Multithreading enhances sales applications by enabling simultaneous execution of multiple tasks, improving responsiveness and efficiency during customer interactions. Parallelization divides large sales data processing into smaller segments processed concurrently, significantly accelerating analytics and forecasting accuracy. Explore these techniques further to optimize your sales operations and drive higher revenue.
Why it is important
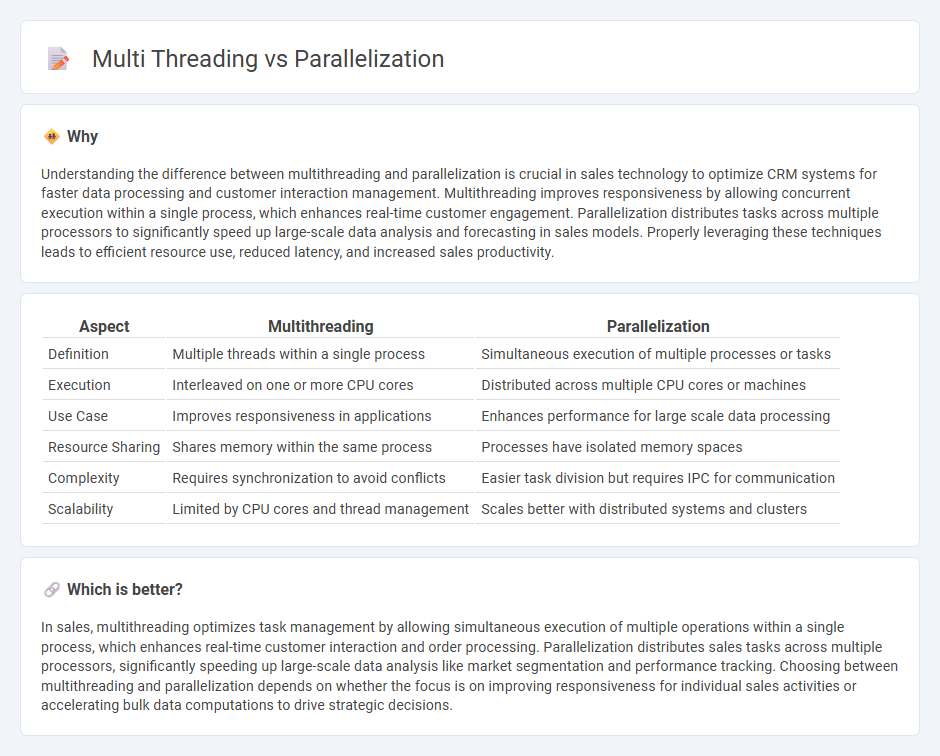
Understanding the difference between multithreading and parallelization is crucial in sales technology to optimize CRM systems for faster data processing and customer interaction management. Multithreading improves responsiveness by allowing concurrent execution within a single process, which enhances real-time customer engagement. Parallelization distributes tasks across multiple processors to significantly speed up large-scale data analysis and forecasting in sales models. Properly leveraging these techniques leads to efficient resource use, reduced latency, and increased sales productivity.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Multithreading | Parallelization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple threads within a single process | Simultaneous execution of multiple processes or tasks |
| Execution | Interleaved on one or more CPU cores | Distributed across multiple CPU cores or machines |
| Use Case | Improves responsiveness in applications | Enhances performance for large scale data processing |
| Resource Sharing | Shares memory within the same process | Processes have isolated memory spaces |
| Complexity | Requires synchronization to avoid conflicts | Easier task division but requires IPC for communication |
| Scalability | Limited by CPU cores and thread management | Scales better with distributed systems and clusters |
Which is better?
In sales, multithreading optimizes task management by allowing simultaneous execution of multiple operations within a single process, which enhances real-time customer interaction and order processing. Parallelization distributes sales tasks across multiple processors, significantly speeding up large-scale data analysis like market segmentation and performance tracking. Choosing between multithreading and parallelization depends on whether the focus is on improving responsiveness for individual sales activities or accelerating bulk data computations to drive strategic decisions.
Connection
Multi-threading and parallelization enhance sales data processing by enabling simultaneous execution of multiple tasks, such as customer segmentation and sales forecasting. This connection improves real-time analytics, allowing sales teams to quickly identify trends and optimize strategies. Optimized parallel processing reduces latency and increases throughput in sales platforms, driving higher conversion rates and revenue growth.
Key Terms
Task Distribution
Parallelization involves breaking down a large task into smaller, independent sub-tasks that can run simultaneously across multiple processors or cores, maximizing computational efficiency and reducing execution time. Multi-threading specifically refers to a single process managing multiple threads that share resources but execute concurrently, improving responsiveness and resource utilization within applications. To explore the distinct approaches and benefits of task distribution in parallelization and multi-threading, discover more insights here.
Efficiency
Parallelization leverages multiple processors to perform tasks simultaneously, significantly boosting computational efficiency for large-scale problems. Multithreading allows concurrent execution within a single process, efficiently managing shared resources but may face limitations due to thread synchronization and context switching overhead. Explore deeper insights into optimizing performance through parallelization and multithreading techniques.
Concurrent Processing
Parallelization divides tasks into smaller sub-tasks that run simultaneously across multiple processors or cores, enhancing performance by reducing overall execution time. Multi-threading enables a single process to manage multiple threads, improving resource utilization and responsiveness through concurrent execution within shared memory space. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which approach best suits your concurrent processing needs.
Source and External Links
What is Parallelization & the Different Types | Lenovo US - Parallelization is the technique of dividing a large computational task into smaller sub-tasks that can be executed concurrently on multiple processors or cores to reduce computation time and improve performance in computing systems, with applications in scientific simulations, data analysis, machine learning, and more.
Parallel computing - Wikipedia - Parallel computing involves performing many calculations simultaneously by dividing problems into smaller ones solved concurrently, with types like bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism, and is widely used due to limitations in frequency scaling and power consumption in processors.
Introduction to Parallelization - MolSSI Education - Parallelization speeds up computation by splitting workload among multiple processors, ideally reducing runtime proportionally to the number of units but introduces communication overhead that complicates efficient scaling, especially in high-performance computing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com