A ghost pipeline consists of sales opportunities that appear promising but lack genuine engagement or progress, often inflating forecast accuracy. Cold leads are potential customers who have shown little to no prior interest or interaction, requiring more effort to nurture into qualified prospects. Explore effective strategies to differentiate and manage ghost pipelines versus cold leads for improved sales performance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a ghost pipeline and a cold lead is crucial for accurate sales forecasting and resource allocation. A ghost pipeline contains deals that appear active but have little chance of closing, while cold leads are prospects with minimal engagement and low immediate buying intent. Identifying these distinctions helps sales teams prioritize efforts, avoid wasted time, and improve conversion rates. Effective pipeline management ultimately drives higher revenue and operational efficiency.
Comparison Table
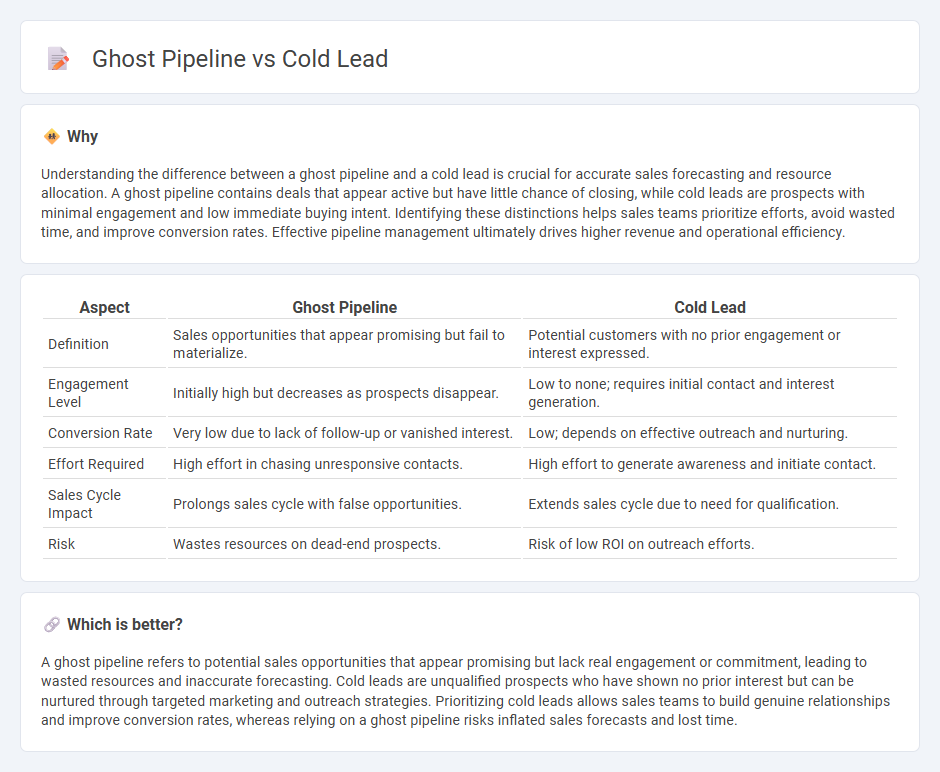
| Aspect | Ghost Pipeline | Cold Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sales opportunities that appear promising but fail to materialize. | Potential customers with no prior engagement or interest expressed. |
| Engagement Level | Initially high but decreases as prospects disappear. | Low to none; requires initial contact and interest generation. |
| Conversion Rate | Very low due to lack of follow-up or vanished interest. | Low; depends on effective outreach and nurturing. |
| Effort Required | High effort in chasing unresponsive contacts. | High effort to generate awareness and initiate contact. |
| Sales Cycle Impact | Prolongs sales cycle with false opportunities. | Extends sales cycle due to need for qualification. |
| Risk | Wastes resources on dead-end prospects. | Risk of low ROI on outreach efforts. |
Which is better?
A ghost pipeline refers to potential sales opportunities that appear promising but lack real engagement or commitment, leading to wasted resources and inaccurate forecasting. Cold leads are unqualified prospects who have shown no prior interest but can be nurtured through targeted marketing and outreach strategies. Prioritizing cold leads allows sales teams to build genuine relationships and improve conversion rates, whereas relying on a ghost pipeline risks inflated sales forecasts and lost time.
Connection
Ghost pipeline refers to sales opportunities that appear active but lack genuine buyer interest, often leading to wasted resources and inaccurate sales forecasting. Cold leads are prospects who have shown minimal to no engagement, making them prime contributors to a ghost pipeline when pursued without proper qualification. Effectively distinguishing cold leads from genuinely interested prospects prevents the inflation of a ghost pipeline, improving sales efficiency and forecast accuracy.
Key Terms
Lead Qualification
Cold leads refer to potential customers who have shown little to no interest or engagement, often requiring targeted lead qualification to assess their viability. Ghost pipelines consist of leads that appear promising but fail to convert or respond, making it crucial to identify and eliminate these stagnant prospects during lead qualification. Explore effective lead qualification strategies to optimize sales pipelines and improve conversion rates.
Follow-up Strategy
A cold lead requires a tailored follow-up strategy that re-engages interest through personalized communication and timely reminders, often involving email sequences or phone calls to nurture the prospect. In contrast, a ghost pipeline demands reactivation tactics that identify reasons for silence, validate the lead's current status, and deliver value propositions that reignite conversations. Explore effective follow-up techniques to convert cold leads and revive ghost pipelines for improved sales performance.
Sales Funnel
A cold lead refers to a prospect who has shown little to no interest or engagement with your product or service, while a ghost pipeline consists of deals that appear to be active but have stalled or vanished without explanation in the sales funnel. Identifying and addressing cold leads early prevents resource wastage, whereas managing a ghost pipeline ensures accurate forecasting and sustained sales momentum. Explore strategies to effectively differentiate and revitalize these leads for a more robust sales funnel.
Source and External Links
Hot Lead vs Cold Lead: What's the Difference? - Breakcold - A cold lead is a potential customer who has shown little or no interest in your product or service, often unaware of your brand and requiring nurturing and relationship-building to convert them into customers.
Cold Leads: What They Are and How to Convert Them - GMass - Cold leads are people or businesses with little to no interest in your products or services who usually don't respond to outreach and must be warmed up through gradual engagement before they become hot leads ready to buy.
Understanding Cold Leads: Real-World Examples and Tips - Cold leads have not interacted with your business before, may not know they need your products, and require personalized and careful initial contact to build awareness and convert them into customers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com