Distributed ledger marketplaces operate on decentralized networks where multiple participants maintain a synchronized ledger, enhancing transparency and reducing fraud. Consortium blockchain marketplaces restrict access to a select group of trusted entities, providing greater control and privacy while still leveraging blockchain's security features. Explore the key differences and benefits of each marketplace model to understand their impact on modern commerce.
Why it is important
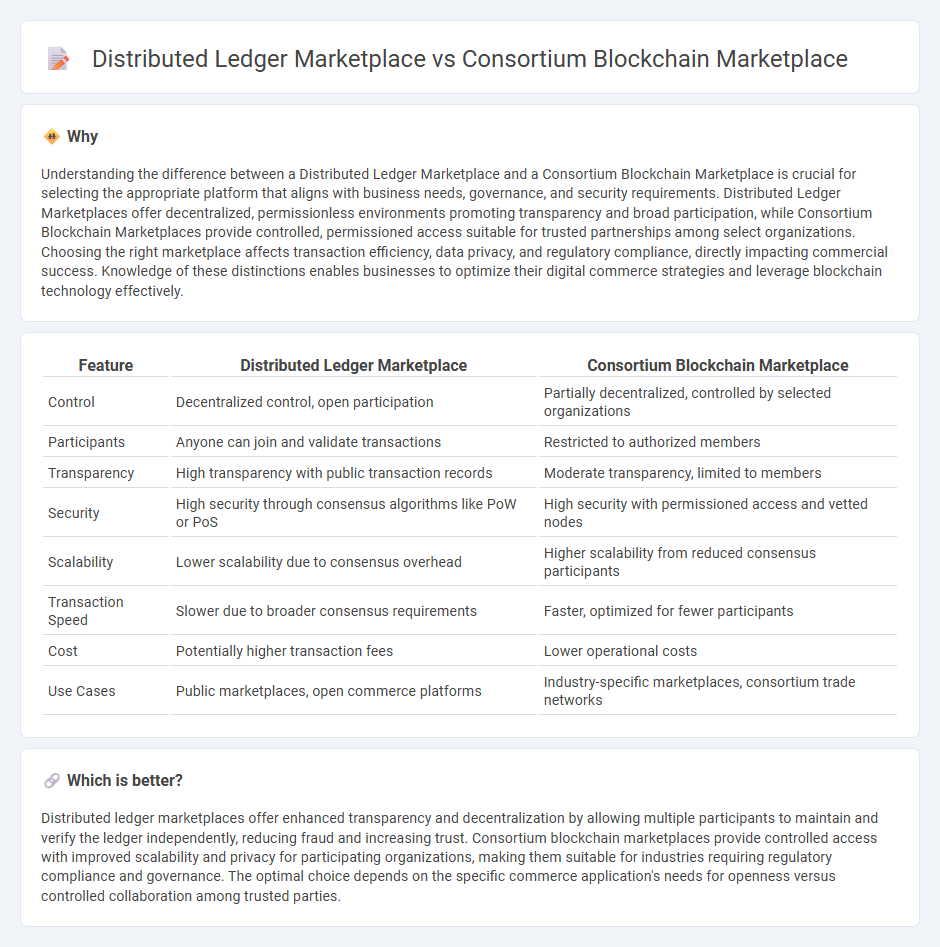
Understanding the difference between a Distributed Ledger Marketplace and a Consortium Blockchain Marketplace is crucial for selecting the appropriate platform that aligns with business needs, governance, and security requirements. Distributed Ledger Marketplaces offer decentralized, permissionless environments promoting transparency and broad participation, while Consortium Blockchain Marketplaces provide controlled, permissioned access suitable for trusted partnerships among select organizations. Choosing the right marketplace affects transaction efficiency, data privacy, and regulatory compliance, directly impacting commercial success. Knowledge of these distinctions enables businesses to optimize their digital commerce strategies and leverage blockchain technology effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Distributed Ledger Marketplace | Consortium Blockchain Marketplace |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Decentralized control, open participation | Partially decentralized, controlled by selected organizations |
| Participants | Anyone can join and validate transactions | Restricted to authorized members |
| Transparency | High transparency with public transaction records | Moderate transparency, limited to members |
| Security | High security through consensus algorithms like PoW or PoS | High security with permissioned access and vetted nodes |
| Scalability | Lower scalability due to consensus overhead | Higher scalability from reduced consensus participants |
| Transaction Speed | Slower due to broader consensus requirements | Faster, optimized for fewer participants |
| Cost | Potentially higher transaction fees | Lower operational costs |
| Use Cases | Public marketplaces, open commerce platforms | Industry-specific marketplaces, consortium trade networks |
Which is better?
Distributed ledger marketplaces offer enhanced transparency and decentralization by allowing multiple participants to maintain and verify the ledger independently, reducing fraud and increasing trust. Consortium blockchain marketplaces provide controlled access with improved scalability and privacy for participating organizations, making them suitable for industries requiring regulatory compliance and governance. The optimal choice depends on the specific commerce application's needs for openness versus controlled collaboration among trusted parties.
Connection
Distributed ledger marketplaces utilize decentralized databases to enable transparent, secure, and tamper-proof transactions, while consortium blockchain marketplaces operate within a permissioned network controlled by a group of organizations. Both models enhance trust and efficiency in commerce by facilitating verified data sharing and reducing intermediaries. They intersect by leveraging blockchain technology to create collaborative ecosystems that streamline supply chain management and digital asset exchange.
Key Terms
Governance Model
Consortium blockchain marketplaces operate under a governance model where a pre-selected group of organizations collaboratively manage the network, ensuring controlled participation and decision-making transparency. Distributed ledger marketplaces employ a decentralized governance structure that allows diverse participants to validate transactions and enforce rules through consensus protocols, promoting inclusivity and resilience. Explore deeper insights into how governance impacts security, scalability, and trust within these marketplace frameworks.
Access Control
Consortium blockchain marketplaces leverage selective access control, allowing only pre-approved participants to validate transactions and manage data, enhancing privacy and security among trusted entities. Distributed ledger marketplaces, however, may offer varying access control models, ranging from permissioned to permissionless, affecting transparency and participation scope. Explore deeper comparisons to understand which access control model suits your marketplace needs.
Data Transparency
Consortium blockchain marketplaces leverage permissioned networks where selected entities validate transactions, enhancing data transparency through controlled access and shared ledgers among known participants. Distributed ledger marketplaces, often public or permissionless, provide broader data visibility but face challenges in ensuring participant trust and transaction privacy. Explore in-depth comparisons of data transparency mechanisms and their impact on marketplace integrity.
Source and External Links
What is a Consortium Blockchain? - A Complete Guide - Shardeum - A consortium blockchain is a semi-decentralized network formed by multiple organizations, combining their private blockchains to allow controlled data sharing and collaboration, often used in industries like finance, logistics, and healthcare to improve processes and transparency within a marketplace context.
Consortium Blockchain: What You Need to Know - Kaleido - Consortium blockchains offer a collaborative platform for multiple organizations to work securely and efficiently with controlled network access, enabling marketplaces where participants maintain autonomy while sharing data and transactions in a private yet decentralized network.
What is Consortium Blockchain? A Complete Guide - CFTE - Consortium blockchains facilitate marketplaces by enabling multiple stakeholders such as banks, logistics providers, or healthcare companies to share and validate data on a permissioned network with low transaction fees, high scalability, and no single entity control, enhancing trust and operational efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com