Value selling focuses on highlighting the unique benefits and overall worth of a product or service to meet the specific needs of the customer, aiming to build long-term relationships and increase customer satisfaction. Cross-selling involves offering complementary products or services to existing customers to enhance their experience and boost revenue by maximizing the value of each transaction. Explore deeper insights on how mastering value selling and cross-selling can transform your sales strategy and drive growth.
Why it is important
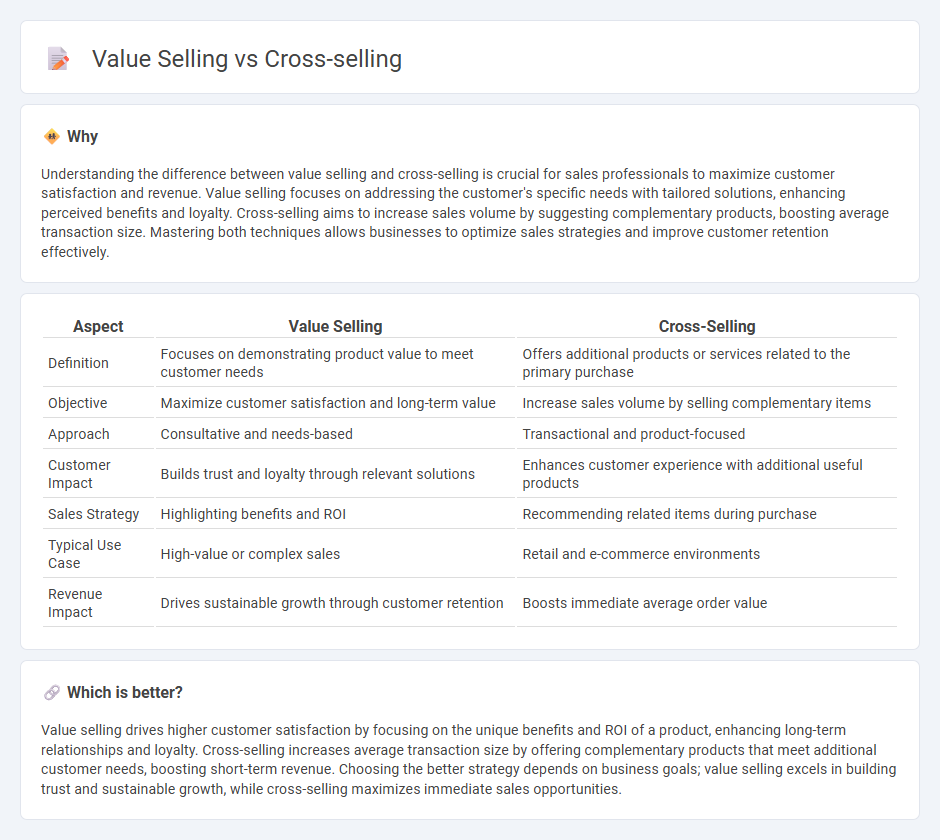
Understanding the difference between value selling and cross-selling is crucial for sales professionals to maximize customer satisfaction and revenue. Value selling focuses on addressing the customer's specific needs with tailored solutions, enhancing perceived benefits and loyalty. Cross-selling aims to increase sales volume by suggesting complementary products, boosting average transaction size. Mastering both techniques allows businesses to optimize sales strategies and improve customer retention effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Value Selling | Cross-Selling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on demonstrating product value to meet customer needs | Offers additional products or services related to the primary purchase |
| Objective | Maximize customer satisfaction and long-term value | Increase sales volume by selling complementary items |
| Approach | Consultative and needs-based | Transactional and product-focused |
| Customer Impact | Builds trust and loyalty through relevant solutions | Enhances customer experience with additional useful products |
| Sales Strategy | Highlighting benefits and ROI | Recommending related items during purchase |
| Typical Use Case | High-value or complex sales | Retail and e-commerce environments |
| Revenue Impact | Drives sustainable growth through customer retention | Boosts immediate average order value |
Which is better?
Value selling drives higher customer satisfaction by focusing on the unique benefits and ROI of a product, enhancing long-term relationships and loyalty. Cross-selling increases average transaction size by offering complementary products that meet additional customer needs, boosting short-term revenue. Choosing the better strategy depends on business goals; value selling excels in building trust and sustainable growth, while cross-selling maximizes immediate sales opportunities.
Connection
Value selling enhances customer satisfaction by focusing on delivering tailored solutions that address specific needs, which naturally opens opportunities for cross-selling complementary products. Cross-selling leverages the trust built through value selling to introduce additional offerings that increase overall transaction value and customer retention. Together, these strategies drive revenue growth by aligning product benefits with customer priorities, fostering long-term business relationships.
Key Terms
Complementary Products (cross-selling)
Cross-selling targets customers with complementary products that enhance or complete their initial purchase, increasing overall transaction value and customer satisfaction. Value selling, by contrast, emphasizes the intrinsic benefits and problem-solving capabilities of a product, focusing on the customer's specific needs rather than on additional items. Explore how leveraging complementary products through cross-selling can maximize revenue and improve client retention.
Customer Needs (value selling)
Value selling centers on addressing specific customer needs by highlighting the unique benefits and solutions tailored to those needs, unlike cross-selling which aims to increase sales by suggesting complementary products. This approach fosters stronger customer relationships and enhances perceived product value, driving long-term satisfaction and loyalty. Discover how focusing on customer needs can transform your sales strategy and boost revenue.
Solution Fit
Cross-selling targets increasing revenue by promoting complementary products, while value selling emphasizes matching solutions to customer needs for maximum benefit. Solution Fit centers on understanding specific client challenges and delivering tailored offerings that resonate deeply with their business goals. Discover how mastering Solution Fit enhances both cross-selling and value selling strategies effectively.
Source and External Links
What Is Cross-Selling? Intro, Steps, and Pro Tips [+Data] - Cross-selling is offering customers extra products or services that complement their original purchase, like suggesting fries and a drink when someone buys a burger.
Cross-Sell - Overview, How It Works, and Examples - Cross-selling is the sale of an additional product or service related to the primary purchase, such as offering fries to a burger customer, and is widely used to boost revenue and strengthen customer relationships.
What is Cross-Selling? - Cross-selling involves selling related, supplementary products or services based on a customer's interest in or purchase of one of your products, increasing both sales revenue and customer satisfaction.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com