Green hushing refers to companies deliberately underreporting or minimizing their environmental efforts to avoid scrutiny, while greenwashing involves exaggerating or falsely promoting sustainability claims to appear eco-friendly. Understanding the subtle differences between these two practices is crucial for evaluating corporate transparency and environmental accountability in marketing strategies. Explore further to distinguish genuine green initiatives from misleading claims.
Why it is important
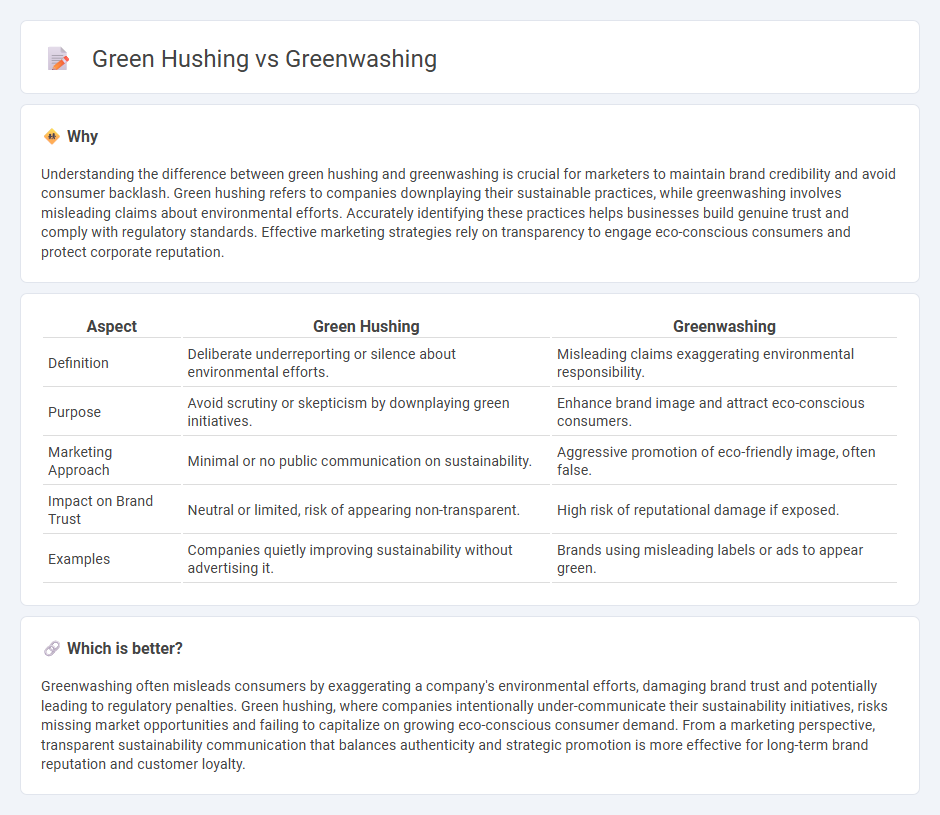
Understanding the difference between green hushing and greenwashing is crucial for marketers to maintain brand credibility and avoid consumer backlash. Green hushing refers to companies downplaying their sustainable practices, while greenwashing involves misleading claims about environmental efforts. Accurately identifying these practices helps businesses build genuine trust and comply with regulatory standards. Effective marketing strategies rely on transparency to engage eco-conscious consumers and protect corporate reputation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Hushing | Greenwashing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate underreporting or silence about environmental efforts. | Misleading claims exaggerating environmental responsibility. |
| Purpose | Avoid scrutiny or skepticism by downplaying green initiatives. | Enhance brand image and attract eco-conscious consumers. |
| Marketing Approach | Minimal or no public communication on sustainability. | Aggressive promotion of eco-friendly image, often false. |
| Impact on Brand Trust | Neutral or limited, risk of appearing non-transparent. | High risk of reputational damage if exposed. |
| Examples | Companies quietly improving sustainability without advertising it. | Brands using misleading labels or ads to appear green. |
Which is better?
Greenwashing often misleads consumers by exaggerating a company's environmental efforts, damaging brand trust and potentially leading to regulatory penalties. Green hushing, where companies intentionally under-communicate their sustainability initiatives, risks missing market opportunities and failing to capitalize on growing eco-conscious consumer demand. From a marketing perspective, transparent sustainability communication that balances authenticity and strategic promotion is more effective for long-term brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Connection
Green hushing and greenwashing are connected by their impact on corporate environmental communication, both distorting public perception of sustainability efforts. Greenwashing involves exaggerating or falsifying eco-friendly practices to attract environmentally conscious consumers, while green hushing refers to companies deliberately minimizing or hiding their genuine sustainability achievements to avoid scrutiny or backlash. These contradictory approaches undermine trust in green marketing and complicate consumer decision-making regarding authentic environmental responsibility.
Key Terms
Sustainability Claims
Greenwashing involves companies making misleading sustainability claims to appear more environmentally friendly, while green hushing refers to deliberately downplaying or withholding such claims to avoid scrutiny or criticism. Both practices impact consumer trust and market transparency in sustainability efforts. Explore the differences and implications of these tactics to better understand authentic environmental accountability.
Transparency
Greenwashing involves companies misleading consumers by exaggerating their environmental efforts, while green hushing refers to businesses underreporting their sustainability initiatives to avoid scrutiny or criticism. Transparency in corporate environmental communication is crucial to build trust and allow stakeholders to make informed decisions based on accurate, verifiable information. Explore strategies to enhance transparency and navigate the balance between greenwashing and green hushing for authentic sustainability reporting.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Greenwashing involves companies misleading consumers by exaggerating their environmental efforts in Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) reports, while green hushing refers to firms downplaying or concealing their sustainability initiatives to avoid scrutiny or criticism. Both practices undermine transparency and accountability in CSR, hindering genuine progress toward environmental sustainability. Discover effective strategies to enhance authenticity and trust in corporate environmental commitments.
Source and External Links
Explainer: What Is Greenwashing and How to Avoid It? - This article discusses greenwashing, a deceptive marketing practice where companies appear more sustainable than they actually are, and how to identify such tactics.
Greenwashing Examples for 2024 & 2025 | Products & Brands - This blog post provides examples of brands engaging in greenwashing, including McDonald's and Coca-Cola, highlighting the difference between appearance and actual sustainability.
Greenwashing - This Wikipedia page defines greenwashing as a form of advertising that makes exaggerated environmental claims, mentioning historical examples and initiatives often criticized for being misleading.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com