Multi-threading in sales enables concurrent management of multiple customer interactions, increasing efficiency and response times compared to single-threading where efforts focus on one lead at a time. This approach leverages parallel processing to optimize task handling and boost overall productivity in sales operations. Explore how multi-threading can transform your sales strategy for enhanced results.
Why it is important
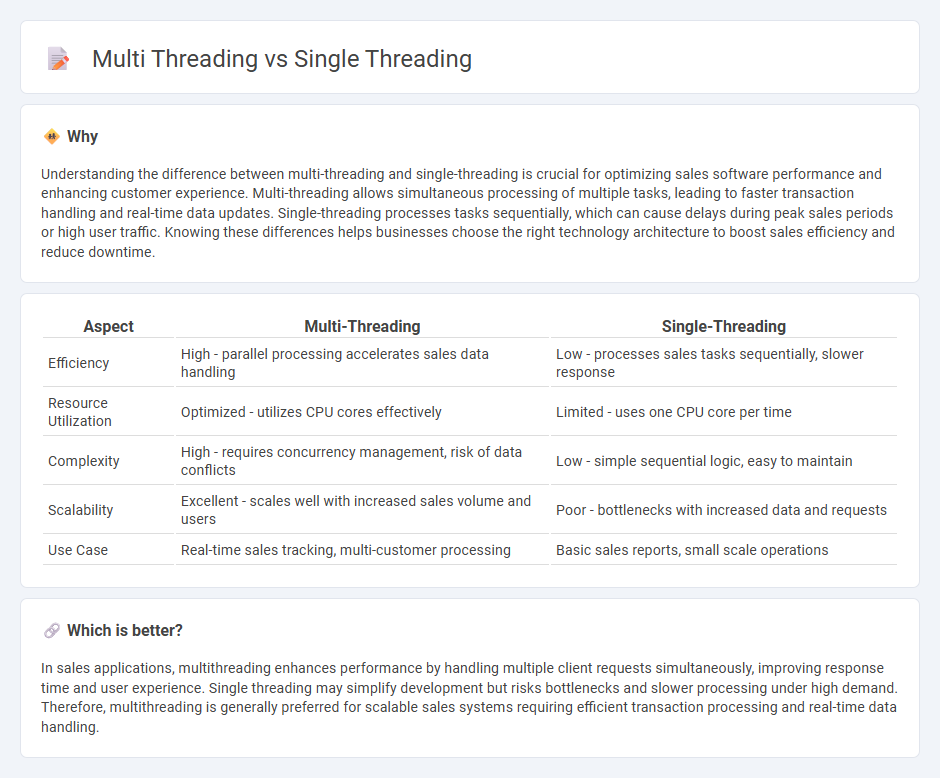
Understanding the difference between multi-threading and single-threading is crucial for optimizing sales software performance and enhancing customer experience. Multi-threading allows simultaneous processing of multiple tasks, leading to faster transaction handling and real-time data updates. Single-threading processes tasks sequentially, which can cause delays during peak sales periods or high user traffic. Knowing these differences helps businesses choose the right technology architecture to boost sales efficiency and reduce downtime.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Multi-Threading | Single-Threading |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High - parallel processing accelerates sales data handling | Low - processes sales tasks sequentially, slower response |
| Resource Utilization | Optimized - utilizes CPU cores effectively | Limited - uses one CPU core per time |
| Complexity | High - requires concurrency management, risk of data conflicts | Low - simple sequential logic, easy to maintain |
| Scalability | Excellent - scales well with increased sales volume and users | Poor - bottlenecks with increased data and requests |
| Use Case | Real-time sales tracking, multi-customer processing | Basic sales reports, small scale operations |
Which is better?
In sales applications, multithreading enhances performance by handling multiple client requests simultaneously, improving response time and user experience. Single threading may simplify development but risks bottlenecks and slower processing under high demand. Therefore, multithreading is generally preferred for scalable sales systems requiring efficient transaction processing and real-time data handling.
Connection
Sales processes benefit from the application of multi-threading and single-threading techniques in sales management software, optimizing task execution and improving response times. Multi-threading enables concurrent handling of multiple customer interactions, boosting efficiency and accelerating lead follow-ups, whereas single-threading ensures sequential, focused processing ideal for complex, detail-oriented sales tasks. Integrating both threading approaches within CRM systems enhances workflow flexibility and maximizes overall sales team productivity.
Key Terms
Decision-maker
Decision-makers evaluating single threading versus multi-threading should consider application performance, resource utilization, and complexity. Single threading offers simplicity and low overhead but may underperform in multi-core environments, whereas multi-threading enhances responsiveness and efficiency by parallel task execution, though it introduces synchronization challenges. Explore detailed insights to determine the best threading model for your project's needs.
Stakeholder engagement
Single threading in stakeholder engagement ensures focused communication and streamlined decision-making by addressing one concern at a time, which minimizes confusion and enhances clarity. Multi-threading allows simultaneous interactions with multiple stakeholders, increasing responsiveness but requiring careful coordination to avoid misunderstandings and information overload. Explore deeper strategies to optimize stakeholder engagement efficiency and effectiveness.
Deal risk
Single threading processes one task at a time, which minimizes complexity and reduces the likelihood of deal risk associated with race conditions and deadlocks. Multi-threading increases efficiency by running multiple threads concurrently but introduces risks such as data inconsistency and synchronization errors that can jeopardize deal integrity. Explore more to understand how balancing threading models impacts risk management in deal processing.
Source and External Links
difference between single thread and multi thread - JustAcademy - A single-threaded application processes one task at a time using a single sequence of instructions, lacking context switching and halting entirely if a task blocks; suitable for simple applications but less efficient for multitasking compared to multi-threading which handles multiple tasks concurrently for better responsiveness and performance.
Thread in Operating System - GeeksforGeeks - A thread is a lightweight sequence stream within a process, where a single-thread runs one sequence of instructions and shares process resources but has its own CPU state and stack, impacting performance improvements in concurrent applications.
Thread (computing) - Wikipedia - Single-threading refers to executing one instruction at a time within a program, where kernel threads are lightweight and context switches are relatively cheap compared to full process switches, but single-threaded programs cannot perform concurrent tasks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com