Voice shopping leverages AI-powered virtual assistants to enable hands-free, quick purchases through spoken commands, enhancing convenience and speed for consumers. Mail-order shopping relies on catalogs and online order forms, often involving longer delivery times but offering a broad selection from remote locations. Explore the key differences and evolving trends between these two retail channels to optimize your shopping strategy.
Why it is important
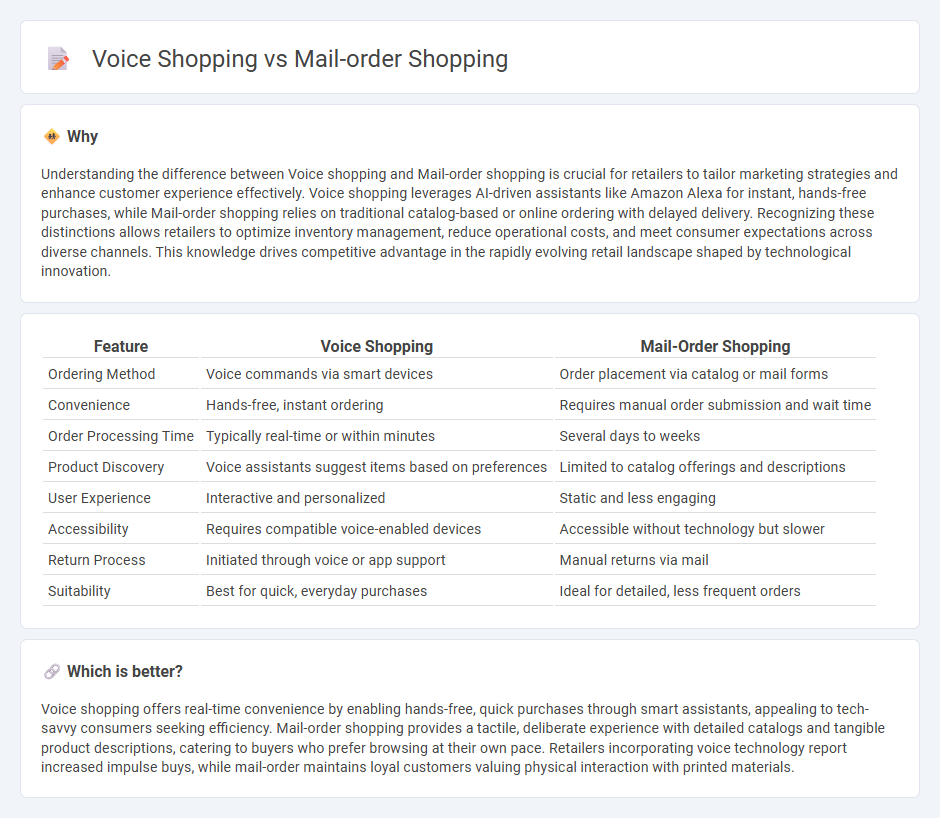
Understanding the difference between Voice shopping and Mail-order shopping is crucial for retailers to tailor marketing strategies and enhance customer experience effectively. Voice shopping leverages AI-driven assistants like Amazon Alexa for instant, hands-free purchases, while Mail-order shopping relies on traditional catalog-based or online ordering with delayed delivery. Recognizing these distinctions allows retailers to optimize inventory management, reduce operational costs, and meet consumer expectations across diverse channels. This knowledge drives competitive advantage in the rapidly evolving retail landscape shaped by technological innovation.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Voice Shopping | Mail-Order Shopping |
|---|---|---|
| Ordering Method | Voice commands via smart devices | Order placement via catalog or mail forms |
| Convenience | Hands-free, instant ordering | Requires manual order submission and wait time |
| Order Processing Time | Typically real-time or within minutes | Several days to weeks |
| Product Discovery | Voice assistants suggest items based on preferences | Limited to catalog offerings and descriptions |
| User Experience | Interactive and personalized | Static and less engaging |
| Accessibility | Requires compatible voice-enabled devices | Accessible without technology but slower |
| Return Process | Initiated through voice or app support | Manual returns via mail |
| Suitability | Best for quick, everyday purchases | Ideal for detailed, less frequent orders |
Which is better?
Voice shopping offers real-time convenience by enabling hands-free, quick purchases through smart assistants, appealing to tech-savvy consumers seeking efficiency. Mail-order shopping provides a tactile, deliberate experience with detailed catalogs and tangible product descriptions, catering to buyers who prefer browsing at their own pace. Retailers incorporating voice technology report increased impulse buys, while mail-order maintains loyal customers valuing physical interaction with printed materials.
Connection
Voice shopping leverages conversational AI to enable customers to place orders hands-free, streamlining the purchase process often fulfilled through mail-order systems. Both methods emphasize convenience by allowing consumers to shop remotely without visiting a physical store, integrating with retailers' supply chains for efficient delivery. The synergy between voice-activated commands and mail-order logistics enhances personalized shopping experiences and accelerates order fulfillment cycles in retail.
Key Terms
Convenience
Mail-order shopping offers the convenience of browsing and purchasing products from home, with deliveries often scheduled to fit customers' availability. Voice shopping enhances this experience by enabling hands-free, instant ordering through smart devices, streamlining routine purchases without needing to navigate websites. Explore how these technologies revolutionize convenience in consumer behavior.
Personalization
Mail-order shopping offers personalized catalogs and targeted promotions based on customer purchase history and preferences. Voice shopping leverages AI assistants to provide real-time, context-aware recommendations, enabling seamless, hands-free customization. Explore how these personalization strategies are transforming consumer experiences in digital retail.
Accessibility
Mail-order shopping offers accessibility through detailed catalogs and the ability to order from home without internet access, catering to individuals with limited digital skills. Voice shopping enhances accessibility by enabling hands-free, intuitive purchases via smart speakers or mobile devices, benefiting visually impaired users and those with mobility challenges. Explore how these shopping methods redefine convenience and inclusivity in modern retail.
Source and External Links
Mail order - Wikipedia - Mail order refers to buying goods or services by mail delivery, where customers place orders via mail, phone, traveling agents, or websites and receive products directly at their address or nearby pickup points, with catalogues commonly used to market products to customers.
View Our Online Shopping Catalogs - Heartland America - Heartland America offers an online digital replica of their popular mail-order catalog, allowing shoppers to browse and order products much like traditional mail-order shopping.
Zingerman's: Online Shopping for Food and Gifts - Zingerman's provides mail-order service for food and gifts nationwide, shipping specialty products like classic deli fare and gift boxes with options for subscription-based food clubs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com