Algorithmic bias in marketing arises when automated systems reinforce existing prejudices, leading to unfair targeting and exclusion of key audience segments. Personalization leverages data-driven insights to tailor content and offers, enhancing customer engagement and conversion rates. Explore how balancing algorithmic fairness and personalized marketing can optimize campaign effectiveness.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between algorithmic bias and personalization is crucial in marketing to ensure fair and ethical targeting while enhancing customer experience. Algorithmic bias can lead to discriminatory outcomes that damage brand reputation and customer trust. Personalization improves marketing effectiveness by tailoring content to individual preferences without unfairly excluding groups. Recognizing these distinctions helps marketers optimize campaigns and maintain compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Comparison Table
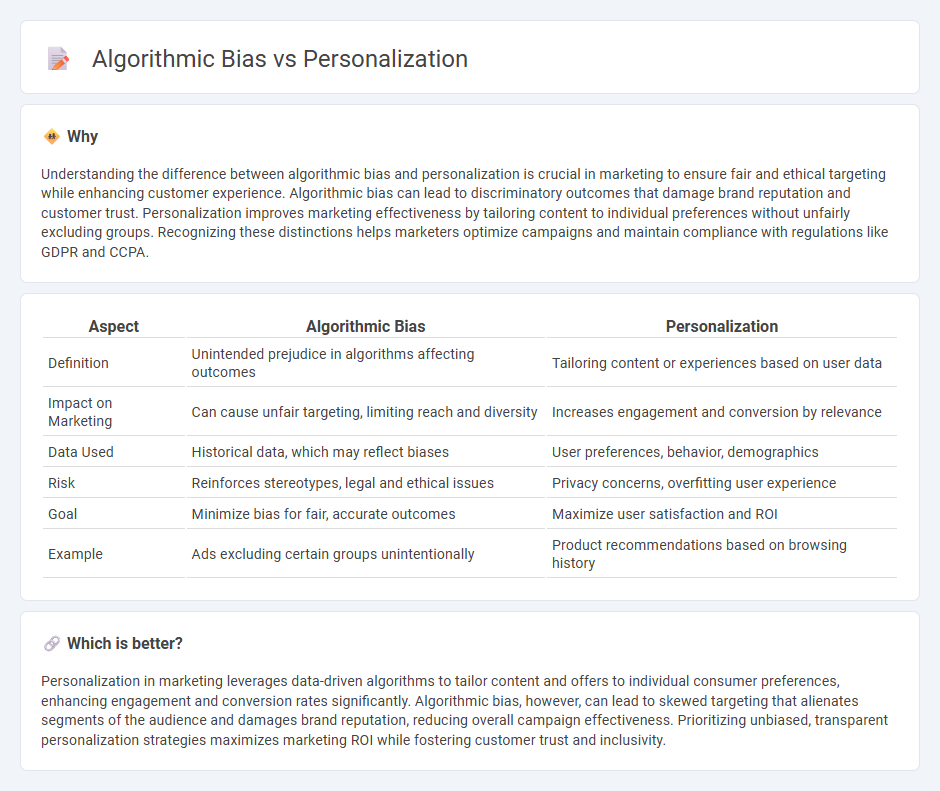
| Aspect | Algorithmic Bias | Personalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unintended prejudice in algorithms affecting outcomes | Tailoring content or experiences based on user data |
| Impact on Marketing | Can cause unfair targeting, limiting reach and diversity | Increases engagement and conversion by relevance |
| Data Used | Historical data, which may reflect biases | User preferences, behavior, demographics |
| Risk | Reinforces stereotypes, legal and ethical issues | Privacy concerns, overfitting user experience |
| Goal | Minimize bias for fair, accurate outcomes | Maximize user satisfaction and ROI |
| Example | Ads excluding certain groups unintentionally | Product recommendations based on browsing history |
Which is better?
Personalization in marketing leverages data-driven algorithms to tailor content and offers to individual consumer preferences, enhancing engagement and conversion rates significantly. Algorithmic bias, however, can lead to skewed targeting that alienates segments of the audience and damages brand reputation, reducing overall campaign effectiveness. Prioritizing unbiased, transparent personalization strategies maximizes marketing ROI while fostering customer trust and inclusivity.
Connection
Algorithmic bias in marketing often arises from personalization techniques that rely on historical customer data, which may inadvertently reinforce existing stereotypes or preferences. Personalization algorithms optimize campaign targeting by analyzing user behavior and demographics, but this optimization can perpetuate discriminatory patterns embedded in the datasets. Addressing algorithmic bias requires refining data inputs and algorithmic models to ensure equitable and inclusive marketing strategies across diverse consumer segments.
Key Terms
Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation leverages personalization techniques to deliver tailored experiences, enhancing customer satisfaction and engagement. However, algorithmic bias in segmentation models can lead to unfair targeting, misclassification, and exclusion of diverse groups, impacting marketing effectiveness. Explore more on balancing personalization and mitigating bias to optimize customer segmentation strategies.
Recommendation Systems
Recommendation systems leverage personalization to tailor content, products, and services based on user preferences and behavior, enhancing user satisfaction and engagement. However, algorithmic bias can arise when data or model design inadvertently promotes unfair or skewed results, impacting diversity and perpetuating stereotypes in recommendations. Explore how balancing personalization and mitigating algorithmic bias can create fair and effective recommendation systems.
Fairness
Personalization in digital platforms tailors user experiences by analyzing individual preferences, but it can inadvertently reinforce algorithmic bias, leading to unfair treatment of certain groups. Fairness in algorithms requires proactive measures such as diverse data representation, transparency, and continuous bias audits to ensure equitable outcomes. Explore deeper insights on balancing personalization with fairness to foster inclusive, unbiased AI systems.
Source and External Links
What is Marketing Personalization? | Salesforce US - Personalization uses customer data to tailor brand messages and experiences automatically to individual interests, differing from customization which requires user effort to change settings or preferences.
Personalization 101: What it is, importance, and examples - Zendesk - Personalization in business involves tailoring interactions by leveraging combined customer data across departments to improve marketing, sales, and support with a 360-degree customer view.
What Is Personalization? Personalization Definition and Benefits - Personalization tailors products or services to individual needs using data and predictive technology, enhancing customer satisfaction and marketing effectiveness by addressing customers' unique preferences and cutting through marketing noise.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com