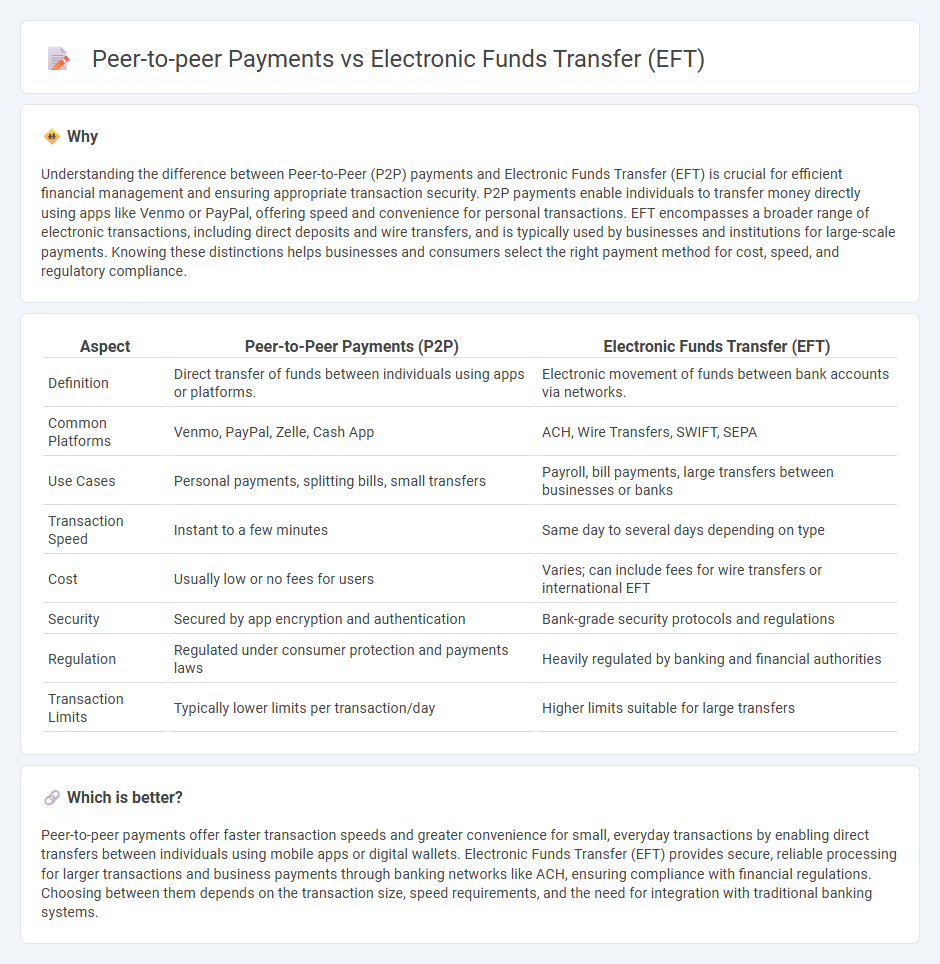
Understanding the difference between Peer-to-Peer (P2P) payments and Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) is crucial for efficient financial management and ensuring appropriate transaction security. P2P payments enable individuals to transfer money directly using apps like Venmo or PayPal, offering speed and convenience for personal transactions. EFT encompasses a broader range of electronic transactions, including direct deposits and wire transfers, and is typically used by businesses and institutions for large-scale payments. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses and consumers select the right payment method for cost, speed, and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Peer-to-Peer Payments (P2P) | Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct transfer of funds between individuals using apps or platforms. | Electronic movement of funds between bank accounts via networks. |
| Common Platforms | Venmo, PayPal, Zelle, Cash App | ACH, Wire Transfers, SWIFT, SEPA |
| Use Cases | Personal payments, splitting bills, small transfers | Payroll, bill payments, large transfers between businesses or banks |
| Transaction Speed | Instant to a few minutes | Same day to several days depending on type |
| Cost | Usually low or no fees for users | Varies; can include fees for wire transfers or international EFT |
| Security | Secured by app encryption and authentication | Bank-grade security protocols and regulations |
| Regulation | Regulated under consumer protection and payments laws | Heavily regulated by banking and financial authorities |
| Transaction Limits | Typically lower limits per transaction/day | Higher limits suitable for large transfers |
Which is better?
Peer-to-peer payments offer faster transaction speeds and greater convenience for small, everyday transactions by enabling direct transfers between individuals using mobile apps or digital wallets. Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) provides secure, reliable processing for larger transactions and business payments through banking networks like ACH, ensuring compliance with financial regulations. Choosing between them depends on the transaction size, speed requirements, and the need for integration with traditional banking systems.
Connection
Peer-to-peer payments leverage Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) technology to enable direct digital transactions between individuals without intermediaries, speeding up money transfers. EFT systems underpin the secure transfer of funds across banks and financial institutions, ensuring seamless, real-time transaction processing. This connection enhances commerce by facilitating instant payments, reducing transaction costs, and increasing financial accessibility.
Key Terms
Bank-to-bank transfer
Electronic funds transfer (EFT) encompasses bank-to-bank transfers where funds move securely between financial institutions via networks like ACH or wire transfers, ensuring efficient processing of payroll, bill payments, and business transactions. Peer-to-peer (P2P) payments, facilitated by apps such as Venmo or Zelle, enable individuals to send money instantly using linked bank accounts or debit cards without direct bank-to-bank infrastructure involvement. Explore deeper insights into bank-to-bank EFT mechanisms and their advantages over P2P platforms for business and consumer use.
Digital wallets
Electronic funds transfer (EFT) enables secure, bank-backed movement of money across accounts and institutions, widely used for payroll, bill payments, and direct deposits. Peer-to-peer (P2P) payments, often facilitated by digital wallets like PayPal, Venmo, and Cash App, focus on instant, user-friendly transfers between individuals via mobile devices, integrating contactless features and real-time notifications. Explore how digital wallets revolutionize convenience, security, and speed in personal finance.
Real-time settlement
Electronic funds transfer (EFT) facilitates the movement of funds between bank accounts through networks like ACH or wire transfers, often with settlement times ranging from same-day to several days. Peer-to-peer (P2P) payments leverage mobile apps and digital wallets to enable instant, real-time settlement directly between individuals without traditional bank intermediaries. Explore how real-time settlement in P2P payments transforms consumer transactions and financial services.
Source and External Links
What is Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT)? - EBANX - An electronic funds transfer (EFT) is a digital money movement from one bank account to another, replacing paper checks with faster, simpler, and paperless transactions completed typically within a few days.
EFT Payments Explained: A Business Guide On How They Work - EFT is a secure, efficient digital method for businesses to transfer money between accounts using systems like ACH, Fedwire, or SWIFT, enabling automation and rapid payment settlement.
What is Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT)? - Modern Treasury - EFTs are digital transfers of money between bank accounts initiated online or at a terminal, widely used by businesses and individuals to replace checks and speed up payments with minimal bank employee involvement.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com