Dropshipping offers retailers a low-overhead model by eliminating the need for physical inventory and storefronts, enabling rapid scalability and diverse product offerings. Brick-and-mortar stores provide tangible customer experiences, immediate product availability, and localized brand presence that fosters community trust. Discover how each model shapes the future of retail and which suits your business goals best.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dropshipping and brick-and-mortar retail is crucial for optimizing supply chain management and customer experience. Dropshipping eliminates inventory costs by shipping products directly from suppliers, while brick-and-mortar stores require physical inventory and offer in-person shopping. Retailers must evaluate cost structures, logistics, and consumer preferences to select the best sales model. Effective differentiation enhances competitive advantage and profit margins in the retail industry.
Comparison Table
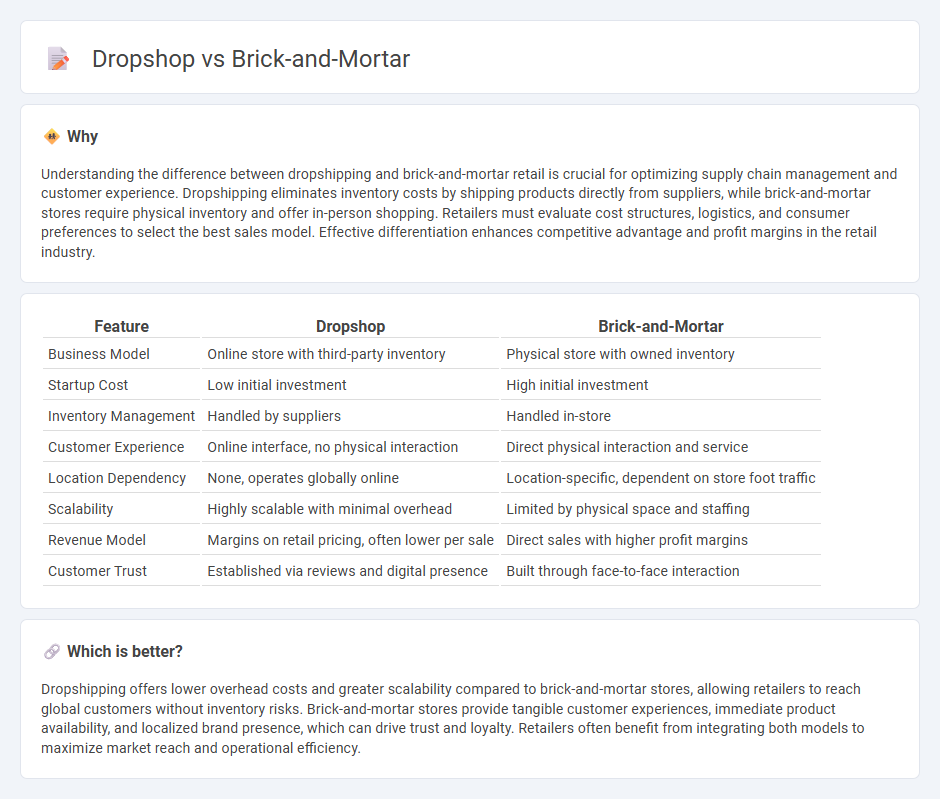
| Feature | Dropshop | Brick-and-Mortar |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Online store with third-party inventory | Physical store with owned inventory |
| Startup Cost | Low initial investment | High initial investment |
| Inventory Management | Handled by suppliers | Handled in-store |
| Customer Experience | Online interface, no physical interaction | Direct physical interaction and service |
| Location Dependency | None, operates globally online | Location-specific, dependent on store foot traffic |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with minimal overhead | Limited by physical space and staffing |
| Revenue Model | Margins on retail pricing, often lower per sale | Direct sales with higher profit margins |
| Customer Trust | Established via reviews and digital presence | Built through face-to-face interaction |
Which is better?
Dropshipping offers lower overhead costs and greater scalability compared to brick-and-mortar stores, allowing retailers to reach global customers without inventory risks. Brick-and-mortar stores provide tangible customer experiences, immediate product availability, and localized brand presence, which can drive trust and loyalty. Retailers often benefit from integrating both models to maximize market reach and operational efficiency.
Connection
Dropshop and brick-and-mortar retail share integrated inventory management systems that streamline product availability across online and physical stores. Consumers benefit from unified shopping experiences, such as click-and-collect services and in-store returns for online purchases. Retailers leverage data analytics from both channels to optimize stock levels and personalize marketing strategies.
Key Terms
Physical Storefront
Brick-and-mortar stores provide tangible customer experiences through physical storefronts, enabling direct product interaction and personalized service. These establishments often benefit from local foot traffic and immediate inventory access, but incur higher overhead costs such as rent and utilities. Explore more insights into how physical storefronts impact retail strategy.
Inventory Management
Brick-and-mortar stores require physical inventory storage, often leading to higher carrying costs and the need for efficient stock rotation to prevent obsolescence. Dropshipping relies on third-party suppliers to manage inventory, reducing startup costs and minimizing storage challenges but demanding strong supplier coordination to avoid stockouts. Explore detailed strategies to optimize inventory management in both retail models.
Supply Chain Integration
Brick-and-mortar stores rely heavily on localized inventory management and in-store logistics, creating a tightly controlled supply chain that supports immediate product availability and customer service. Dropshipping eliminates the need for physical inventory by integrating directly with third-party suppliers, streamlining order fulfillment while reducing overhead costs and minimizing supply chain risk. Explore how businesses optimize supply chain integration by balancing physical presence and dropshipping efficiency.
Source and External Links
Brick and mortar - A brick-and-mortar business refers to a company with a physical presence such as retail shops or warehouses, contrasting with online-only businesses that lack face-to-face customer interaction.
Brick & Mortar Business | Definition & Information - The term originated in the 1850s describing physical storefronts customers visit in person, which still account for 80% of shopping despite the rise of online commerce.
BRICK-AND-MORTAR definition | Cambridge English Dictionary - Used as an adjective or noun, brick-and-mortar denotes traditional businesses operating in physical buildings rather than solely online.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com