Sales strategies often include both selling and up-selling, but understanding survivor bias is crucial for maximizing effectiveness. Survivor bias can lead to overestimating the success of up-selling techniques by focusing only on successful transactions while ignoring failed attempts. Explore the impact of survivor bias on your sales methods to enhance revenue growth and customer satisfaction.
Why it is important
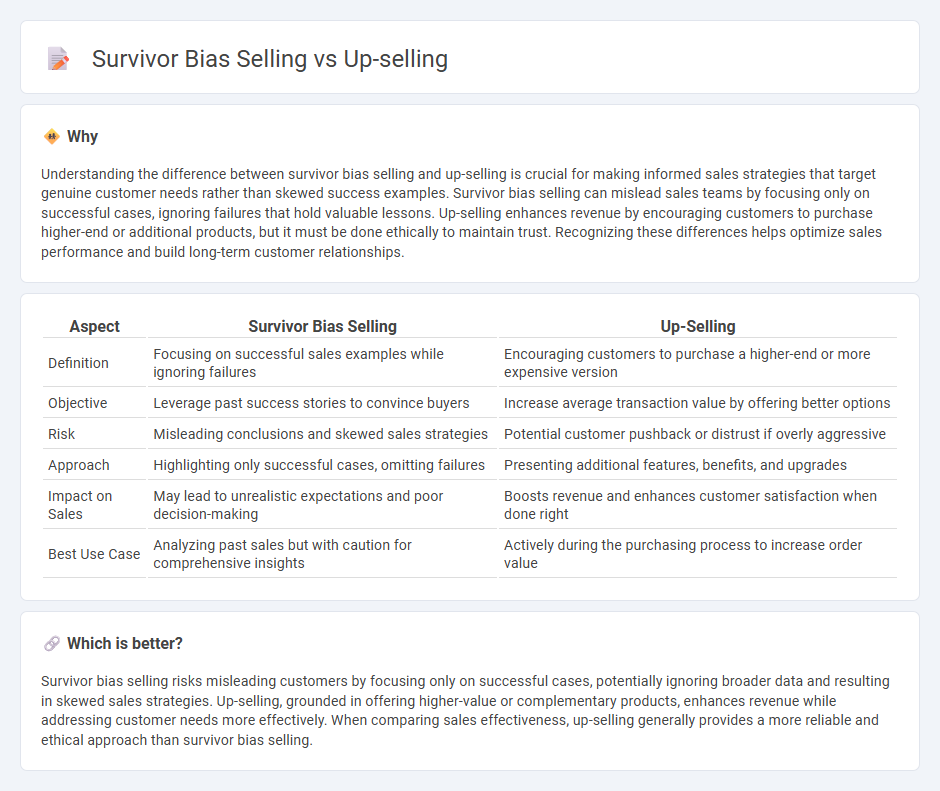
Understanding the difference between survivor bias selling and up-selling is crucial for making informed sales strategies that target genuine customer needs rather than skewed success examples. Survivor bias selling can mislead sales teams by focusing only on successful cases, ignoring failures that hold valuable lessons. Up-selling enhances revenue by encouraging customers to purchase higher-end or additional products, but it must be done ethically to maintain trust. Recognizing these differences helps optimize sales performance and build long-term customer relationships.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Survivor Bias Selling | Up-Selling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focusing on successful sales examples while ignoring failures | Encouraging customers to purchase a higher-end or more expensive version |
| Objective | Leverage past success stories to convince buyers | Increase average transaction value by offering better options |
| Risk | Misleading conclusions and skewed sales strategies | Potential customer pushback or distrust if overly aggressive |
| Approach | Highlighting only successful cases, omitting failures | Presenting additional features, benefits, and upgrades |
| Impact on Sales | May lead to unrealistic expectations and poor decision-making | Boosts revenue and enhances customer satisfaction when done right |
| Best Use Case | Analyzing past sales but with caution for comprehensive insights | Actively during the purchasing process to increase order value |
Which is better?
Survivor bias selling risks misleading customers by focusing only on successful cases, potentially ignoring broader data and resulting in skewed sales strategies. Up-selling, grounded in offering higher-value or complementary products, enhances revenue while addressing customer needs more effectively. When comparing sales effectiveness, up-selling generally provides a more reliable and ethical approach than survivor bias selling.
Connection
Survivor bias in sales leads to overestimating the success of selling and upselling strategies by focusing only on top performers while ignoring those who fail. This bias skews data analysis, causing sales teams to adopt techniques that may not be universally effective. Recognizing survivor bias helps develop more accurate sales models and optimize upselling approaches for diverse market segments.
Key Terms
Cross-selling
Cross-selling leverages the opportunity to offer complementary products that enhance the customer's original purchase, increasing overall revenue without relying on consumer misconceptions. Unlike survivor bias selling, which targets only top performers or successful cases, cross-selling provides tailored solutions based on customer needs and preferences to drive satisfaction and loyalty. Explore effective cross-selling strategies to maximize customer value and business growth.
Anchoring
Up-selling involves guiding customers toward higher-value products by anchoring their perception of worth, while survivor bias selling overlooks failed attempts and emphasizes only successful sales outcomes, skewing judgment. Anchoring in up-selling strategically sets a reference price, making premium options appear more attractive and justifiable. Explore how mastering anchoring techniques can enhance both sales strategies for improved customer engagement and revenue growth.
Confirmation bias
Up-selling techniques often exploit confirmation bias by reinforcing customers' existing beliefs about product quality or value, leading to increased sales through personalized recommendations. Survivor bias selling, on the other hand, presents only successful case studies or outcomes, skewing customer perception by ignoring failures and thus confirming optimism about the product. Explore deeper insights into how cognitive biases shape effective sales strategies and consumer decision-making.
Source and External Links
Upselling - Wikipedia - Upselling is a sales technique where a seller invites the customer to purchase more expensive items, upgrades, or add-ons to increase revenue, distinct from cross-selling which involves selling additional products; it often involves understanding customer needs, creating urgency, or offering extended warranties.
What Is Upselling? Definition, Examples, & Expert Tips - Plaky - Upselling involves offering a higher-end or upgraded version of a product to meet customer needs better, which can increase sales revenue, boost customer retention, and improve brand reputation by aligning recommendations with customer pain points.
What Is Upselling? Upselling Definition and Examples - Shopify - Upselling is a legitimate sales strategy encouraging customers to purchase more expensive items or upgrades, aimed at deepening customer relationships and enhancing the customer experience while increasing business revenue.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com