Distributed ledger marketplaces utilize blockchain technology to record transactions transparently and immutably, enabling peer-to-peer commerce without central intermediaries. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) specifically focus on cryptocurrency trading, allowing users to swap tokens directly from their wallets through smart contracts while maintaining control over assets. Explore more about how these platforms reshape modern commerce and digital asset trading.
Why it is important
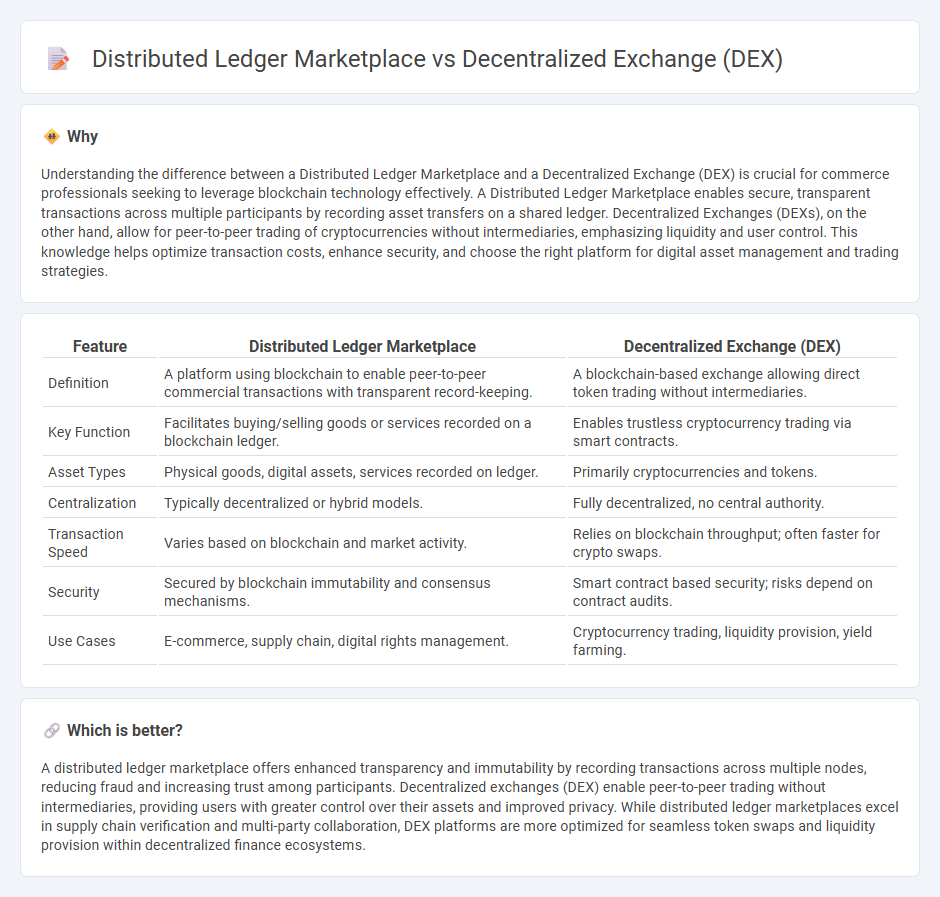
Understanding the difference between a Distributed Ledger Marketplace and a Decentralized Exchange (DEX) is crucial for commerce professionals seeking to leverage blockchain technology effectively. A Distributed Ledger Marketplace enables secure, transparent transactions across multiple participants by recording asset transfers on a shared ledger. Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs), on the other hand, allow for peer-to-peer trading of cryptocurrencies without intermediaries, emphasizing liquidity and user control. This knowledge helps optimize transaction costs, enhance security, and choose the right platform for digital asset management and trading strategies.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Distributed Ledger Marketplace | Decentralized Exchange (DEX) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A platform using blockchain to enable peer-to-peer commercial transactions with transparent record-keeping. | A blockchain-based exchange allowing direct token trading without intermediaries. |
| Key Function | Facilitates buying/selling goods or services recorded on a blockchain ledger. | Enables trustless cryptocurrency trading via smart contracts. |
| Asset Types | Physical goods, digital assets, services recorded on ledger. | Primarily cryptocurrencies and tokens. |
| Centralization | Typically decentralized or hybrid models. | Fully decentralized, no central authority. |
| Transaction Speed | Varies based on blockchain and market activity. | Relies on blockchain throughput; often faster for crypto swaps. |
| Security | Secured by blockchain immutability and consensus mechanisms. | Smart contract based security; risks depend on contract audits. |
| Use Cases | E-commerce, supply chain, digital rights management. | Cryptocurrency trading, liquidity provision, yield farming. |
Which is better?
A distributed ledger marketplace offers enhanced transparency and immutability by recording transactions across multiple nodes, reducing fraud and increasing trust among participants. Decentralized exchanges (DEX) enable peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries, providing users with greater control over their assets and improved privacy. While distributed ledger marketplaces excel in supply chain verification and multi-party collaboration, DEX platforms are more optimized for seamless token swaps and liquidity provision within decentralized finance ecosystems.
Connection
Distributed ledger marketplaces leverage blockchain technology to enable transparent, secure, and tamper-proof transactions, forming the foundational infrastructure for Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs). DEXs operate directly on distributed ledgers, allowing users to trade digital assets peer-to-peer without intermediaries, enhancing liquidity and reducing counterparty risk. The integration of smart contracts within these marketplaces automates trade settlements, ensuring trustless and efficient commerce across global decentralized financial ecosystems.
Key Terms
Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) enable users to trade assets directly from pooled reserves without intermediaries, enhancing transaction speed and reducing costs. Distributed ledger marketplaces integrate liquidity pools with blockchain technology to ensure transparency, immutability, and real-time asset tracking, fostering trust among participants. Explore the distinct mechanisms of liquidity management in DEXs and distributed ledger marketplaces to better understand their impact on digital asset trading.
Smart Contracts
Decentralized exchanges (DEX) leverage smart contracts to enable peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries, ensuring transparency and automated transaction execution on blockchain networks like Ethereum. Distributed ledger marketplaces use smart contracts to facilitate secure asset exchanges across multiple parties, enhancing trust and reducing fraud by recording transactions immutably and enabling programmable agreements. Explore deeper insights on how smart contracts revolutionize decentralized financial ecosystems.
Peer-to-Peer Trading
A decentralized exchange (DEX) enables direct peer-to-peer trading of cryptocurrencies without intermediaries, leveraging smart contracts on blockchain networks like Ethereum to ensure transparency and security. Distributed ledger marketplaces extend this concept by using blockchain technology to facilitate peer-to-peer transactions across various digital assets and services, often incorporating broader consensus mechanisms beyond token swaps. Explore the intricacies of peer-to-peer trading dynamics and the technological frameworks that differentiate DEXs from distributed ledger marketplaces to optimize your understanding of decentralized finance.
Source and External Links
The Ins and Outs of Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) - Hedera - A DEX uses smart contracts to allow users to trade cryptocurrencies directly from their wallets without intermediaries, enhancing privacy and control over funds, with types including automated market makers, order books, and aggregators.
Decentralized Exchange (DEX) - XRP Ledger - The XRP Ledger hosts one of the oldest DEXs enabling peer-to-peer token trading without centralized intermediaries, using smart contracts and offering an order book model without mandatory AMMs.
What is a DEX? - Coinbase - A DEX is a peer-to-peer crypto marketplace where trades between tokens happen on-chain through smart contracts and liquidity pools, contrasting with centralized exchanges that handle fiat and crypto with internal order books.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com