Cultural codes represent shared beliefs, values, and symbols that shape consumer behavior within a broader society, influencing marketing strategies at a macro level. Subcultures consist of distinct groups within the larger culture, characterized by unique preferences and identities that require targeted marketing approaches. Explore how understanding cultural codes and subcultures can enhance the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns.
Why it is important
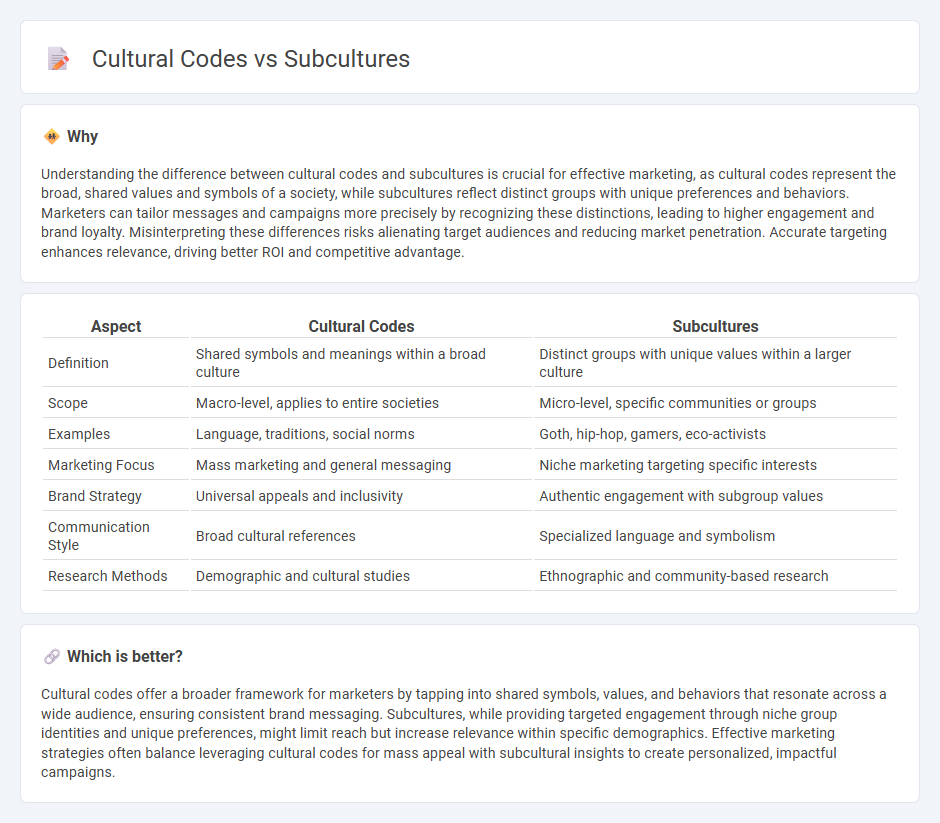
Understanding the difference between cultural codes and subcultures is crucial for effective marketing, as cultural codes represent the broad, shared values and symbols of a society, while subcultures reflect distinct groups with unique preferences and behaviors. Marketers can tailor messages and campaigns more precisely by recognizing these distinctions, leading to higher engagement and brand loyalty. Misinterpreting these differences risks alienating target audiences and reducing market penetration. Accurate targeting enhances relevance, driving better ROI and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cultural Codes | Subcultures |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared symbols and meanings within a broad culture | Distinct groups with unique values within a larger culture |
| Scope | Macro-level, applies to entire societies | Micro-level, specific communities or groups |
| Examples | Language, traditions, social norms | Goth, hip-hop, gamers, eco-activists |
| Marketing Focus | Mass marketing and general messaging | Niche marketing targeting specific interests |
| Brand Strategy | Universal appeals and inclusivity | Authentic engagement with subgroup values |
| Communication Style | Broad cultural references | Specialized language and symbolism |
| Research Methods | Demographic and cultural studies | Ethnographic and community-based research |
Which is better?
Cultural codes offer a broader framework for marketers by tapping into shared symbols, values, and behaviors that resonate across a wide audience, ensuring consistent brand messaging. Subcultures, while providing targeted engagement through niche group identities and unique preferences, might limit reach but increase relevance within specific demographics. Effective marketing strategies often balance leveraging cultural codes for mass appeal with subcultural insights to create personalized, impactful campaigns.
Connection
Cultural codes shape the shared meanings and values within societies, influencing consumer behavior and brand perception in marketing. Subcultures emerge as distinct groups that interpret and adapt these cultural codes uniquely, creating niche markets with specific preferences and identities. Marketers leverage the interplay between cultural codes and subcultures to craft targeted campaigns that resonate authentically with diverse audience segments.
Key Terms
Values
Subcultures embody distinct value systems that differentiate them from mainstream culture, often emphasizing alternative beliefs, norms, and priorities. Cultural codes represent the underlying shared values and symbols that guide behavior and communication within a society or group. Explore these dynamics further to understand how values shape social identity and interaction.
Symbols
Subcultures develop unique symbols that distinguish their identity and values from mainstream culture, often conveying specific meanings within their group. Cultural codes encompass broader symbolic systems, including language, rituals, and artifacts, that guide social interactions and shared understanding across society. Explore how symbols function in shaping group identity and communication by diving deeper into the study of subcultures and cultural codes.
Identity
Subcultures represent distinct groups within a larger culture, characterized by unique values, norms, and identity markers that differentiate them from mainstream society. Cultural codes consist of shared symbols, language, and behaviors that convey meaning and reinforce group identity across various social contexts. Explore how understanding these dynamics enhances insights into identity formation and social belonging.
Source and External Links
Subculture | Definition, Types & Examples - Lesson - Study.com - Subcultures are groups within a society that share distinct values, behaviors, and identities, often forming in resistance to or marginalization from mainstream culture, and include examples like Deaf culture, drag, and skinheads.
Subcultures - Introduction to Consumer Behaviour - Subcultures emerge from shared secondary values, experiences, or traits--such as income level, participation in social institutions, shared beliefs, artistic interests, or language--and can range from biker communities to ethnic groups and support networks like Alcoholics Anonymous.
Subculture - Wikipedia - Subcultures differentiate themselves from dominant culture through voluntary, informal groups that often express symbolic resistance to mainstream norms, using distinctive styles and cultural practices that are sometimes co-opted by mass culture and media.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com