Sales teams often leverage multithreading by simultaneously engaging multiple prospects across various channels to increase conversion rates and optimize lead generation. Multitasking in sales involves handling multiple tasks such as client follow-ups, data entry, and proposal preparation, but may reduce focus on critical interactions. Explore how mastering multithreading versus multitasking can boost your sales performance and efficiency.
Why it is important
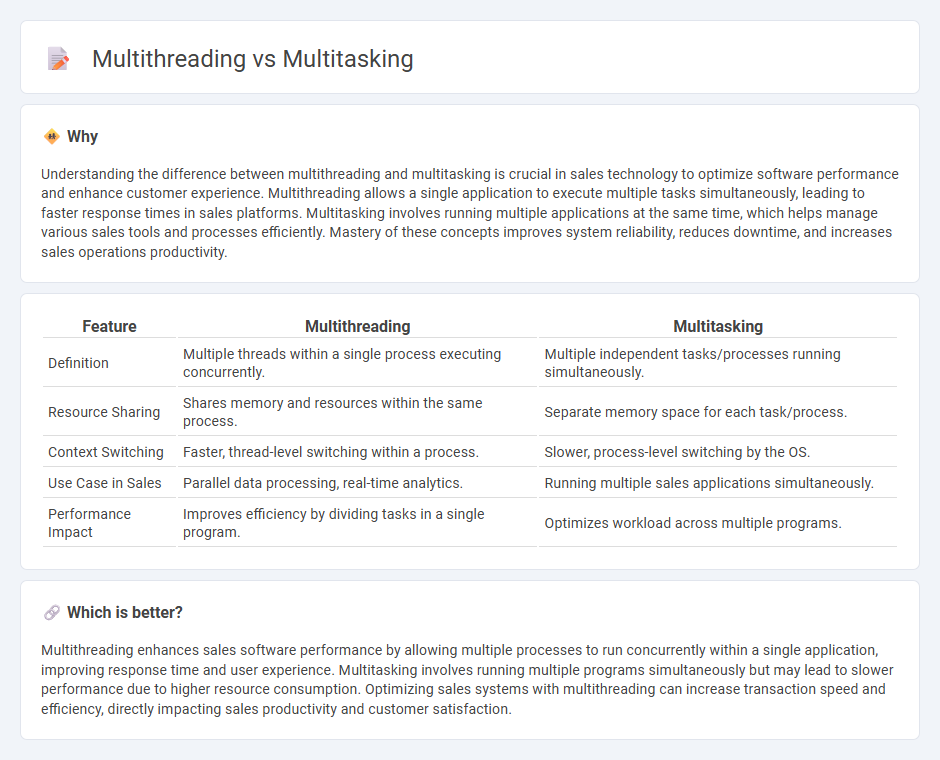
Understanding the difference between multithreading and multitasking is crucial in sales technology to optimize software performance and enhance customer experience. Multithreading allows a single application to execute multiple tasks simultaneously, leading to faster response times in sales platforms. Multitasking involves running multiple applications at the same time, which helps manage various sales tools and processes efficiently. Mastery of these concepts improves system reliability, reduces downtime, and increases sales operations productivity.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Multithreading | Multitasking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple threads within a single process executing concurrently. | Multiple independent tasks/processes running simultaneously. |
| Resource Sharing | Shares memory and resources within the same process. | Separate memory space for each task/process. |
| Context Switching | Faster, thread-level switching within a process. | Slower, process-level switching by the OS. |
| Use Case in Sales | Parallel data processing, real-time analytics. | Running multiple sales applications simultaneously. |
| Performance Impact | Improves efficiency by dividing tasks in a single program. | Optimizes workload across multiple programs. |
Which is better?
Multithreading enhances sales software performance by allowing multiple processes to run concurrently within a single application, improving response time and user experience. Multitasking involves running multiple programs simultaneously but may lead to slower performance due to higher resource consumption. Optimizing sales systems with multithreading can increase transaction speed and efficiency, directly impacting sales productivity and customer satisfaction.
Connection
Sales teams benefit from multithreading by managing multiple customer interactions simultaneously across different communication channels, increasing outreach efficiency. Multitasking supports sales representatives in handling diverse tasks such as follow-ups, product demos, and CRM updates concurrently, enhancing productivity. Integrating multithreading with multitasking enables seamless coordination, leading to faster lead conversion and improved sales pipeline management.
Key Terms
Task Management
Multitasking involves managing multiple tasks by sharing CPU time among processes, while multithreading allows concurrent execution within a single process through multiple threads, optimizing resource utilization and responsiveness. Task management in multitasking focuses on context switching between independent processes, whereas multithreading manages parallel threads within the same process environment for efficient communication and data sharing. Explore further to understand how these approaches impact system performance and application design.
Parallel Processing
Multithreading enables parallel processing by running multiple threads within a single process, sharing resources to increase efficiency and responsiveness, whereas multitasking involves managing multiple independent processes simultaneously on a CPU. Multithreading improves parallel execution by dividing tasks into smaller threads that can operate concurrently, optimizing CPU utilization and reducing latency. Explore further to understand how these techniques impact system performance and application design.
Resource Allocation
Multitasking involves the operating system managing multiple processes, each with dedicated resources such as CPU time and memory, allowing simultaneous task execution without direct resource sharing. Multithreading enables multiple threads within the same process to share resources like memory space while executing concurrently, optimizing CPU utilization and resource allocation efficiency. Explore the key differences in resource allocation strategies between multitasking and multithreading to enhance system performance.
Source and External Links
The Pros and Cons of Multitasking - Multitasking is the simultaneous performance of more than one activity and is often sought after by employers for its potential to save time and increase productivity, but also entails shifting attention and handling several tasks in quick succession.
Multitasking Doesn't Work--Here's What Does - Despite feeling efficient, multitasking is largely a myth, as the human brain is not wired to perform multiple tasks at once; instead, it quickly switches between tasks, which leads to reduced efficiency, more errors, and poorer mental health outcomes.
Human multitasking - Human multitasking involves splitting attention between multiple tasks, but research shows it can result in wasted time due to context switching, increased errors, and greater mental stress, even if some individuals perceive themselves as proficient at it.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com