Circular supply chains focus on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency by reusing, refurbishing, and recycling materials throughout the product lifecycle, promoting sustainability and cost savings. Decentralized supply chains distribute operations across multiple locations to enhance flexibility, reduce risks, and improve responsiveness to local demand variations. Explore the key differences and benefits of circular versus decentralized supply chains to optimize your commerce strategy.
Why it is important
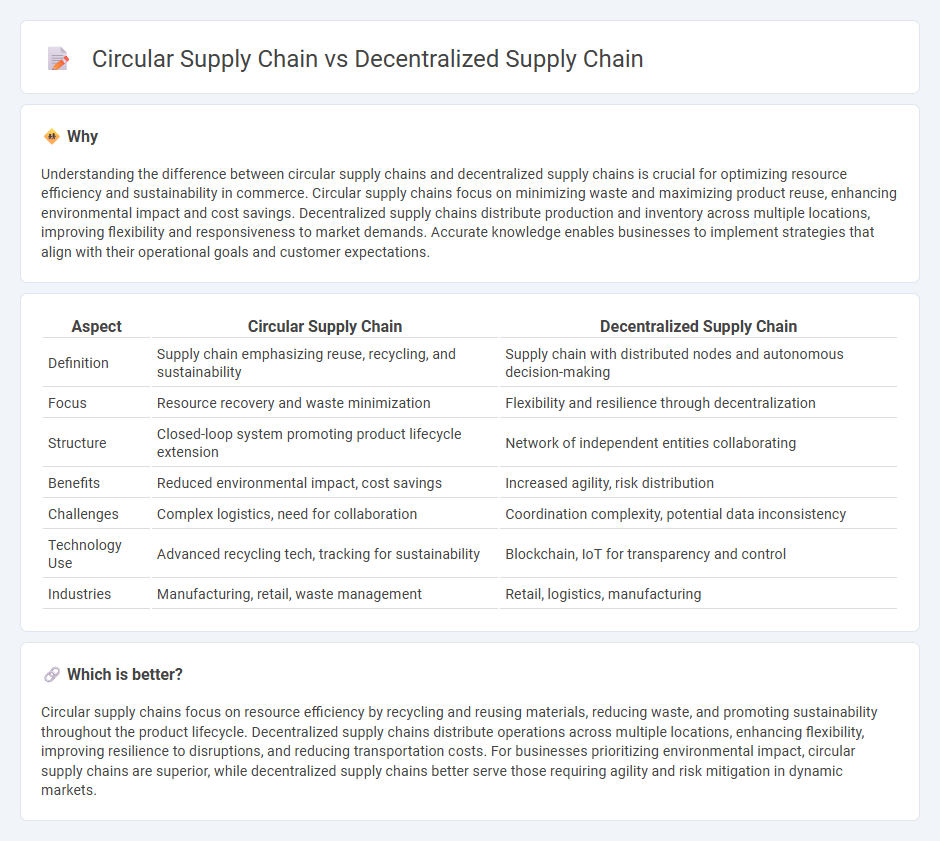
Understanding the difference between circular supply chains and decentralized supply chains is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and sustainability in commerce. Circular supply chains focus on minimizing waste and maximizing product reuse, enhancing environmental impact and cost savings. Decentralized supply chains distribute production and inventory across multiple locations, improving flexibility and responsiveness to market demands. Accurate knowledge enables businesses to implement strategies that align with their operational goals and customer expectations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Supply Chain | Decentralized Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supply chain emphasizing reuse, recycling, and sustainability | Supply chain with distributed nodes and autonomous decision-making |
| Focus | Resource recovery and waste minimization | Flexibility and resilience through decentralization |
| Structure | Closed-loop system promoting product lifecycle extension | Network of independent entities collaborating |
| Benefits | Reduced environmental impact, cost savings | Increased agility, risk distribution |
| Challenges | Complex logistics, need for collaboration | Coordination complexity, potential data inconsistency |
| Technology Use | Advanced recycling tech, tracking for sustainability | Blockchain, IoT for transparency and control |
| Industries | Manufacturing, retail, waste management | Retail, logistics, manufacturing |
Which is better?
Circular supply chains focus on resource efficiency by recycling and reusing materials, reducing waste, and promoting sustainability throughout the product lifecycle. Decentralized supply chains distribute operations across multiple locations, enhancing flexibility, improving resilience to disruptions, and reducing transportation costs. For businesses prioritizing environmental impact, circular supply chains are superior, while decentralized supply chains better serve those requiring agility and risk mitigation in dynamic markets.
Connection
Circular supply chains focus on minimizing waste by reusing, refurbishing, and recycling products within the supply network, enhancing sustainability across commerce operations. Decentralized supply chains distribute decision-making and resources across multiple nodes, increasing agility and responsiveness to local market demands, which aligns with circular principles by enabling localized reuse and resource optimization. Integrating these supply chain models fosters resilient, sustainable commerce systems that reduce environmental impact while maintaining efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Key Terms
Autonomy
Decentralized supply chains enhance autonomy by distributing decision-making power across multiple independent nodes, reducing reliance on central authorities and improving responsiveness. Circular supply chains prioritize resource reuse and sustainability, promoting autonomy through closed-loop systems that minimize waste and extend product life cycles. Explore how these approaches transform supply chain autonomy and drive innovation in modern industries.
Resource Looping
Decentralized supply chains distribute control and decision-making across multiple nodes, enhancing transparency and reducing bottlenecks in resource flow, while circular supply chains prioritize resource looping by designing processes to reuse, refurbish, and recycle materials continuously, minimizing waste and environmental impact. Integrating decentralized systems with circular principles accelerates resource looping efficiency, promoting sustainable resource management and reducing reliance on virgin materials. Explore how combining these strategies transforms supply chain resilience and sustainability for businesses embracing the circular economy.
Traceability
Decentralized supply chains enhance traceability by distributing data across multiple nodes, reducing the risk of tampering and increasing transparency for all stakeholders. Circular supply chains focus on traceability to track material flows and ensure the reuse, recycling, and recovery of resources, promoting sustainability and regulatory compliance. Explore detailed comparisons and benefits of traceability in both supply chain models to optimize your operational strategy.
Source and External Links
Centralized vs. Decentralized Supply Chains | Wayfindr - A decentralized supply chain features multiple warehouses (nodes) strategically placed near production or customers, offering benefits like wider customer reach, faster shipping, disaster resilience, and agility but requires complex logistics coordination and incurs higher overhead costs.
When to Centralize Or Decentralize Your Supply Chain - GEP - Decentralized supply chains leverage local advantages and regional factors for flexibility and localized solutions, making them especially suitable for small businesses, whereas centralized chains focus on unified processes for better control and efficiency, favoring larger businesses.
Centralised vs. decentralised supply chains -- the pros and cons - Decentralized supply chains reduce logistical costs by operating close to customers and suppliers, increase flexibility by allowing nodes semi-autonomy to respond to local market opportunities or trials, but require managing dispersed operations and decision-making.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com