Tiered customer segmentation categorizes buyers based on their purchasing behavior, value, or engagement level, enabling personalized marketing strategies that maximize revenue potential. Geographic segmentation divides customers by location, allowing businesses to tailor offers and services according to regional preferences and market conditions. Discover how these segmentation approaches can optimize your sales strategy and boost customer satisfaction.
Why it is important
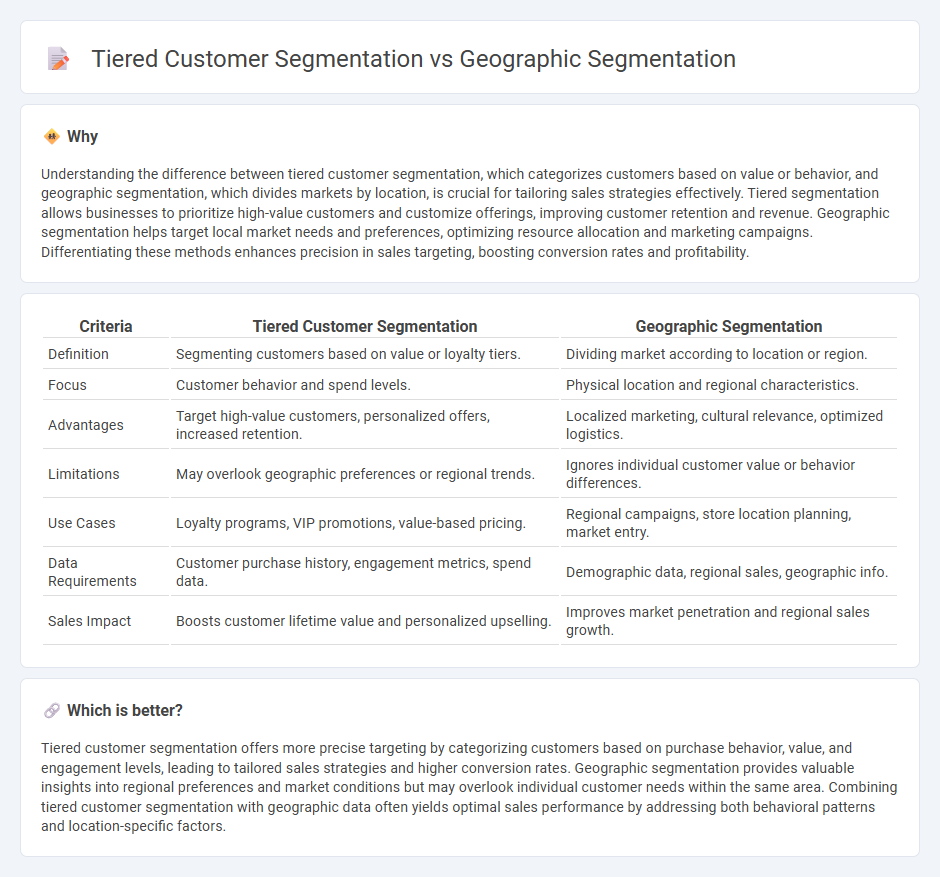
Understanding the difference between tiered customer segmentation, which categorizes customers based on value or behavior, and geographic segmentation, which divides markets by location, is crucial for tailoring sales strategies effectively. Tiered segmentation allows businesses to prioritize high-value customers and customize offerings, improving customer retention and revenue. Geographic segmentation helps target local market needs and preferences, optimizing resource allocation and marketing campaigns. Differentiating these methods enhances precision in sales targeting, boosting conversion rates and profitability.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Tiered Customer Segmentation | Geographic Segmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Segmenting customers based on value or loyalty tiers. | Dividing market according to location or region. |
| Focus | Customer behavior and spend levels. | Physical location and regional characteristics. |
| Advantages | Target high-value customers, personalized offers, increased retention. | Localized marketing, cultural relevance, optimized logistics. |
| Limitations | May overlook geographic preferences or regional trends. | Ignores individual customer value or behavior differences. |
| Use Cases | Loyalty programs, VIP promotions, value-based pricing. | Regional campaigns, store location planning, market entry. |
| Data Requirements | Customer purchase history, engagement metrics, spend data. | Demographic data, regional sales, geographic info. |
| Sales Impact | Boosts customer lifetime value and personalized upselling. | Improves market penetration and regional sales growth. |
Which is better?
Tiered customer segmentation offers more precise targeting by categorizing customers based on purchase behavior, value, and engagement levels, leading to tailored sales strategies and higher conversion rates. Geographic segmentation provides valuable insights into regional preferences and market conditions but may overlook individual customer needs within the same area. Combining tiered customer segmentation with geographic data often yields optimal sales performance by addressing both behavioral patterns and location-specific factors.
Connection
Tiered customer segmentation and geographic segmentation are interconnected by enabling businesses to tailor sales strategies based on both customer value and location-specific preferences, maximizing market penetration and resource allocation. Analyzing high-value customers within specific geographic regions allows companies to prioritize sales efforts and optimize targeting for regional demands. Integrating these segmentation methods enhances predictive analytics and personalized marketing, driving higher conversion rates and customer loyalty.
Key Terms
**Geographic Segmentation:**
Geographic segmentation divides markets based on locations such as countries, regions, cities, or climates, enabling businesses to tailor marketing strategies to local preferences and environmental factors. This approach improves product relevance and distribution efficiency by addressing regional needs and cultural differences. Explore geographic segmentation further to enhance your market targeting and customer engagement strategies.
Location
Geographic segmentation divides customers based on physical location such as country, region, or city, enabling tailored marketing strategies that account for climate, culture, and local preferences. Tiered customer segmentation classifies clients by their value or engagement levels rather than solely by location, focusing on factors like purchase frequency or revenue contribution. Explore more to understand how integrating location data with customer tiers can optimize targeted marketing efforts.
Region
Geographic segmentation divides customers based on their physical locations such as countries, states, or cities, allowing businesses to tailor marketing strategies according to regional preferences and cultural differences. Tiered customer segmentation, on the other hand, classifies consumers within a specific region into hierarchical levels based on factors like spending behavior, loyalty, or engagement, enabling more personalized targeting within the same geographic area. Explore further insights on how region-focused segmentation can enhance your marketing precision and customer engagement.
Source and External Links
Geographic Segmentation: Definition, Characteristics & Examples - Geographic segmentation divides the market based on location-related factors such as economics, food habits, clothing, languages, and traditions to tailor marketing strategies accordingly, for example, preferences for warm clothing in colder regions versus air conditioning in hotter ones.
Tips and Best Practices for Geographic Segmentation - HubSpot Blog - Geographic segmentation organizes audiences by physical location like country or postal code to identify regional buying trends, enabling more targeted marketing efforts that save money, maintain relevance, and foster growth.
Geographic Segmentation: A Complete Guide to Targeted Marketing - Geographic segmentation relies on variables such as cultural, economic, climatic, social-demographic, technological, and regulatory factors to develop marketing strategies tailored specifically to different regions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com