Phantom tagging inflates advertising metrics by falsely attributing user actions to marketing campaigns, while click fraud generates illegitimate clicks to deplete ad budgets without genuine engagement. Both practices distort data analytics and undermine digital advertising ROI, making accurate detection crucial for marketers. Explore effective strategies to combat phantom tagging and click fraud for optimized marketing performance.
Why it is important
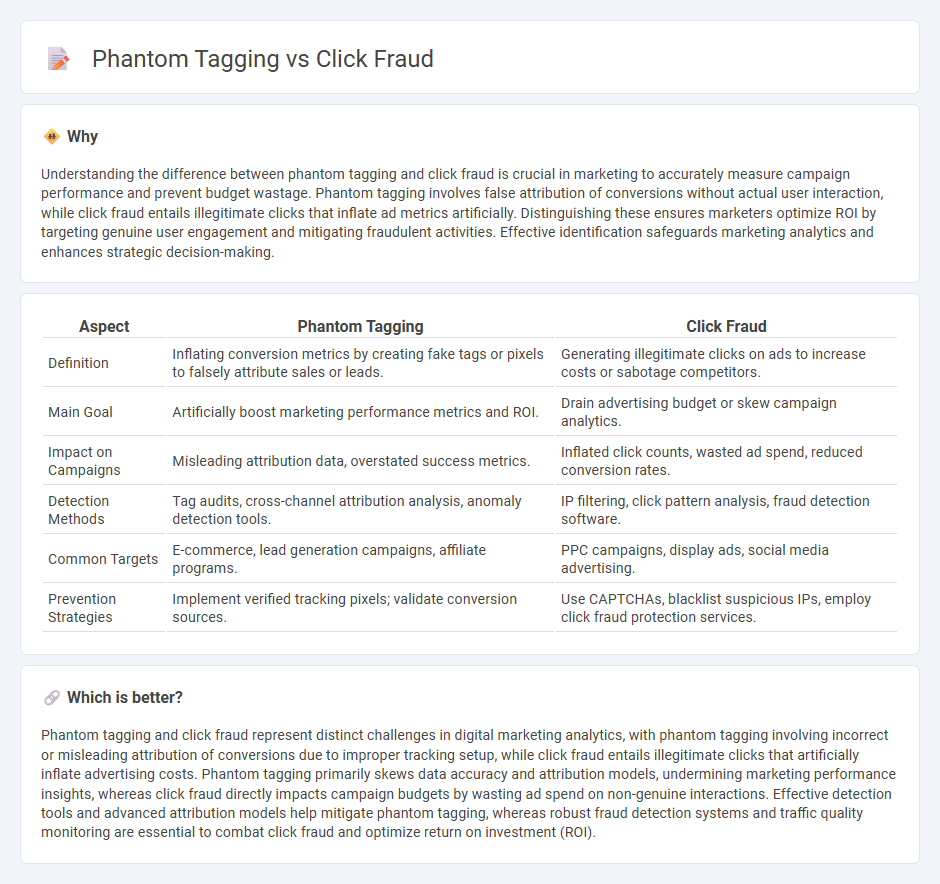
Understanding the difference between phantom tagging and click fraud is crucial in marketing to accurately measure campaign performance and prevent budget wastage. Phantom tagging involves false attribution of conversions without actual user interaction, while click fraud entails illegitimate clicks that inflate ad metrics artificially. Distinguishing these ensures marketers optimize ROI by targeting genuine user engagement and mitigating fraudulent activities. Effective identification safeguards marketing analytics and enhances strategic decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Phantom Tagging | Click Fraud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflating conversion metrics by creating fake tags or pixels to falsely attribute sales or leads. | Generating illegitimate clicks on ads to increase costs or sabotage competitors. |
| Main Goal | Artificially boost marketing performance metrics and ROI. | Drain advertising budget or skew campaign analytics. |
| Impact on Campaigns | Misleading attribution data, overstated success metrics. | Inflated click counts, wasted ad spend, reduced conversion rates. |
| Detection Methods | Tag audits, cross-channel attribution analysis, anomaly detection tools. | IP filtering, click pattern analysis, fraud detection software. |
| Common Targets | E-commerce, lead generation campaigns, affiliate programs. | PPC campaigns, display ads, social media advertising. |
| Prevention Strategies | Implement verified tracking pixels; validate conversion sources. | Use CAPTCHAs, blacklist suspicious IPs, employ click fraud protection services. |
Which is better?
Phantom tagging and click fraud represent distinct challenges in digital marketing analytics, with phantom tagging involving incorrect or misleading attribution of conversions due to improper tracking setup, while click fraud entails illegitimate clicks that artificially inflate advertising costs. Phantom tagging primarily skews data accuracy and attribution models, undermining marketing performance insights, whereas click fraud directly impacts campaign budgets by wasting ad spend on non-genuine interactions. Effective detection tools and advanced attribution models help mitigate phantom tagging, whereas robust fraud detection systems and traffic quality monitoring are essential to combat click fraud and optimize return on investment (ROI).
Connection
Phantom tagging and click fraud both manipulate digital advertising metrics to create false engagement signals, inflating campaign performance data. Phantom tagging involves embedding invisible tracking tags that simulate user actions, while click fraud generates illegitimate clicks to drain ad budgets and distort analytics. Together, these deceptive practices undermine the accuracy of marketing attribution and ROI measurement.
Key Terms
Invalid Traffic
Click fraud involves deceptive clicks generated to inflate ad costs, while phantom tagging refers to fake user interactions that distort campaign analytics, both contributing to invalid traffic. Invalid traffic includes non-human or illegitimate ad engagements that skew performance metrics, leading to wasted ad spend and inaccurate ROI assessments. Explore in-depth strategies to detect and prevent invalid traffic for optimized ad campaign results.
Bot Activity
Click fraud involves automated bots generating illegitimate clicks on ads to deplete budgets, while phantom tagging refers to bots creating fake user tags or conversions to skew analytics data. Both exploit bot activity to manipulate digital marketing metrics, but click fraud directly impacts ad spend whereas phantom tagging distorts user behavior insights. Explore how advanced bot detection technologies differentiate and mitigate these threats for improved campaign accuracy.
Ad Attribution
Click fraud involves artificially inflating ad clicks through bots or malicious users to deplete budgets and skew performance metrics, while phantom tagging refers to incorrect or fraudulent attribution of user actions using fake or manipulated tags. Both practices distort ad attribution, leading to misleading ROI data and inefficient marketing spend. Explore how to detect and prevent these issues to ensure accurate ad campaign measurement and optimization.
Source and External Links
What Is Click Fraud? How to Identify and Prevent It - Click fraud is the practice of artificially inflating clicks on pay-per-click ads using methods such as click farms, botnets, pixel stuffing, and competitor sabotage.
What is click fraud? | How click bots work - Click fraud involves fake clicks on ads, links, or social media to deceive platforms into thinking real users are interacting, often driven by bots for financial gain or to harm competitors.
Click fraud - Click fraud occurs in pay-per-click advertising when a person, script, or program imitates a legitimate user to click on ads without genuine interest, increasing costs for advertisers and potentially benefiting publishers and ad networks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com