The loyalty loop model emphasizes customer retention and repeat purchases by creating seamless, personalized experiences that foster brand loyalty. The Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) model quantifies the total revenue a business can expect from a single customer over the entire duration of their relationship. Explore how integrating both models can enhance marketing strategies and maximize long-term profitability.
Why it is important
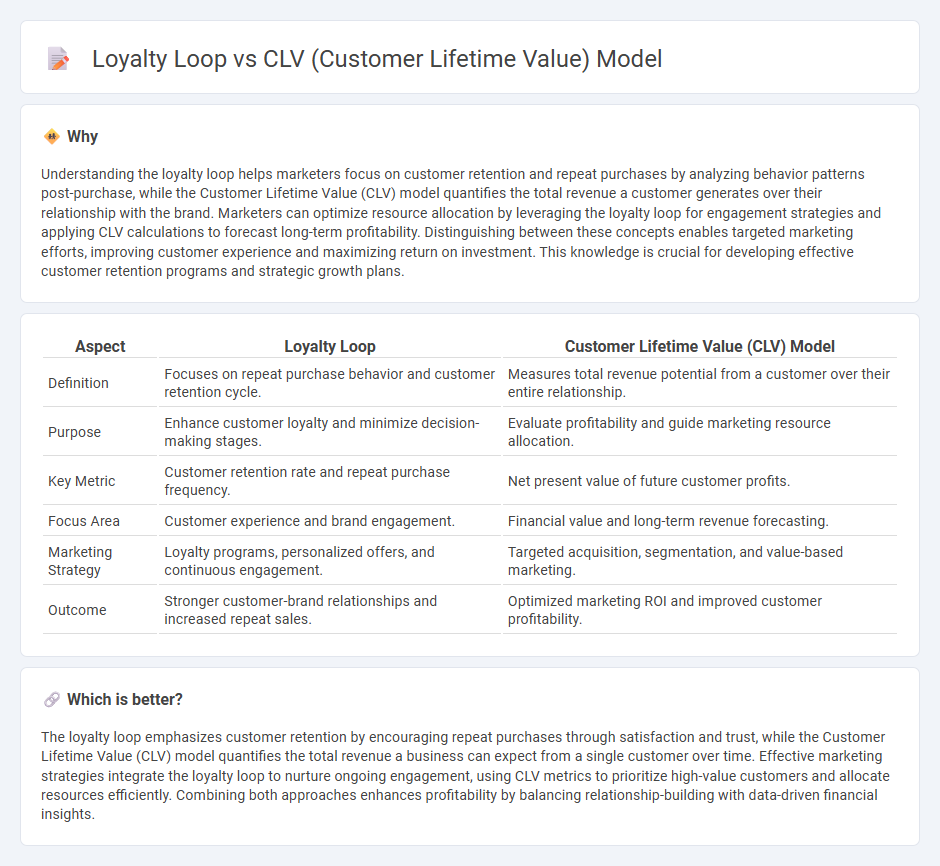
Understanding the loyalty loop helps marketers focus on customer retention and repeat purchases by analyzing behavior patterns post-purchase, while the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) model quantifies the total revenue a customer generates over their relationship with the brand. Marketers can optimize resource allocation by leveraging the loyalty loop for engagement strategies and applying CLV calculations to forecast long-term profitability. Distinguishing between these concepts enables targeted marketing efforts, improving customer experience and maximizing return on investment. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective customer retention programs and strategic growth plans.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Loyalty Loop | Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) Model |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on repeat purchase behavior and customer retention cycle. | Measures total revenue potential from a customer over their entire relationship. |
| Purpose | Enhance customer loyalty and minimize decision-making stages. | Evaluate profitability and guide marketing resource allocation. |
| Key Metric | Customer retention rate and repeat purchase frequency. | Net present value of future customer profits. |
| Focus Area | Customer experience and brand engagement. | Financial value and long-term revenue forecasting. |
| Marketing Strategy | Loyalty programs, personalized offers, and continuous engagement. | Targeted acquisition, segmentation, and value-based marketing. |
| Outcome | Stronger customer-brand relationships and increased repeat sales. | Optimized marketing ROI and improved customer profitability. |
Which is better?
The loyalty loop emphasizes customer retention by encouraging repeat purchases through satisfaction and trust, while the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) model quantifies the total revenue a business can expect from a single customer over time. Effective marketing strategies integrate the loyalty loop to nurture ongoing engagement, using CLV metrics to prioritize high-value customers and allocate resources efficiently. Combining both approaches enhances profitability by balancing relationship-building with data-driven financial insights.
Connection
The loyalty loop enhances Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) by fostering repeated purchases and deeper customer engagement through personalized experiences and consistent satisfaction. By focusing on retaining customers within the loyalty loop, businesses increase the frequency and value of transactions, directly boosting CLV metrics. Integrating loyalty loop strategies with CLV analysis enables marketers to identify high-value customers and allocate resources efficiently for maximum long-term profitability.
Key Terms
Retention Rate
The Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) model quantifies the total revenue a business can expect from a customer throughout their relationship, emphasizing long-term profitability by optimizing retention rate and maximizing repeat purchases. The loyalty loop, meanwhile, centers on creating a seamless experience post-purchase that fosters ongoing customer engagement and loyalty, directly impacting retention rate through continuous satisfaction and brand advocacy. Explore how integrating CLV modeling with loyalty loop strategies can elevate retention rates and drive sustainable business growth.
Customer Journey
The CLV (Customer Lifetime Value) model emphasizes quantifying the total revenue a customer will generate over their entire relationship with a brand, guiding marketing decisions based on long-term profitability. The loyalty loop focuses on the customer journey stages--consideration, purchase, retention, and advocacy--to create repeated engagement and drive customer loyalty beyond the initial sale. Explore how integrating CLV metrics with the loyalty loop framework can optimize customer retention and maximize business growth.
Repeat Purchase
The CLV (Customer Lifetime Value) model quantitatively predicts the total revenue a customer will generate over their lifetime, emphasizing long-term profitability through repeat purchases and retention strategies. The loyalty loop focuses on customer behavior patterns that encourage repeat buying by simplifying decision-making and reinforcing brand loyalty without the need for traditional marketing funnels. Explore how integrating CLV analytics with loyalty loop mechanisms can maximize customer retention and business growth.
Source and External Links
What is Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)? - Customer lifetime value (CLV) is the total profit or worth a customer brings to a business over the entire duration of their relationship, helping organizations understand customer retention and loyalty beyond single transactions.
What Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) Is & How to Calculate It - CLV measures the average revenue a company expects from a customer throughout their relationship, aiding in better marketing, sales, and customer segmentation decisions.
What is Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)? - CLV is calculated by multiplying the average revenue per customer by their typical lifespan and subtracting the total costs of serving them, providing a net profit perspective for each customer relationship.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com