Circular supply chains focus on minimizing waste through resource recovery, reuse, and recycling across multiple product life cycles, promoting sustainability in commerce. Closed-loop supply chains emphasize the direct return of products to the manufacturer for refurbishment or remanufacturing, ensuring higher control over quality and reducing raw material dependency. Explore how these supply chain models transform business practices and drive eco-friendly commerce.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between circular supply chain and closed-loop supply chain is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and sustainability in commerce. Circular supply chains focus on maximizing product and material reuse throughout the entire lifecycle, reducing waste and environmental impact. Closed-loop supply chains specifically emphasize reclaiming and recycling products to reintroduce materials into the production process. This knowledge enables businesses to design effective strategies for cost reduction, regulatory compliance, and enhanced brand reputation.
Comparison Table
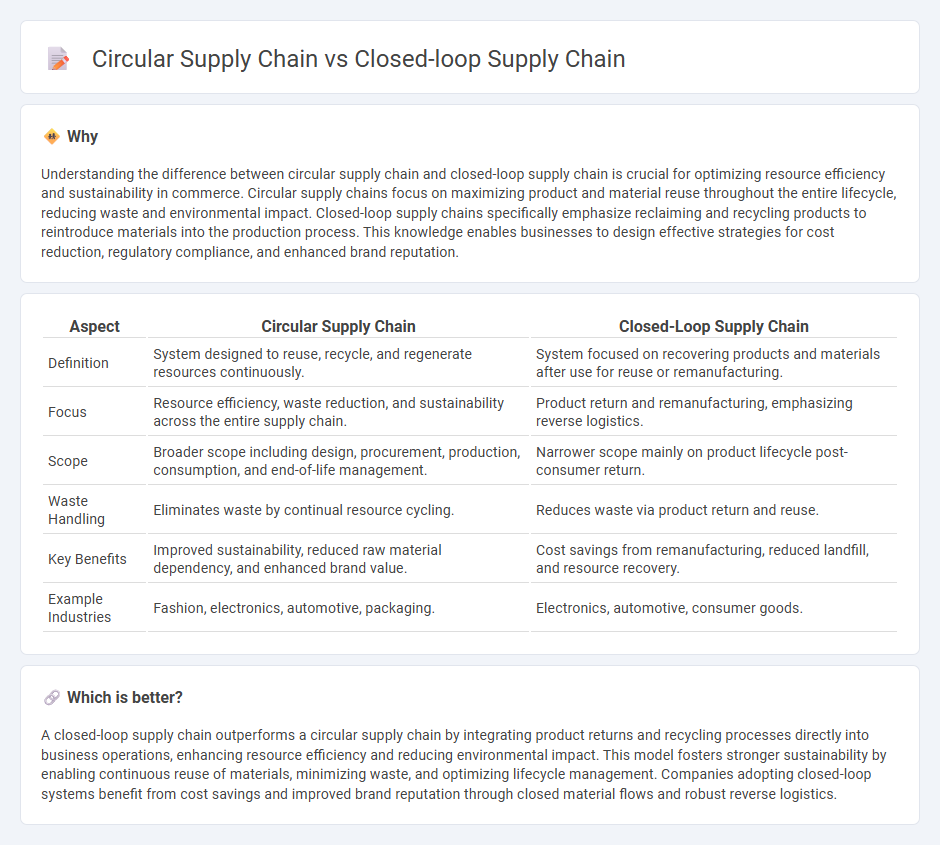
| Aspect | Circular Supply Chain | Closed-Loop Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | System designed to reuse, recycle, and regenerate resources continuously. | System focused on recovering products and materials after use for reuse or remanufacturing. |
| Focus | Resource efficiency, waste reduction, and sustainability across the entire supply chain. | Product return and remanufacturing, emphasizing reverse logistics. |
| Scope | Broader scope including design, procurement, production, consumption, and end-of-life management. | Narrower scope mainly on product lifecycle post-consumer return. |
| Waste Handling | Eliminates waste by continual resource cycling. | Reduces waste via product return and reuse. |
| Key Benefits | Improved sustainability, reduced raw material dependency, and enhanced brand value. | Cost savings from remanufacturing, reduced landfill, and resource recovery. |
| Example Industries | Fashion, electronics, automotive, packaging. | Electronics, automotive, consumer goods. |
Which is better?
A closed-loop supply chain outperforms a circular supply chain by integrating product returns and recycling processes directly into business operations, enhancing resource efficiency and reducing environmental impact. This model fosters stronger sustainability by enabling continuous reuse of materials, minimizing waste, and optimizing lifecycle management. Companies adopting closed-loop systems benefit from cost savings and improved brand reputation through closed material flows and robust reverse logistics.
Connection
Circular supply chains and closed-loop supply chains are interconnected through their focus on sustainability and resource efficiency. Both systems prioritize minimizing waste by reusing, refurbishing, and recycling materials throughout the product lifecycle. Implementing these models reduces environmental impact and enhances economic value by maintaining product value within the supply chain for longer periods.
Key Terms
Reverse Logistics
Closed-loop supply chains emphasize the return and reuse of products through effective reverse logistics to minimize waste and recover value, primarily targeting product lifecycle extension and resource efficiency. Circular supply chains expand this concept by integrating sustainable design, reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling processes, creating a regenerative system that closes material loops throughout the entire supply chain. Discover more about how reverse logistics drives both models toward sustainability and operational excellence.
Product Lifecycle
Closed-loop supply chains emphasize reclaiming and reusing products and materials immediately after consumption to minimize waste within the product lifecycle. Circular supply chains extend this concept by integrating product design, production, and end-of-life processes to ensure continuous resource regeneration and value retention. Explore how these strategies transform sustainability in supply chain management and impact product lifecycle optimization.
Resource Recovery
Closed-loop supply chains prioritize the reuse and remanufacturing of products to minimize waste by returning materials back into the production cycle. Circular supply chains emphasize a broader approach to resource recovery, incorporating recycling, refurbishing, and sustainable design to extend product lifecycle and reduce environmental impact. Explore more about how these strategies optimize resource recovery and drive sustainable business practices.
Source and External Links
Unlocking the Potential of a Closed Loop Supply Chain - A closed loop supply chain integrates forward and reverse logistics to create a circular flow where products are recovered after use and reintegrated into production, reducing costs, waste, and environmental impact.
Closed Loop Supply Chain (CLSC): Meaning & Examples - CLSC manages the entire life cycle of a product by enabling forward product flow and backward flow of used products for reuse or recycling, thereby promoting sustainability and minimizing waste.
Closed-Loop Supply Chain -- What You Need to Know - Closed-loop supply chains reduce waste by reusing or recycling product materials instead of discarding them, benefiting sustainability and resource conservation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com