Trigger event selling focuses on leveraging specific customer incidents or life changes to offer timely solutions, enhancing relevance and conversion rates. Retail selling emphasizes a broader approach, targeting a wide audience through product availability and promotional strategies in physical or online stores. Explore the distinctions to optimize your sales approach effectively.
Why it is important
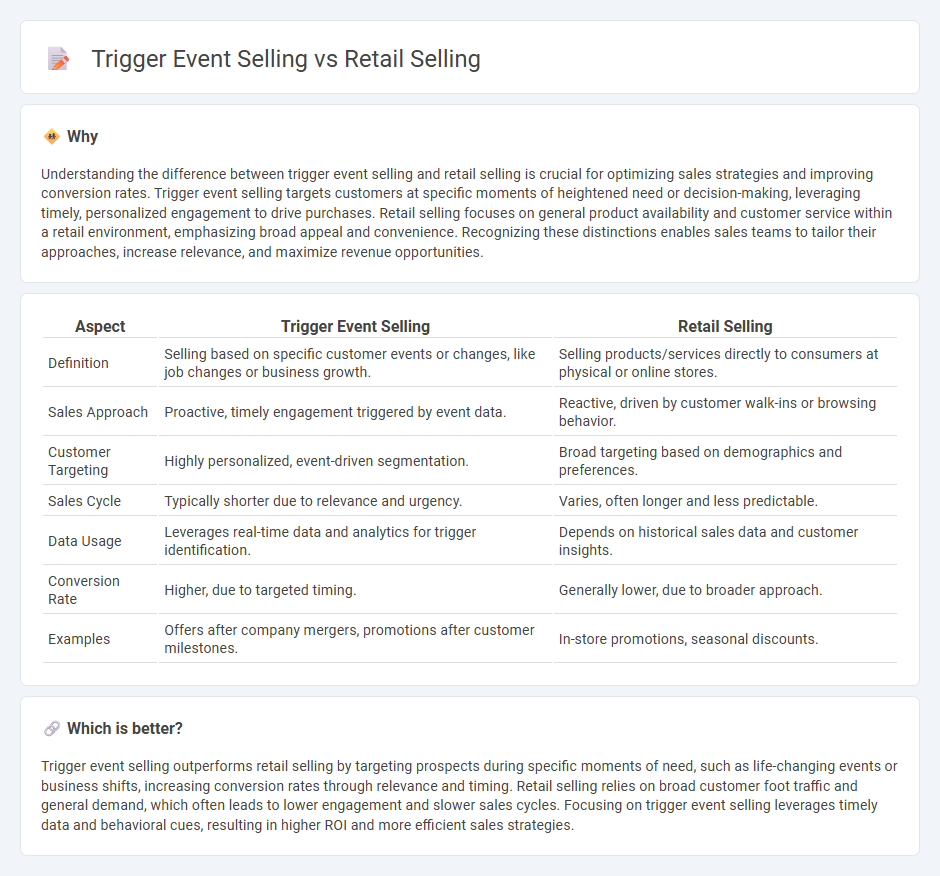
Understanding the difference between trigger event selling and retail selling is crucial for optimizing sales strategies and improving conversion rates. Trigger event selling targets customers at specific moments of heightened need or decision-making, leveraging timely, personalized engagement to drive purchases. Retail selling focuses on general product availability and customer service within a retail environment, emphasizing broad appeal and convenience. Recognizing these distinctions enables sales teams to tailor their approaches, increase relevance, and maximize revenue opportunities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Trigger Event Selling | Retail Selling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Selling based on specific customer events or changes, like job changes or business growth. | Selling products/services directly to consumers at physical or online stores. |
| Sales Approach | Proactive, timely engagement triggered by event data. | Reactive, driven by customer walk-ins or browsing behavior. |
| Customer Targeting | Highly personalized, event-driven segmentation. | Broad targeting based on demographics and preferences. |
| Sales Cycle | Typically shorter due to relevance and urgency. | Varies, often longer and less predictable. |
| Data Usage | Leverages real-time data and analytics for trigger identification. | Depends on historical sales data and customer insights. |
| Conversion Rate | Higher, due to targeted timing. | Generally lower, due to broader approach. |
| Examples | Offers after company mergers, promotions after customer milestones. | In-store promotions, seasonal discounts. |
Which is better?
Trigger event selling outperforms retail selling by targeting prospects during specific moments of need, such as life-changing events or business shifts, increasing conversion rates through relevance and timing. Retail selling relies on broad customer foot traffic and general demand, which often leads to lower engagement and slower sales cycles. Focusing on trigger event selling leverages timely data and behavioral cues, resulting in higher ROI and more efficient sales strategies.
Connection
Trigger event selling and retail selling connect through their focus on timely customer engagement to boost sales. Trigger event selling capitalizes on specific life changes or events that prompt immediate purchasing decisions, while retail selling leverages in-store and online interactions to influence customers' buying behavior. Both strategies rely on understanding customer needs and context to deliver personalized offers that increase conversion rates and customer loyalty.
Key Terms
**Retail Selling:**
Retail selling centers on engaging customers through personalized product recommendations and enhancing in-store experiences to drive immediate purchases. It leverages inventory management, promotions, and customer behavior analytics to optimize sales conversion rates. Discover more about effective retail selling strategies and their impact on consumer buying patterns.
Point of Sale (POS)
Retail selling at the Point of Sale (POS) emphasizes immediate product availability, customer interaction, and transaction efficiency to encourage impulse purchases. Trigger event selling leverages specific life events or milestones, such as birthdays or holidays, to tailor promotions and create personalized buying incentives at the POS. Explore strategies to optimize your POS approach by integrating trigger event insights for increased conversion rates.
Upselling
Retail selling emphasizes transactional exchanges aimed at meeting immediate customer needs, while trigger event selling leverages specific life events or changes to introduce relevant products, enhancing upselling opportunities. Upselling in retail selling relies on product knowledge and customer preferences at the point of sale, whereas trigger event selling uses timing and context to offer tailored solutions that increase average order value. Discover how integrating trigger event strategies can significantly boost upselling effectiveness and customer loyalty.
Source and External Links
Retail - Wikipedia - Retail selling involves selling goods and services to consumers, where retailers buy in large quantities and sell in smaller amounts for profit, using various strategies such as store type, market targeting, product assortment, and customer service to position themselves in the market.
Retail Sales Definition, Categories & Techniques - Study.com - Retail selling consists of key steps like opening the sale with open-ended questions, probing to understand customer needs, demonstrating products, handling objections, and closing the sale to effectively serve customers and increase sales success.
Retail Sales Strategies | Retail 101 - The Retail Doctor - Effective retail selling strategies include greeting shoppers, building rapport, understanding customer wants, handling objections, and closing sales, all aimed at making customer service the key differentiator in a competitive retail environment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com