Sales strategies benefit from multithreading by engaging multiple decision-makers simultaneously, increasing the likelihood of closing deals faster compared to sequencing, which targets contacts one after another. Multithreading enhances communication flow within complex sales cycles, improving relationship building and resource allocation across stakeholders. Explore more about optimizing your sales approach with multithreading to boost conversion rates and shorten sales cycles.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between multi-threading and sequencing in sales processes enhances efficiency by allowing simultaneous handling of multiple customer interactions versus step-by-step task completion. Multi-threading enables sales teams to engage various decision-makers concurrently, shortening sales cycles and increasing conversion rates. Sequencing ensures a structured approach, maintaining follow-ups and nurturing leads systematically to avoid missed opportunities. Mastery of both methods optimizes resource allocation, improves customer experience, and drives higher revenue growth.
Comparison Table
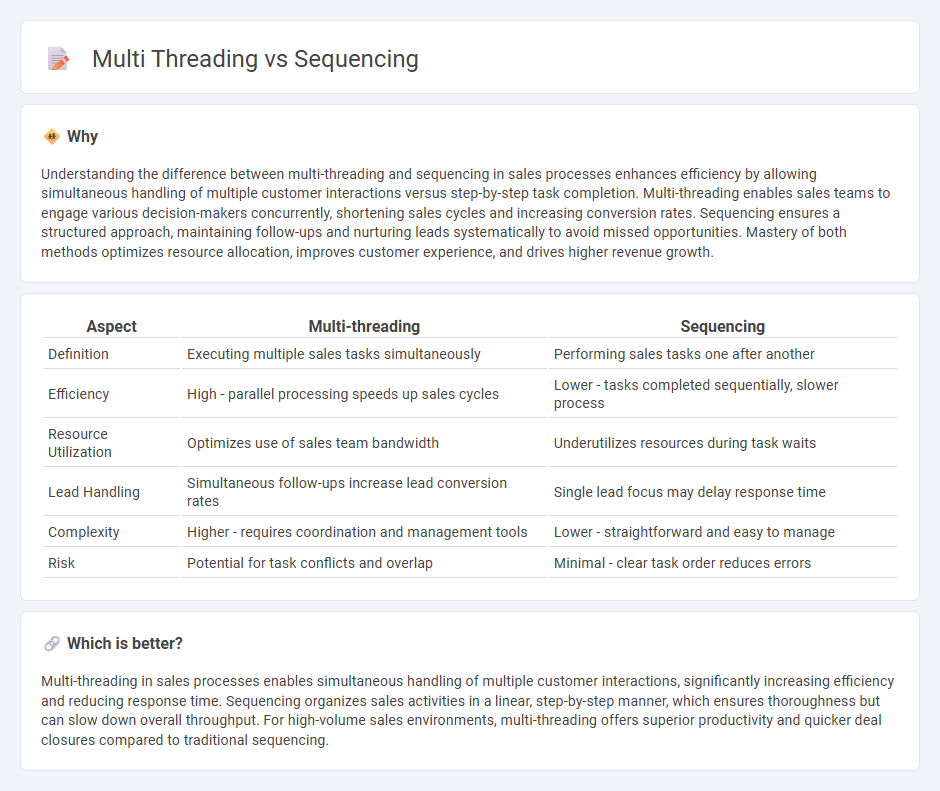
| Aspect | Multi-threading | Sequencing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Executing multiple sales tasks simultaneously | Performing sales tasks one after another |
| Efficiency | High - parallel processing speeds up sales cycles | Lower - tasks completed sequentially, slower process |
| Resource Utilization | Optimizes use of sales team bandwidth | Underutilizes resources during task waits |
| Lead Handling | Simultaneous follow-ups increase lead conversion rates | Single lead focus may delay response time |
| Complexity | Higher - requires coordination and management tools | Lower - straightforward and easy to manage |
| Risk | Potential for task conflicts and overlap | Minimal - clear task order reduces errors |
Which is better?
Multi-threading in sales processes enables simultaneous handling of multiple customer interactions, significantly increasing efficiency and reducing response time. Sequencing organizes sales activities in a linear, step-by-step manner, which ensures thoroughness but can slow down overall throughput. For high-volume sales environments, multi-threading offers superior productivity and quicker deal closures compared to traditional sequencing.
Connection
Multi-threading in sales enables simultaneous handling of multiple customer interactions, increasing efficiency and response time. Sequencing organizes these interactions into prioritized workflows, ensuring that leads and follow-ups are managed in an optimal order. Combining multi-threading with sequencing enhances sales pipeline management, driving higher conversion rates and streamlining sales processes.
Key Terms
Sequencing
Sequencing ensures tasks execute one after another, maintaining strict order and predictable results, critical in scenarios like transaction processing or data pipeline workflows where consistency is paramount. Unlike multithreading, sequencing avoids race conditions and synchronization issues by eliminating concurrent execution, resulting in simpler debugging and lower overhead. Explore more about how sequencing optimizes performance and reliability in complex systems.
Multi-threading
Multi-threading enables concurrent execution of multiple threads within a single program, optimizing CPU utilization and improving application responsiveness by allowing tasks to run simultaneously. Unlike sequencing, which processes tasks one after another, multi-threading can handle complex, real-time operations more efficiently, especially in environments requiring parallel computation or user interface responsiveness. Discover how multi-threading can enhance performance and scalability in software development by exploring advanced threading models and synchronization techniques.
Parallel outreach
Sequencing processes tasks one after another, ensuring each completes before the next begins, which can limit overall throughput in parallel outreach campaigns. Multithreading allows concurrent execution of multiple threads, significantly enhancing the efficiency and speed of message dissemination across diverse channels. Explore more to optimize your parallel outreach strategy using advanced multithreading techniques.
Source and External Links
DNA sequencing - Wikipedia - DNA sequencing is the process of determining the order of nucleotides in DNA using various technologies such as sequencing by ligation (e.g., SOLiD) and semiconductor-based detection (e.g., Ion Torrent), which allow reading DNA sequences for biological and medical research purposes.
Sequencing - Wikipedia - Sequencing in genetics means determining the primary structure or nucleotide order of DNA, important for understanding biological information, with traditional Sanger method and newer technologies like pyrosequencing advancing rapid genome analysis.
How HiFi sequencing works - PacBio - HiFi sequencing is a single-molecule, real-time sequencing technology offering highly accurate and long DNA reads with uniform coverage across complex genomic regions, enhancing variant detection and genome analysis.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com