Loss prevention analytics leverages advanced data mining and predictive modeling to identify patterns and behaviors associated with theft, fraud, and operational inefficiencies in retail environments. Exception reporting focuses on flagging deviations from predefined operational norms and policies, enabling quick identification of anomalies such as unusual transaction sizes or employee activity. Explore deeper insights to understand how integrating both approaches can enhance retail security and profitability.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between loss prevention analytics and exception reporting is crucial for retailers to effectively mitigate risks and enhance operational efficiency. Loss prevention analytics involves analyzing patterns and trends to proactively identify potential fraud and shrinkage risks, while exception reporting highlights anomalies or deviations from standard procedures that require immediate attention. Leveraging loss prevention analytics enables strategic decision-making through predictive insights, whereas exception reporting facilitates reactive measures by pinpointing specific incidents. Retailers who master both tools can significantly reduce financial losses and improve overall store security.
Comparison Table
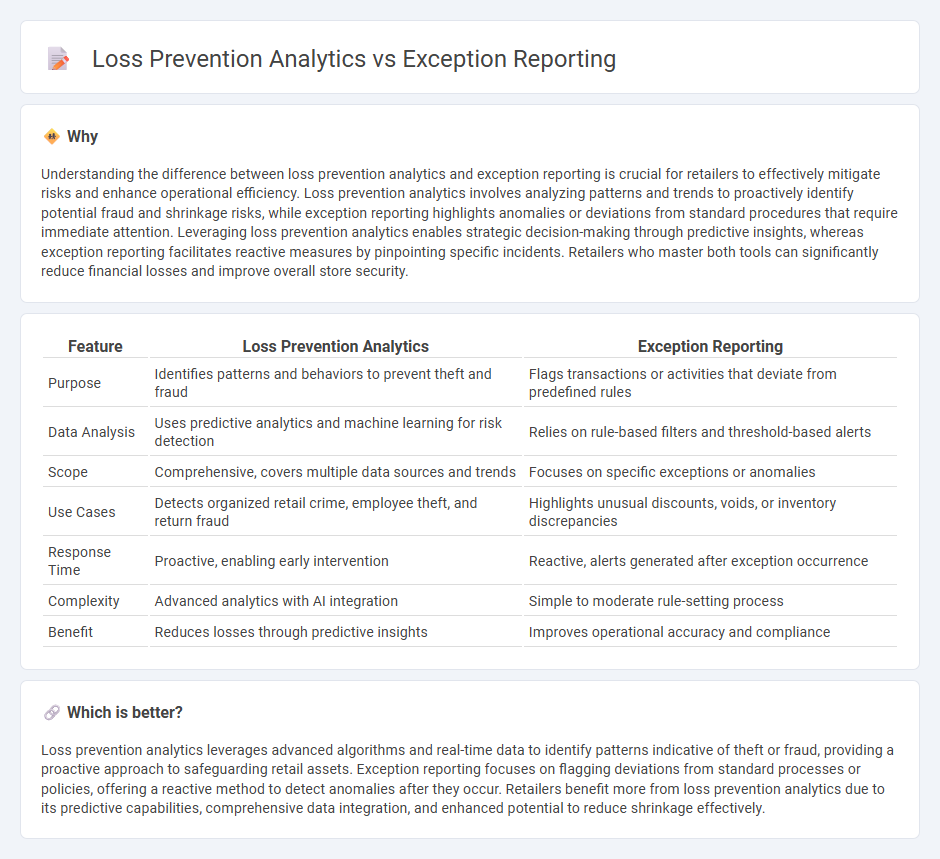
| Feature | Loss Prevention Analytics | Exception Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identifies patterns and behaviors to prevent theft and fraud | Flags transactions or activities that deviate from predefined rules |
| Data Analysis | Uses predictive analytics and machine learning for risk detection | Relies on rule-based filters and threshold-based alerts |
| Scope | Comprehensive, covers multiple data sources and trends | Focuses on specific exceptions or anomalies |
| Use Cases | Detects organized retail crime, employee theft, and return fraud | Highlights unusual discounts, voids, or inventory discrepancies |
| Response Time | Proactive, enabling early intervention | Reactive, alerts generated after exception occurrence |
| Complexity | Advanced analytics with AI integration | Simple to moderate rule-setting process |
| Benefit | Reduces losses through predictive insights | Improves operational accuracy and compliance |
Which is better?
Loss prevention analytics leverages advanced algorithms and real-time data to identify patterns indicative of theft or fraud, providing a proactive approach to safeguarding retail assets. Exception reporting focuses on flagging deviations from standard processes or policies, offering a reactive method to detect anomalies after they occur. Retailers benefit more from loss prevention analytics due to its predictive capabilities, comprehensive data integration, and enhanced potential to reduce shrinkage effectively.
Connection
Loss prevention analytics leverages data to identify patterns of theft, fraud, and operational inefficiencies within retail environments, enhancing security measures and reducing financial losses. Exception reporting highlights anomalies and deviations from standard processes, providing actionable insights for timely intervention and investigative follow-up. Together, these tools enable retailers to proactively detect risks, optimize inventory management, and improve overall loss control strategies.
Key Terms
**Exception Reporting:**
Exception reporting identifies anomalies or deviations from standard business processes by flagging transactions or activities that fall outside predefined thresholds, enabling quick detection of irregularities. This approach enhances operational efficiency by highlighting only critical exceptions for investigation, reducing data overload for decision-makers. Explore how exception reporting can streamline your risk management and compliance strategies further.
Outlier Detection
Exception reporting targets identifying anomalies and deviations from standard processes by highlighting outliers that may indicate errors or fraud, using statistical thresholds and rule-based filters. Loss prevention analytics employs advanced outlier detection algorithms, including machine learning models, to proactively uncover suspicious patterns in transaction data, enhancing risk mitigation in retail and finance sectors. Explore further to understand how these techniques optimize operational efficiency and security.
Transaction Monitoring
Exception reporting in transaction monitoring identifies unusual or suspicious activities by flagging deviations from established norms, enabling targeted investigations. Loss prevention analytics leverages predictive models and real-time data to detect fraud patterns and minimize financial losses proactively. Explore how integrating these approaches enhances transaction monitoring effectiveness and safeguards assets.
Source and External Links
Understanding the Exception Report in Project Management - An exception report collects data on project deviations and mistakes, documents them to prevent recurrence, and helps organizations identify and address issues promptly to stay on schedule and budget.
Exception report definition - AccountingTools - An exception report highlights instances where actual performance deviates significantly, usually negatively, from expectations, focusing management attention on areas requiring immediate corrective action.
Exception Reports - LeapFrogBI - Exception reports identify out-of-range or unexpected situations such as data entry errors, reconciliation mismatches, and business process exceptions, providing early detection and facilitating issue resolution.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com