Sales professionals often face challenges distinguishing between ghost demos--situations where prospects attend presentations without genuine buying intent--and stalling, where potential clients delay decisions to avoid commitment. Recognizing these behaviors improves forecasting accuracy and tailors follow-up strategies, ultimately boosting conversion rates. Explore effective techniques to identify and overcome ghost demos and stalling in your sales process.
Why it is important
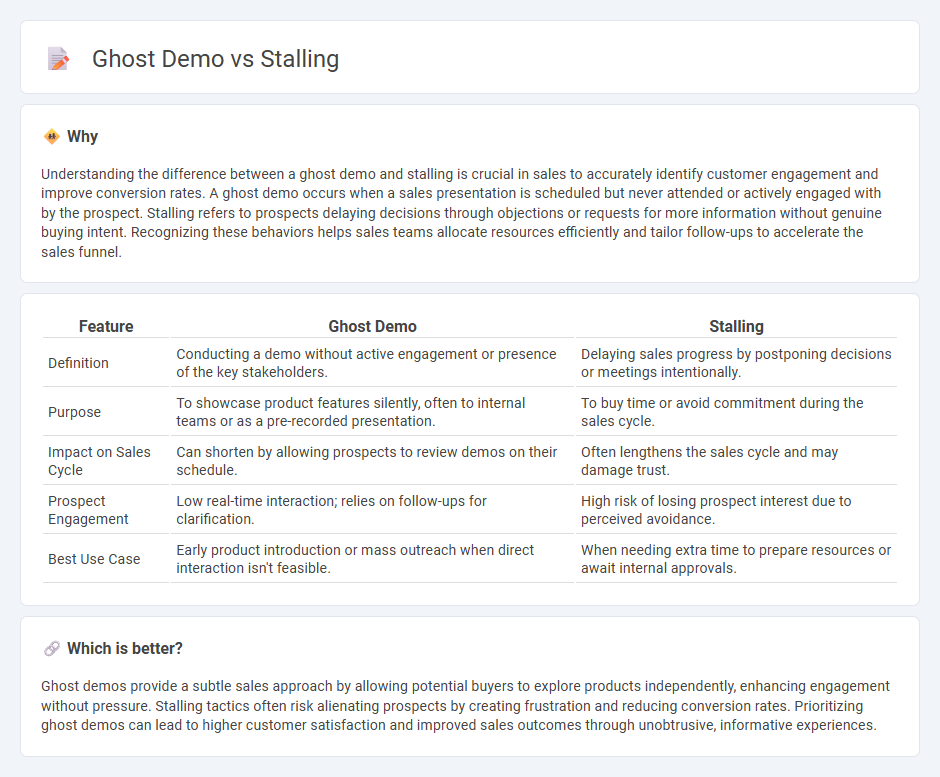
Understanding the difference between a ghost demo and stalling is crucial in sales to accurately identify customer engagement and improve conversion rates. A ghost demo occurs when a sales presentation is scheduled but never attended or actively engaged with by the prospect. Stalling refers to prospects delaying decisions through objections or requests for more information without genuine buying intent. Recognizing these behaviors helps sales teams allocate resources efficiently and tailor follow-ups to accelerate the sales funnel.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Ghost Demo | Stalling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conducting a demo without active engagement or presence of the key stakeholders. | Delaying sales progress by postponing decisions or meetings intentionally. |
| Purpose | To showcase product features silently, often to internal teams or as a pre-recorded presentation. | To buy time or avoid commitment during the sales cycle. |
| Impact on Sales Cycle | Can shorten by allowing prospects to review demos on their schedule. | Often lengthens the sales cycle and may damage trust. |
| Prospect Engagement | Low real-time interaction; relies on follow-ups for clarification. | High risk of losing prospect interest due to perceived avoidance. |
| Best Use Case | Early product introduction or mass outreach when direct interaction isn't feasible. | When needing extra time to prepare resources or await internal approvals. |
Which is better?
Ghost demos provide a subtle sales approach by allowing potential buyers to explore products independently, enhancing engagement without pressure. Stalling tactics often risk alienating prospects by creating frustration and reducing conversion rates. Prioritizing ghost demos can lead to higher customer satisfaction and improved sales outcomes through unobtrusive, informative experiences.
Connection
Ghost demos occur when sales representatives schedule product demonstrations but fail to attend or engage, causing delays in the sales process. Stalling often results from these no-shows, leading to postponed decisions and extended sales cycles. Addressing ghost demos can significantly reduce stalling, improving conversion rates and accelerating revenue growth.
Key Terms
Objection Handling
Stalling and ghosting during sales demos signal distinct buyer objections requiring tailored objection handling strategies. Stalling involves buyers expressing hesitation or requests for more information, signaling a need for reassurance and clarity on value propositions and ROI. To effectively address these concerns and prevent ghosting - when buyers suddenly stop responding - sales professionals should implement proactive follow-up techniques and refine objection handling skills; discover advanced methods to enhance your engagement success.
Follow-up Cadence
Stalling involves delaying responses during the follow-up cadence, signaling hesitance or unresolved objections from prospects. Ghosting occurs when prospects abruptly stop all communications, disrupting the sales or engagement rhythm completely. Explore strategies to optimize follow-up cadence and convert stalled or ghosted leads into meaningful conversations.
Pipeline Management
Stalling in pipeline management occurs when deals are delayed due to insufficient follow-up or unclear next steps, often resulting in prolonged sales cycles and reduced forecast accuracy. Ghosting happens when prospects abruptly stop responding, leaving pipeline managers with incomplete information and unpredictable revenue outcomes. Understanding these challenges enhances pipeline visibility and control--discover more strategies to optimize your sales pipeline management effectively.
Source and External Links
Car stalling: Why it happens and how to avoid it | RAC Drive - Car stalling occurs when the engine suddenly stops due to insufficient power or incorrect clutch use, with common causes including battery faults, fuel issues, clogged filters, worn spark plugs, and incorrect clutch control especially when pulling away from a stop.
7 Usual Reasons Why Your Car Stalls | Hanania Acura of Orange Park - Stalling can be caused by exhaust problems like a clogged catalytic converter or transmission issues such as clutch problems in manuals or torque converter problems in automatics disrupting power delivery.
Stall (fluid dynamics) - Wikipedia - In fluid dynamics and aviation, a stall is the loss of lift occurring when an aircraft's angle of attack exceeds a critical point, causing airflow separation and a decrease in lift force.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com