Ethnographic listening captures authentic consumer behaviors through immersive observation, revealing deep insights into customer experiences and cultural contexts. Mystery shopping evaluates service quality and compliance by simulating real customer interactions, providing actionable feedback from a covert perspective. Explore more to understand how these methods complement each other in crafting effective marketing strategies.
Why it is important
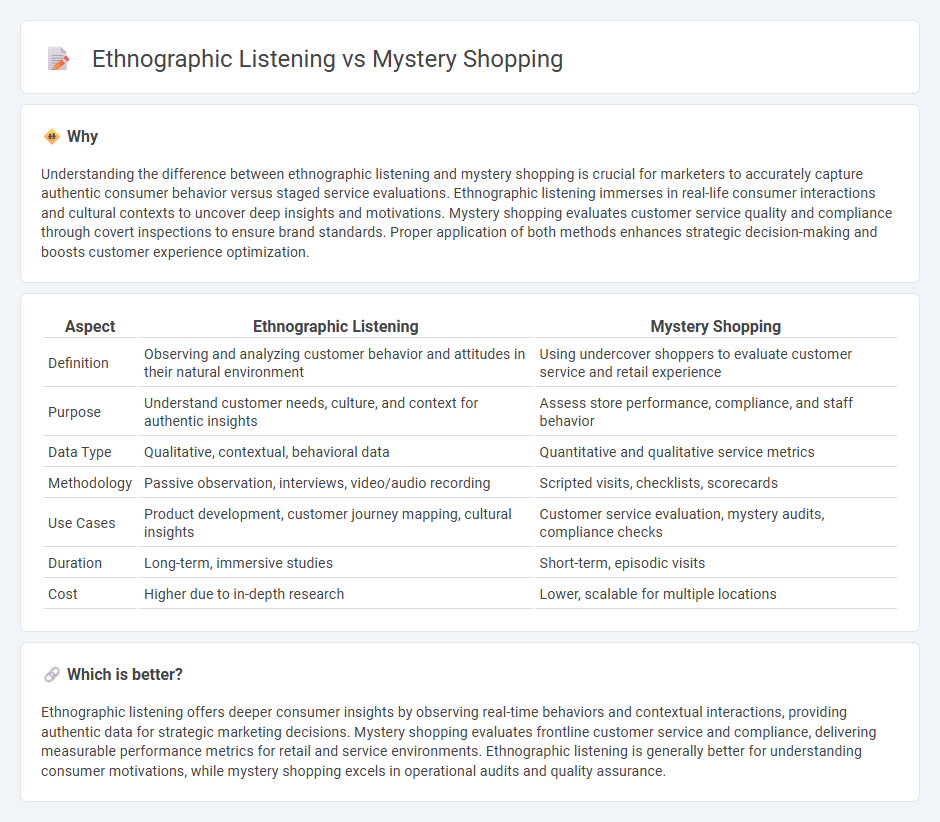
Understanding the difference between ethnographic listening and mystery shopping is crucial for marketers to accurately capture authentic consumer behavior versus staged service evaluations. Ethnographic listening immerses in real-life consumer interactions and cultural contexts to uncover deep insights and motivations. Mystery shopping evaluates customer service quality and compliance through covert inspections to ensure brand standards. Proper application of both methods enhances strategic decision-making and boosts customer experience optimization.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ethnographic Listening | Mystery Shopping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Observing and analyzing customer behavior and attitudes in their natural environment | Using undercover shoppers to evaluate customer service and retail experience |
| Purpose | Understand customer needs, culture, and context for authentic insights | Assess store performance, compliance, and staff behavior |
| Data Type | Qualitative, contextual, behavioral data | Quantitative and qualitative service metrics |
| Methodology | Passive observation, interviews, video/audio recording | Scripted visits, checklists, scorecards |
| Use Cases | Product development, customer journey mapping, cultural insights | Customer service evaluation, mystery audits, compliance checks |
| Duration | Long-term, immersive studies | Short-term, episodic visits |
| Cost | Higher due to in-depth research | Lower, scalable for multiple locations |
Which is better?
Ethnographic listening offers deeper consumer insights by observing real-time behaviors and contextual interactions, providing authentic data for strategic marketing decisions. Mystery shopping evaluates frontline customer service and compliance, delivering measurable performance metrics for retail and service environments. Ethnographic listening is generally better for understanding consumer motivations, while mystery shopping excels in operational audits and quality assurance.
Connection
Ethnographic listening and mystery shopping both provide deep insights into consumer behavior by capturing authentic customer experiences and interactions in real-world settings. Ethnographic listening focuses on understanding customer emotions and cultural context through observation and conversation analysis, while mystery shopping evaluates service quality and operational compliance from a customer's perspective. Together, these methods enable marketers to design targeted strategies based on genuine consumer feedback and behavior patterns.
Key Terms
Participant Observation
Mystery shopping involves trained evaluators anonymously assessing customer service and store operations, offering quantitative data on compliance and performance. Ethnographic listening emphasizes deep participant observation, capturing rich qualitative insights into consumer behavior and cultural context over extended periods. Explore how these methodologies complement each other to enhance market research effectiveness.
Customer Experience
Mystery shopping offers structured, scenario-based assessments that capture specific customer service interactions, providing quantifiable insights into operational standards. Ethnographic listening delves deeper into customer emotions and behaviors through natural, real-time observation and immersive data collection, enhancing understanding of customer experience on a holistic level. Explore further to discover which method best elevates your customer experience strategy.
Behavioral Insights
Mystery shopping provides direct observational data by simulating customer experiences to evaluate service quality and employee behavior, while ethnographic listening captures natural, unfiltered consumer interactions and emotions in real-life settings, revealing deeper behavioral insights. Both methods are essential for understanding customer journeys; mystery shopping focuses on service compliance, and ethnographic listening uncovers underlying motivations and cultural context. Explore further to discover how combining these approaches enhances comprehensive behavioral analysis.
Source and External Links
FAQ: How Does Mystery Shopping Work? | Indeed.com - Mystery shopping involves acting as a customer to evaluate service quality and overall experience at businesses, helping companies identify areas for improvement through detailed observations and reports.
The 5 Best Mystery Shopper Companies to Work For in 2025 - Mystery shopping pays individuals to pose as customers, assess cleanliness, employee interaction, and other factors, submit reports, and often reimburse purchase costs, making it a flexible way to earn money.
Mystery Shopping Scams - Federal Trade Commission - Mystery shopping is generally part-time work where shoppers pay for products or services upfront and then get reimbursed, but caution is advised to avoid scams demanding fees or upfront payments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com