Nano targeting focuses on hyper-specific audience segments using detailed consumer data and behaviors to deliver highly personalized marketing messages. Contextual targeting places ads based on the content and context of the environment, ensuring relevance to the viewer's immediate interests without relying on personal data. Explore the nuances of nano targeting versus contextual targeting to enhance your marketing strategy.
Why it is important
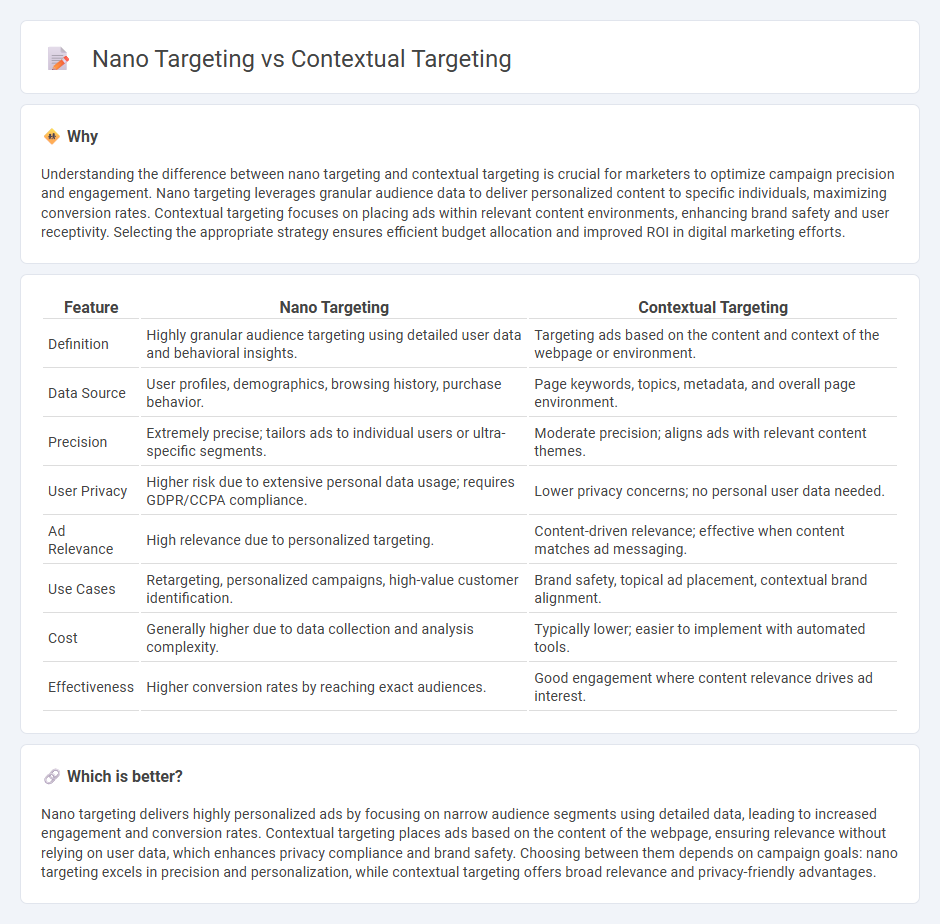
Understanding the difference between nano targeting and contextual targeting is crucial for marketers to optimize campaign precision and engagement. Nano targeting leverages granular audience data to deliver personalized content to specific individuals, maximizing conversion rates. Contextual targeting focuses on placing ads within relevant content environments, enhancing brand safety and user receptivity. Selecting the appropriate strategy ensures efficient budget allocation and improved ROI in digital marketing efforts.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Nano Targeting | Contextual Targeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Highly granular audience targeting using detailed user data and behavioral insights. | Targeting ads based on the content and context of the webpage or environment. |
| Data Source | User profiles, demographics, browsing history, purchase behavior. | Page keywords, topics, metadata, and overall page environment. |
| Precision | Extremely precise; tailors ads to individual users or ultra-specific segments. | Moderate precision; aligns ads with relevant content themes. |
| User Privacy | Higher risk due to extensive personal data usage; requires GDPR/CCPA compliance. | Lower privacy concerns; no personal user data needed. |
| Ad Relevance | High relevance due to personalized targeting. | Content-driven relevance; effective when content matches ad messaging. |
| Use Cases | Retargeting, personalized campaigns, high-value customer identification. | Brand safety, topical ad placement, contextual brand alignment. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to data collection and analysis complexity. | Typically lower; easier to implement with automated tools. |
| Effectiveness | Higher conversion rates by reaching exact audiences. | Good engagement where content relevance drives ad interest. |
Which is better?
Nano targeting delivers highly personalized ads by focusing on narrow audience segments using detailed data, leading to increased engagement and conversion rates. Contextual targeting places ads based on the content of the webpage, ensuring relevance without relying on user data, which enhances privacy compliance and brand safety. Choosing between them depends on campaign goals: nano targeting excels in precision and personalization, while contextual targeting offers broad relevance and privacy-friendly advantages.
Connection
Nano targeting and contextual targeting intersect by leveraging precise audience segmentation and relevant environmental cues to optimize ad performance. Nano targeting focuses on hyper-specific audience groups based on detailed data analytics, while contextual targeting places ads in environments that match the content and user intent. Together, they enhance marketing effectiveness by aligning targeted messages with the most appropriate digital contexts, increasing engagement and conversion rates.
Key Terms
**Contextual Targeting:**
Contextual targeting leverages real-time analysis of website content to deliver ads relevant to the user's immediate environment, enhancing engagement and brand safety. This strategy prioritizes keywords, topics, and themes within the page, ensuring ads align naturally with the content without relying on personal user data. Discover how contextual targeting can boost ad relevance and improve campaign effectiveness in today's privacy-conscious landscape.
Content Relevance
Contextual targeting delivers ads based on the specific content users are engaging with, ensuring high relevance by matching keywords, topics, and themes directly to the ad's message. Nano targeting takes personalization further by using granular data about individual users' behaviors, preferences, and micro-moments to tailor ads, achieving precise content relevance at a one-to-one level. Explore the differences in how each approach enhances user engagement through content relevance.
Keyword Matching
Contextual targeting leverages keyword matching by analyzing webpage content to serve ads relevant to specific keywords, enhancing ad relevance without relying on personal data. Nano targeting, while precise, focuses on hyper-personalized audience segments and may use behavioral data beyond keyword matches, often limiting its application to broader contextual relevance. Discover how keyword matching distinctions impact ad strategies by exploring deeper insights.
Source and External Links
What is Contextual Advertising? Why is it Important? - Amazon Ads - Contextual targeting relies solely on the current page content to display relevant ads, ensuring real-time relevance and high-quality environments.
Contextual Advertising: What it is, how it works, and why to use it - Contextual advertising uses a demand side platform (DSP) to place ads based on selected targeting parameters like keywords, topics, and more.
What is Contextual Targeting? - Integral Ad Science - Contextual targeting allows advertisers to reach audiences based on specific interests and events, enhancing ad relevance and ROI through AI-driven content classification.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com