Circular supply chains focus on resource efficiency by reusing, recycling, and regenerating materials, reducing waste and environmental impact, while centralized supply chains concentrate operations and inventory management in a single or few locations to optimize control and reduce costs. Circular supply chains promote sustainability and resilience by closing the loop on product lifecycles, whereas centralized supply chains prioritize centralized decision-making for streamlined logistics and economies of scale. Explore the advantages and challenges of each approach to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Why it is important
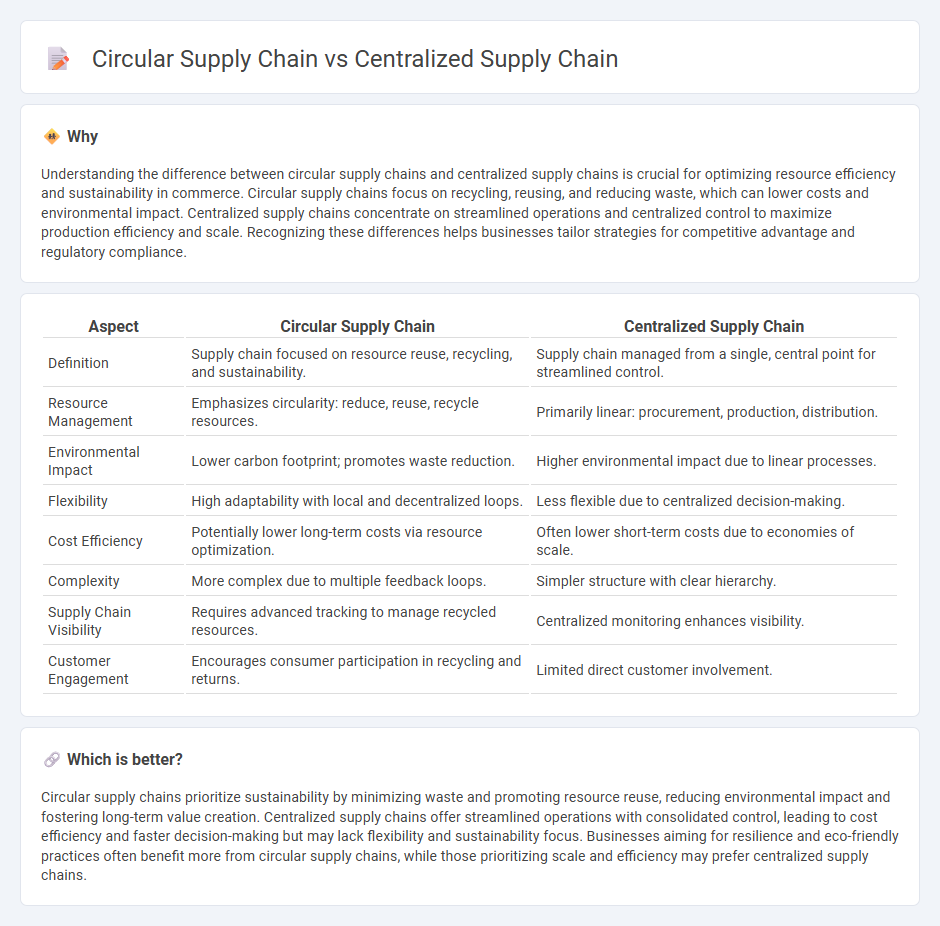
Understanding the difference between circular supply chains and centralized supply chains is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and sustainability in commerce. Circular supply chains focus on recycling, reusing, and reducing waste, which can lower costs and environmental impact. Centralized supply chains concentrate on streamlined operations and centralized control to maximize production efficiency and scale. Recognizing these differences helps businesses tailor strategies for competitive advantage and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Supply Chain | Centralized Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supply chain focused on resource reuse, recycling, and sustainability. | Supply chain managed from a single, central point for streamlined control. |
| Resource Management | Emphasizes circularity: reduce, reuse, recycle resources. | Primarily linear: procurement, production, distribution. |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint; promotes waste reduction. | Higher environmental impact due to linear processes. |
| Flexibility | High adaptability with local and decentralized loops. | Less flexible due to centralized decision-making. |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially lower long-term costs via resource optimization. | Often lower short-term costs due to economies of scale. |
| Complexity | More complex due to multiple feedback loops. | Simpler structure with clear hierarchy. |
| Supply Chain Visibility | Requires advanced tracking to manage recycled resources. | Centralized monitoring enhances visibility. |
| Customer Engagement | Encourages consumer participation in recycling and returns. | Limited direct customer involvement. |
Which is better?
Circular supply chains prioritize sustainability by minimizing waste and promoting resource reuse, reducing environmental impact and fostering long-term value creation. Centralized supply chains offer streamlined operations with consolidated control, leading to cost efficiency and faster decision-making but may lack flexibility and sustainability focus. Businesses aiming for resilience and eco-friendly practices often benefit more from circular supply chains, while those prioritizing scale and efficiency may prefer centralized supply chains.
Connection
Circular supply chains and centralized supply chains intersect through their shared focus on efficiency and resource optimization, where centralized systems streamline inventory management and distribution, enabling effective reintegration of recycled materials and waste reduction. Centralized supply chains facilitate data consolidation and coordination, critical for tracking product lifecycle stages essential to circular economy principles. This integration supports sustainable commerce by minimizing resource consumption and enhancing product reuse within a unified operational framework.
Key Terms
Control
Centralized supply chains emphasize strict control through a hierarchical structure, ensuring streamlined decision-making and efficient resource allocation from a singular point. Circular supply chains prioritize control over resource recovery and waste reduction by integrating processes that enable reuse, recycling, and regeneration of materials. Explore deeper insights on how control mechanisms differ and impact sustainability in supply chain management.
Resource Recovery
Centralized supply chains concentrate resources and processes in a single hub to optimize efficiency and reduce costs but often face challenges in minimizing waste and recovering materials. Circular supply chains emphasize resource recovery by designing systems that reuse, remanufacture, and recycle materials, thereby extending product life cycles and reducing environmental impact. Explore more about how resource recovery innovations drive the shift from centralized to circular supply chain models.
Waste Minimization
Centralized supply chains typically concentrate inventory and production in a few locations, which can lead to higher waste due to overproduction and inefficient transportation. Circular supply chains emphasize resource recovery, reuse, and recycling to minimize waste and extend product life cycles. Explore how circular models reduce environmental impact and drive sustainable waste management in modern supply networks.
Source and External Links
Centralized vs. Decentralized Supply Chains | Wayfindr - A centralized supply chain is managed from a single headquarters or warehouse where operations, decision-making, inventory, and distribution occur, allowing for cost savings, simplified management, and bulk shipping but suffering from reduced flexibility and higher risk from disruptions.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Supply Chain Structure - In a centralized supply chain, decision-making and control over procurement, production, and inventory are concentrated at a central location, enabling economies of scale, consistent quality, and efficient inventory management, though less responsive to regional variations.
Four Advantages of Centralizing Supply Chain Management - Centralizing supply chain management improves risk identification and mitigation, compliance tracking, and enables faster market response and scalability by coordinating all functions under one unified point.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com