Sales strategies focusing on survivor bias emphasize successful customer acquisitions to replicate winning tactics, while cross-selling aims to maximize revenue by offering complementary products or services to existing clients. Understanding the nuances between these approaches can drive more effective targeting and improved customer lifetime value. Explore how integrating both methods can optimize your sales performance and growth.
Why it is important
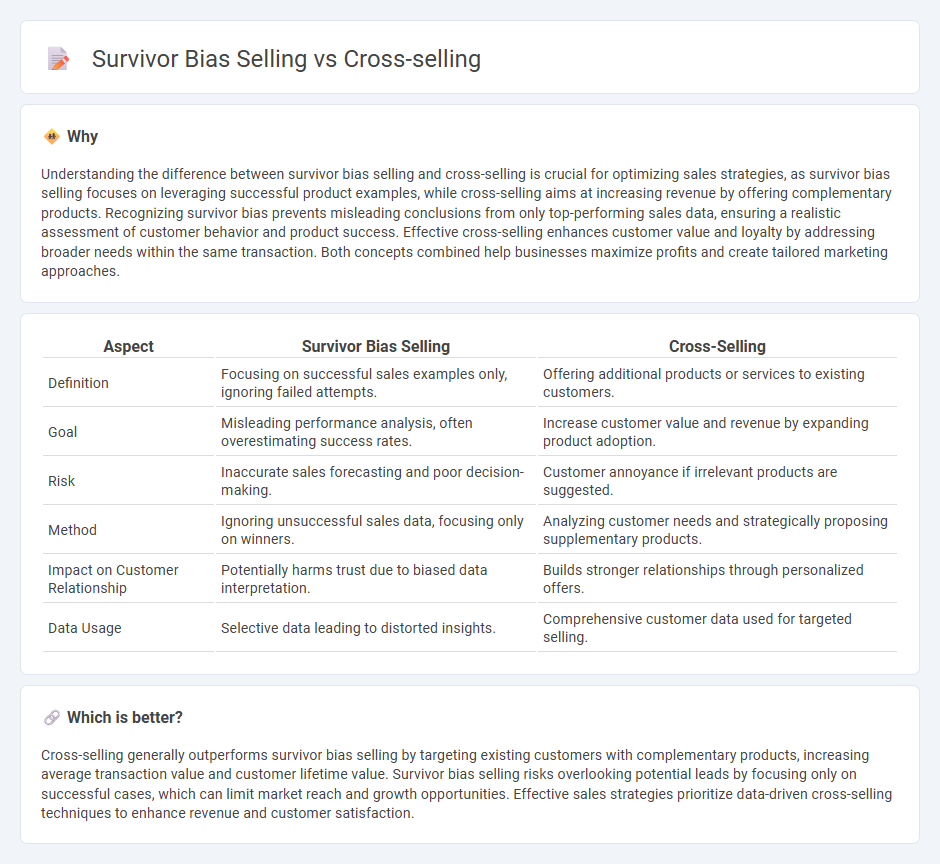
Understanding the difference between survivor bias selling and cross-selling is crucial for optimizing sales strategies, as survivor bias selling focuses on leveraging successful product examples, while cross-selling aims at increasing revenue by offering complementary products. Recognizing survivor bias prevents misleading conclusions from only top-performing sales data, ensuring a realistic assessment of customer behavior and product success. Effective cross-selling enhances customer value and loyalty by addressing broader needs within the same transaction. Both concepts combined help businesses maximize profits and create tailored marketing approaches.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Survivor Bias Selling | Cross-Selling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focusing on successful sales examples only, ignoring failed attempts. | Offering additional products or services to existing customers. |
| Goal | Misleading performance analysis, often overestimating success rates. | Increase customer value and revenue by expanding product adoption. |
| Risk | Inaccurate sales forecasting and poor decision-making. | Customer annoyance if irrelevant products are suggested. |
| Method | Ignoring unsuccessful sales data, focusing only on winners. | Analyzing customer needs and strategically proposing supplementary products. |
| Impact on Customer Relationship | Potentially harms trust due to biased data interpretation. | Builds stronger relationships through personalized offers. |
| Data Usage | Selective data leading to distorted insights. | Comprehensive customer data used for targeted selling. |
Which is better?
Cross-selling generally outperforms survivor bias selling by targeting existing customers with complementary products, increasing average transaction value and customer lifetime value. Survivor bias selling risks overlooking potential leads by focusing only on successful cases, which can limit market reach and growth opportunities. Effective sales strategies prioritize data-driven cross-selling techniques to enhance revenue and customer satisfaction.
Connection
Survivor bias in sales skews decision-making by focusing only on successful selling and cross-selling cases, ignoring failures that provide critical lessons. This bias can lead to overestimating the effectiveness of certain sales techniques, causing businesses to replicate strategies that may not universally succeed. Understanding and mitigating survivor bias enables sales teams to develop more realistic, data-driven approaches for both selling new products and expanding existing customer relationships.
Key Terms
Complementary Products
Cross-selling targets complementary products to enhance customer value and increase revenue by offering items that naturally pair with the original purchase, such as a phone case with a smartphone. Survivor bias selling, however, focuses on products that have proven successful and popular among top customers, potentially overlooking niche items that could benefit other segments. Explore how leveraging both strategies can optimize your sales and customer satisfaction.
Upselling
Cross-selling involves promoting complementary products to enhance average order value, whereas survivor bias selling focuses on highlighting successes without addressing failed attempts, potentially misleading customer expectations. Upselling aims to upgrade a customer's purchase to a higher-end or more feature-rich option, driving higher revenue per transaction. Explore effective upselling strategies to maximize customer lifetime value and boost sales performance.
Selective Sampling
Selective sampling in cross-selling targets existing customers based on their purchase behavior to increase sales opportunities, while survivor bias selling overlooks customers who discontinued or did not respond, leading to skewed data and ineffective strategies. Cross-selling leverages comprehensive customer data for upselling complementary products, whereas survivor bias distorts insights by focusing only on successful cases, limiting growth potential. Explore detailed strategies to avoid survivor bias and maximize cross-selling effectiveness.
Source and External Links
What Is Cross-Selling? Intro, Steps, and Pro Tips [+Data] - This article provides an overview of cross-selling, including strategies and examples, and highlights how it complements sales processes by offering additional products that enhance the original purchase.
Cross-Sell - Overview, How It Works, and Examples - This resource explains cross-selling as the sale of adjacent products or services related to a primary purchase, noting its effectiveness in generating additional revenue and strengthening customer relationships.
What is Cross-Selling? - Salesforce - This article describes cross-selling as a strategy to increase customer loyalty by offering supplementary products or services, which can enhance customer satisfaction and improve customer lifetime value.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com