Survivor bias selling focuses on the success stories of top-performing salespeople, highlighting strategies that have led to exceptional results but often overlooking the challenges faced by the majority. Transactional selling emphasizes quick, straightforward exchanges aimed at closing individual deals without necessarily building long-term relationships or considering broader business impact. Explore the nuances between these approaches to enhance your sales techniques and drive sustainable growth.
Why it is important
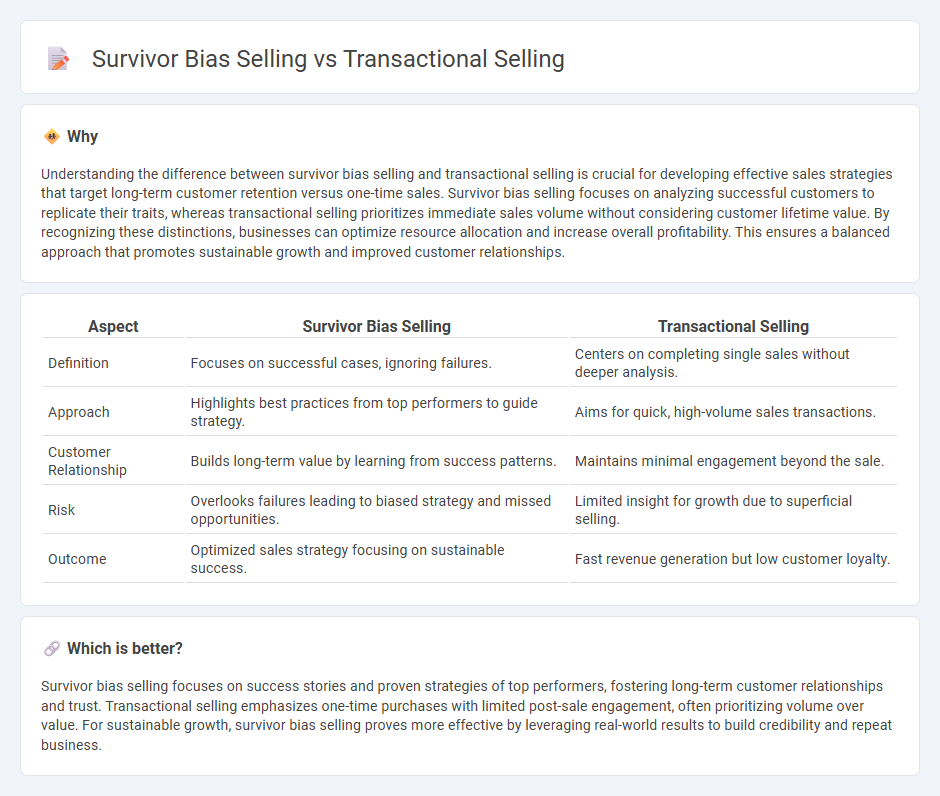
Understanding the difference between survivor bias selling and transactional selling is crucial for developing effective sales strategies that target long-term customer retention versus one-time sales. Survivor bias selling focuses on analyzing successful customers to replicate their traits, whereas transactional selling prioritizes immediate sales volume without considering customer lifetime value. By recognizing these distinctions, businesses can optimize resource allocation and increase overall profitability. This ensures a balanced approach that promotes sustainable growth and improved customer relationships.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Survivor Bias Selling | Transactional Selling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on successful cases, ignoring failures. | Centers on completing single sales without deeper analysis. |
| Approach | Highlights best practices from top performers to guide strategy. | Aims for quick, high-volume sales transactions. |
| Customer Relationship | Builds long-term value by learning from success patterns. | Maintains minimal engagement beyond the sale. |
| Risk | Overlooks failures leading to biased strategy and missed opportunities. | Limited insight for growth due to superficial selling. |
| Outcome | Optimized sales strategy focusing on sustainable success. | Fast revenue generation but low customer loyalty. |
Which is better?
Survivor bias selling focuses on success stories and proven strategies of top performers, fostering long-term customer relationships and trust. Transactional selling emphasizes one-time purchases with limited post-sale engagement, often prioritizing volume over value. For sustainable growth, survivor bias selling proves more effective by leveraging real-world results to build credibility and repeat business.
Connection
Survivor bias selling and transactional selling both focus on short-term gains, often overlooking broader customer lifetime value and potential risks in the sales process. Survivor bias can lead sales teams to prioritize deals that seem successful based on past wins, skewing judgment towards similar transactions and perpetuating transactional selling behaviors. This connection limits strategic growth by emphasizing quick sales cycles over sustainable customer relationships.
Key Terms
One-time Purchase (Transactional Selling)
Transactional selling centers on securing a one-time purchase by emphasizing immediate benefits, price, and product features to close the deal quickly. In contrast, survivor bias selling overlooks failures by focusing solely on successful outcomes, often leading to unrealistic expectations in sales strategies. Discover how mastering transactional selling can improve short-term revenue by exploring effective techniques and best practices.
Customer Retention (Survivor Bias Selling)
Transactional selling emphasizes one-time purchases and short-term gains, often neglecting long-term customer relationships. Survivor bias selling, centered on customer retention, focuses on nurturing loyal clients who continue to generate revenue over time, leveraging insights from successful customer experiences to enhance engagement. Explore effective strategies to shift from transactional approaches to retention-focused selling for sustained business growth.
Short-term Focus (Transactional Selling)
Transactional selling emphasizes immediate sales goals, prioritizing quick deal closures over long-term customer relationships or value creation. This short-term focus often overlooks potential ongoing revenue and repeat business by ignoring deeper client needs and trust-building. Explore more about how shifting from transactional selling to a relationship-driven approach can boost sustainable growth and customer loyalty.
Source and External Links
What is transactional selling, and how does this approach ... - Transactional selling is a sales strategy focused on making quick, one-time sales by emphasizing competitive pricing, social proof, and purchase urgency, with very short sales cycles and low focus on building long-term customer relationships.
Transactional selling: Strategy, definition and how it works - This selling strategy aims to drive immediate revenue through quick sales, relying on minimal personalization and urgency tactics such as scarcity and promotional offers to close deals fast.
The One-Call Close: A guide to transactional sales - Transactional selling focuses on speed and efficiency to close deals rapidly with minimal interactions, thereby accelerating revenue growth and improving sales velocity by moving high volumes of sales quickly.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com