Phantom tagging enhances targeted marketing by embedding invisible metadata within digital content to track user interaction and improve personalization, while content farming relies on producing large volumes of low-quality articles to boost search engine rankings. Marketers seeking efficient strategies must evaluate phantom tagging's precision against the scalability and SEO-driven approach of content farming. Discover how these techniques can transform your marketing strategy by exploring their unique benefits and applications.
Why it is important
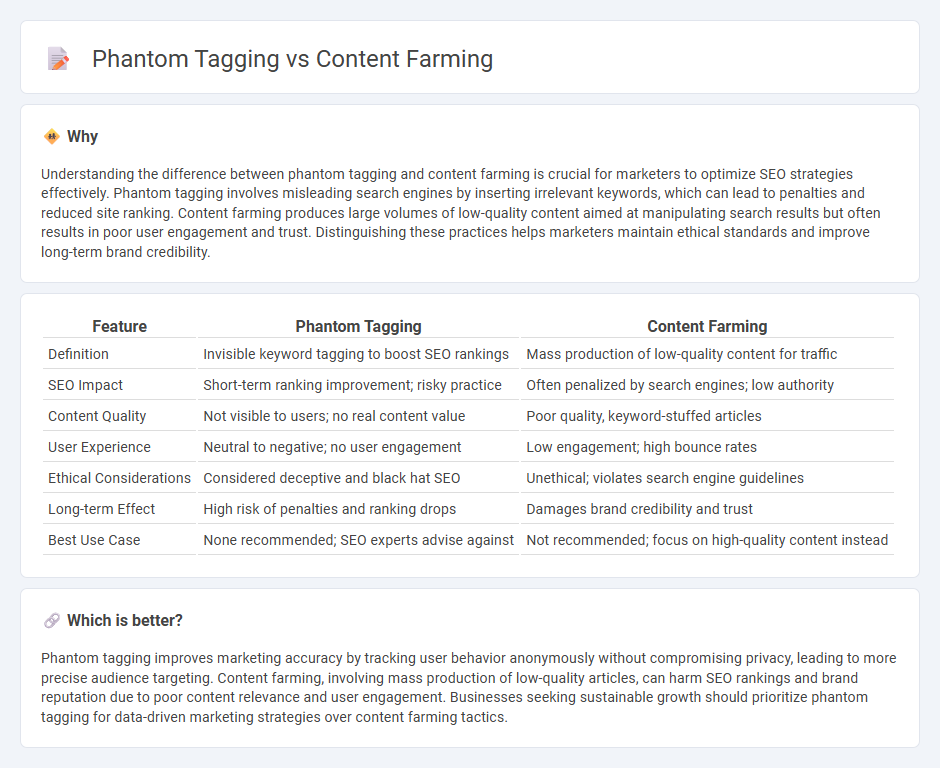
Understanding the difference between phantom tagging and content farming is crucial for marketers to optimize SEO strategies effectively. Phantom tagging involves misleading search engines by inserting irrelevant keywords, which can lead to penalties and reduced site ranking. Content farming produces large volumes of low-quality content aimed at manipulating search results but often results in poor user engagement and trust. Distinguishing these practices helps marketers maintain ethical standards and improve long-term brand credibility.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Phantom Tagging | Content Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Invisible keyword tagging to boost SEO rankings | Mass production of low-quality content for traffic |
| SEO Impact | Short-term ranking improvement; risky practice | Often penalized by search engines; low authority |
| Content Quality | Not visible to users; no real content value | Poor quality, keyword-stuffed articles |
| User Experience | Neutral to negative; no user engagement | Low engagement; high bounce rates |
| Ethical Considerations | Considered deceptive and black hat SEO | Unethical; violates search engine guidelines |
| Long-term Effect | High risk of penalties and ranking drops | Damages brand credibility and trust |
| Best Use Case | None recommended; SEO experts advise against | Not recommended; focus on high-quality content instead |
Which is better?
Phantom tagging improves marketing accuracy by tracking user behavior anonymously without compromising privacy, leading to more precise audience targeting. Content farming, involving mass production of low-quality articles, can harm SEO rankings and brand reputation due to poor content relevance and user engagement. Businesses seeking sustainable growth should prioritize phantom tagging for data-driven marketing strategies over content farming tactics.
Connection
Phantom tagging enhances content farming by embedding hidden keywords that manipulate search engine algorithms, driving more traffic to low-quality or mass-produced articles. This tactic exploits SEO strategies to boost visibility, often resulting in inflated page rankings without genuine user engagement. Both practices undermine authentic marketing efforts by prioritizing quantity and keyword density over valuable content.
Key Terms
SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
Content farming involves producing large volumes of low-quality, keyword-stuffed articles designed to manipulate search engine rankings, often resulting in poor user experience and penalization by algorithms like Google's Panda. Phantom tagging refers to the deceptive practice of embedding hidden keywords or metadata that mislead search engines without providing value to users, which can lead to severe ranking penalties and trust loss. Explore more about sustainable SEO strategies to enhance website visibility and user engagement effectively.
Clickbait
Content farming relies on mass-producing low-quality articles optimized for search engines, often using sensational headlines to generate clicks. Phantom tagging manipulates metadata and invisible keywords to artificially boost content visibility without improving substance, increasing the likelihood of users falling for clickbait. Explore the differences and impacts of these tactics to understand how they influence online engagement and trust.
Algorithm Manipulation
Content farming exploits algorithm manipulation by producing high volumes of low-quality articles stuffed with trending keywords to boost search engine rankings artificially. Phantom tagging involves embedding hidden or irrelevant keywords within content to deceive algorithms into ranking pages higher than their actual relevance justifies. Explore the nuances of these tactics to understand how they impact SEO strategies and search engine integrity.
Source and External Links
What is content farming & how does it work? - Epidemic Sound - Content farming involves websites that publish large volumes of low-quality, often unrelated content like memes, videos, and articles to generate high traffic and monetize through ads and affiliate links, often relying on freelancers or AI for swift production.
Content farm - Wikipedia - Content farms produce massive amounts of web content tailored to exploit search engine algorithms, often using freelance writers or AI, aiming to maximize ad revenue despite criticism for sensationalism, misinformation, and low pay for creators.
INTERNET REVIEWS: THE RISE OF CONTENT FARMS - Content farms research popular web topics and employ freelancers to create articles paid by view counts, generating income primarily through selling advertisements placed on their content pages.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com