Ethnographic listening captures authentic consumer behaviors and environmental context to reveal deep cultural insights, while in-depth interviews gather detailed personal experiences and motivations through direct questioning. Both methods offer unique perspectives on customer needs and preferences, enhancing market research accuracy. Explore how combining these approaches can elevate your marketing strategies.
Why it is important
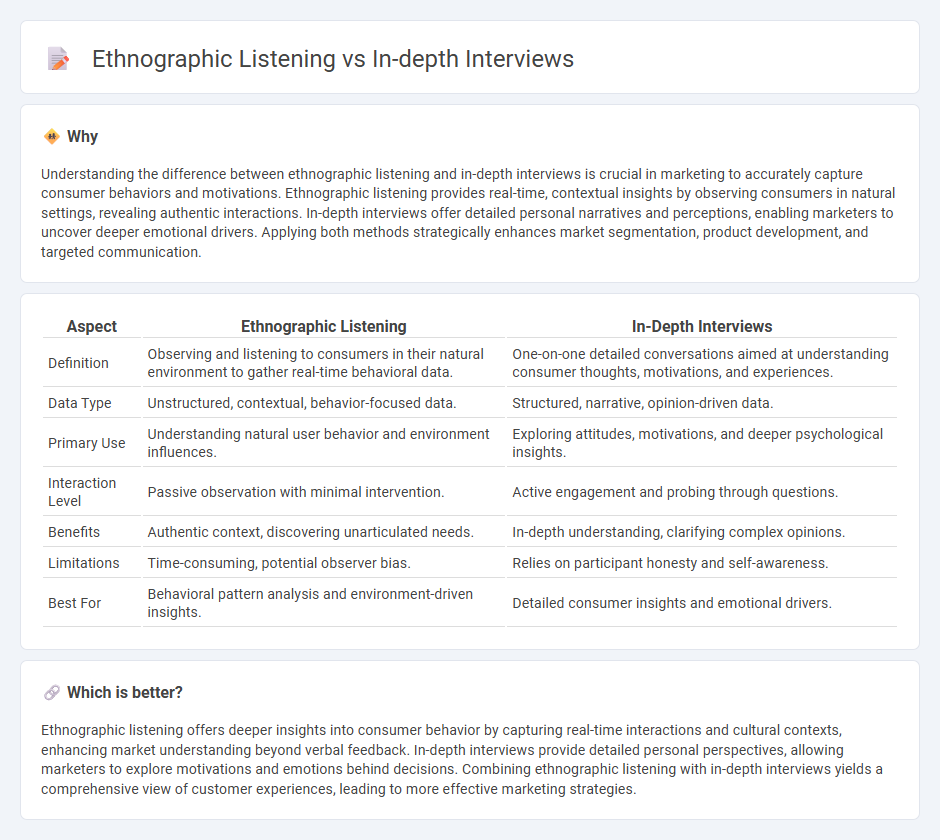
Understanding the difference between ethnographic listening and in-depth interviews is crucial in marketing to accurately capture consumer behaviors and motivations. Ethnographic listening provides real-time, contextual insights by observing consumers in natural settings, revealing authentic interactions. In-depth interviews offer detailed personal narratives and perceptions, enabling marketers to uncover deeper emotional drivers. Applying both methods strategically enhances market segmentation, product development, and targeted communication.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ethnographic Listening | In-Depth Interviews |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Observing and listening to consumers in their natural environment to gather real-time behavioral data. | One-on-one detailed conversations aimed at understanding consumer thoughts, motivations, and experiences. |
| Data Type | Unstructured, contextual, behavior-focused data. | Structured, narrative, opinion-driven data. |
| Primary Use | Understanding natural user behavior and environment influences. | Exploring attitudes, motivations, and deeper psychological insights. |
| Interaction Level | Passive observation with minimal intervention. | Active engagement and probing through questions. |
| Benefits | Authentic context, discovering unarticulated needs. | In-depth understanding, clarifying complex opinions. |
| Limitations | Time-consuming, potential observer bias. | Relies on participant honesty and self-awareness. |
| Best For | Behavioral pattern analysis and environment-driven insights. | Detailed consumer insights and emotional drivers. |
Which is better?
Ethnographic listening offers deeper insights into consumer behavior by capturing real-time interactions and cultural contexts, enhancing market understanding beyond verbal feedback. In-depth interviews provide detailed personal perspectives, allowing marketers to explore motivations and emotions behind decisions. Combining ethnographic listening with in-depth interviews yields a comprehensive view of customer experiences, leading to more effective marketing strategies.
Connection
Ethnographic listening and in-depth interviews are connected through their shared goal of uncovering deep consumer insights by capturing authentic behaviors and emotions within natural contexts. Ethnographic listening focuses on observing and interpreting cultural and social interactions, while in-depth interviews provide personalized, detailed narratives that reveal underlying motivations and attitudes. Combining these qualitative methods enhances the understanding of target audiences, enabling marketers to develop more effective, culturally relevant strategies.
Key Terms
Qualitative Research
In-depth interviews provide structured, direct data collection through targeted questioning, capturing participants' explicit thoughts and feelings. Ethnographic listening involves immersive observation and contextual understanding, revealing implicit behaviors and cultural nuances within natural settings. Explore further to master qualitative research techniques and their strategic applications.
Consumer Insights
In-depth interviews provide detailed consumer perspectives by exploring individual motivations, preferences, and behaviors through structured conversations, enabling brands to uncover explicit insights. Ethnographic listening captures authentic consumer experiences by observing real-life interactions and environments, revealing unconscious patterns and contextual influences on purchasing decisions. Explore how integrating these methods can deepen your understanding of consumer insights and enhance strategic decision-making.
Contextual Understanding
In-depth interviews provide detailed insights through direct questions, revealing individual perspectives and experiences, whereas ethnographic listening captures ambient cultural nuances by observing natural interactions and environments. Ethnographic listening emphasizes immersive context, uncovering unspoken social dynamics that structured interviews might overlook. Explore more to understand how these methods complement each other in qualitative research.
Source and External Links
In-Depth Interviews for Qualitative Analysis - In-depth interviews are open-ended, one-on-one conversations designed to uncover detailed insights into participants' experiences, perspectives, and emotions as part of qualitative research.
WORKBOOK E: CONDUCTING IN-DEPTH INTERVIEWS - In-depth interviews are a discovery-oriented qualitative method used to gather rich, detailed information directly from stakeholders, often helping to refine research focus and identify key areas for further exploration.
A Guide for Designing and Conducting In-Depth Interviews - This technique involves intensive individual interviews with a small number of respondents to deeply explore their views on specific ideas, programs, or situations, providing context and depth to broader research findings.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com