Circular retail focuses on sustainability by promoting product reuse, recycling, and reducing waste throughout the supply chain, enhancing environmental responsibility. Experience-driven retail emphasizes creating immersive and personalized shopping environments that engage customers emotionally and foster brand loyalty. Explore how these two innovative retail models are transforming consumer behavior and business strategies.
Why it is important
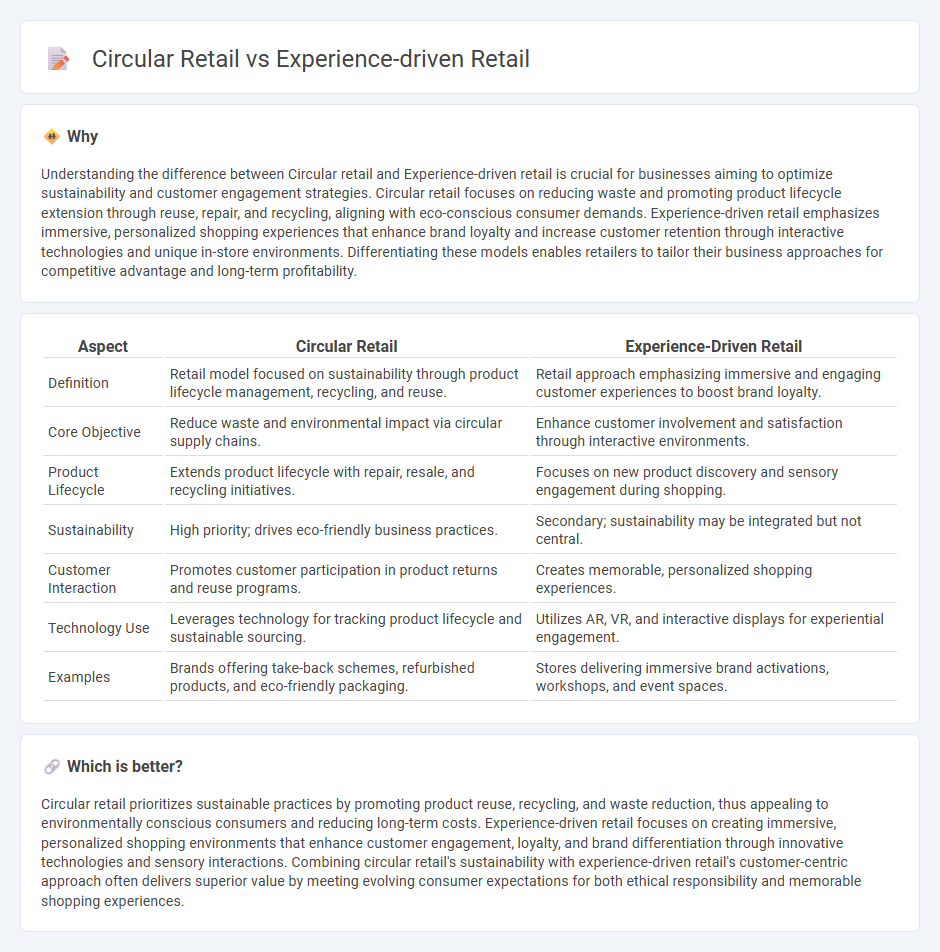
Understanding the difference between Circular retail and Experience-driven retail is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize sustainability and customer engagement strategies. Circular retail focuses on reducing waste and promoting product lifecycle extension through reuse, repair, and recycling, aligning with eco-conscious consumer demands. Experience-driven retail emphasizes immersive, personalized shopping experiences that enhance brand loyalty and increase customer retention through interactive technologies and unique in-store environments. Differentiating these models enables retailers to tailor their business approaches for competitive advantage and long-term profitability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Retail | Experience-Driven Retail |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Retail model focused on sustainability through product lifecycle management, recycling, and reuse. | Retail approach emphasizing immersive and engaging customer experiences to boost brand loyalty. |
| Core Objective | Reduce waste and environmental impact via circular supply chains. | Enhance customer involvement and satisfaction through interactive environments. |
| Product Lifecycle | Extends product lifecycle with repair, resale, and recycling initiatives. | Focuses on new product discovery and sensory engagement during shopping. |
| Sustainability | High priority; drives eco-friendly business practices. | Secondary; sustainability may be integrated but not central. |
| Customer Interaction | Promotes customer participation in product returns and reuse programs. | Creates memorable, personalized shopping experiences. |
| Technology Use | Leverages technology for tracking product lifecycle and sustainable sourcing. | Utilizes AR, VR, and interactive displays for experiential engagement. |
| Examples | Brands offering take-back schemes, refurbished products, and eco-friendly packaging. | Stores delivering immersive brand activations, workshops, and event spaces. |
Which is better?
Circular retail prioritizes sustainable practices by promoting product reuse, recycling, and waste reduction, thus appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and reducing long-term costs. Experience-driven retail focuses on creating immersive, personalized shopping environments that enhance customer engagement, loyalty, and brand differentiation through innovative technologies and sensory interactions. Combining circular retail's sustainability with experience-driven retail's customer-centric approach often delivers superior value by meeting evolving consumer expectations for both ethical responsibility and memorable shopping experiences.
Connection
Circular retail enhances sustainability by emphasizing product reuse and recycling, which aligns with experience-driven retail's focus on engaging customers through meaningful, eco-conscious interactions. Experience-driven retail leverages circular principles to create immersive shopping journeys that foster customer loyalty and brand trust. Integrating circular retail practices into experiential strategies promotes a holistic approach that satisfies consumer demand for both environmental responsibility and memorable shopping experiences.
Key Terms
Customer Engagement
Experience-driven retail emphasizes immersive, personalized shopping environments that enhance customer engagement by appealing to emotions and senses. Circular retail prioritizes sustainability and product life cycle extension, fostering loyalty through eco-conscious practices and transparent sourcing. Discover how integrating these models can revolutionize customer connections and elevate brand value.
Product Lifecycle
Experience-driven retail emphasizes personalized shopping journeys that enhance customer engagement through immersive and interactive touchpoints, extending the product lifecycle by encouraging repeat purchases and brand loyalty. Circular retail prioritizes sustainability by designing products for durability, reuse, and recycling, minimizing waste and promoting a closed-loop system that significantly extends the product lifecycle. Discover how integrating these strategies can revolutionize retail sustainability and customer satisfaction.
Sustainability
Experience-driven retail emphasizes immersive customer interactions that enhance brand loyalty through personalized services and innovative in-store technologies. Circular retail prioritizes sustainability by implementing closed-loop systems such as product take-back programs, recycling initiatives, and durable product design to minimize waste. Explore further to understand how these contrasting retail models shape the future of sustainable commerce.
Source and External Links
What is Experiential Retail? An Inside Look - Lightspeed - Experiential retail focuses on creating engaging, interactive, and memorable shopping experiences that prioritize customer engagement and brand immersion over direct sales, exemplified by brands like Glossier with their personalized, social-media driven, and magical in-store atmosphere.
6 Best Experiential Retail Examples for 2024 - Bridgewater Studio - Experiential retail creates multisensory and interactive environments--including AR, VR, workshops, and community-driven events--to transform shopping into meaningful, immersive brand experiences that go beyond transactions and build lasting customer connections.
Why Brands Need to Embrace Experience-Driven Commerce - Experience-driven retail means delivering seamless, personalized omnichannel experiences by leveraging customer insights and data to engage consumers effectively anytime and anywhere throughout their buying journey.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com