Ethnographic listening captures authentic consumer experiences by observing behaviors and environments, offering deep insights into motivations and cultural contexts often missed by traditional surveys. Surveys provide quantitative data through structured questions, enabling statistical analysis but may lack the nuanced understanding ethnographic methods reveal. Explore how combining ethnographic listening with surveys can enhance your marketing strategies.
Why it is important
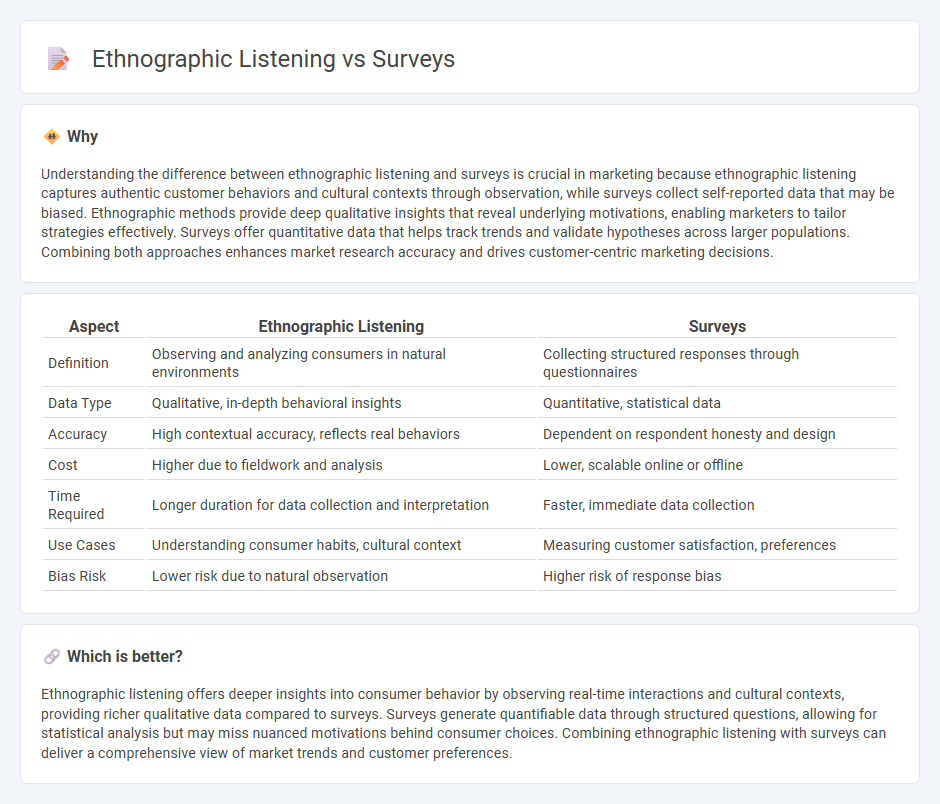
Understanding the difference between ethnographic listening and surveys is crucial in marketing because ethnographic listening captures authentic customer behaviors and cultural contexts through observation, while surveys collect self-reported data that may be biased. Ethnographic methods provide deep qualitative insights that reveal underlying motivations, enabling marketers to tailor strategies effectively. Surveys offer quantitative data that helps track trends and validate hypotheses across larger populations. Combining both approaches enhances market research accuracy and drives customer-centric marketing decisions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ethnographic Listening | Surveys |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Observing and analyzing consumers in natural environments | Collecting structured responses through questionnaires |
| Data Type | Qualitative, in-depth behavioral insights | Quantitative, statistical data |
| Accuracy | High contextual accuracy, reflects real behaviors | Dependent on respondent honesty and design |
| Cost | Higher due to fieldwork and analysis | Lower, scalable online or offline |
| Time Required | Longer duration for data collection and interpretation | Faster, immediate data collection |
| Use Cases | Understanding consumer habits, cultural context | Measuring customer satisfaction, preferences |
| Bias Risk | Lower risk due to natural observation | Higher risk of response bias |
Which is better?
Ethnographic listening offers deeper insights into consumer behavior by observing real-time interactions and cultural contexts, providing richer qualitative data compared to surveys. Surveys generate quantifiable data through structured questions, allowing for statistical analysis but may miss nuanced motivations behind consumer choices. Combining ethnographic listening with surveys can deliver a comprehensive view of market trends and customer preferences.
Connection
Ethnographic listening and surveys complement each other in marketing by combining qualitative insights with quantitative data to deeply understand consumer behaviors and preferences. Ethnographic listening captures real-time customer emotions and context through social media monitoring and direct observation, while surveys provide structured responses that validate trends and measure satisfaction. Together, they enable marketers to create targeted campaigns that resonate emotionally and are backed by statistically significant feedback.
Key Terms
Quantitative Data
Surveys provide structured, quantitative data through standardized questions and large sample sizes, enabling statistical analysis and trend identification. Ethnographic listening captures qualitative insights from in-depth cultural observations, focusing on context rather than numerical measurement. Discover more about the strengths and applications of both methods for effective data collection.
Qualitative Insights
Surveys offer quantitative data through structured questions, ensuring broad demographic coverage but often lacking depth in emotional context and cultural nuances. Ethnographic listening prioritizes immersive, qualitative insights by observing and engaging with participants in their natural environments, capturing authentic behaviors and unspoken motivations. Explore the distinct advantages of each method to enhance your qualitative research strategy.
Respondent Engagement
Surveys typically provide structured data through direct questions, enabling quantifiable insights into respondent engagement but can limit depth of understanding due to fixed answer formats. Ethnographic listening captures natural behavior and unfiltered emotions by observing participants in real-life environments, offering richer context and deeper insight into engagement nuances. Explore how combining both methods enhances comprehensive understanding of respondent engagement.
Source and External Links
What is a Survey? Benefits, Tips & Free Tool - Qualtrics - Surveys collect information from a sample of people to understand populations and are commonly conducted face-to-face, by phone, on paper, or online, with online surveys offering faster, more accurate data collection and broader reach.
Free Online Survey Maker | Questionnaire Creator - Jotform - Surveys are structured tools for gathering feedback or data from a population segment, useful for businesses and individuals, and can be conducted via pen and paper or preferably using online tools for ease of distribution and wider audience access.
Learn how to conduct a survey in these simple steps - SurveyMonkey - Conducting surveys involves defining your goals, selecting your target demographic, deciding sample size, designing questions carefully, and using surveys to gain insights that improve decisions related to products, services, and customer understanding.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com