Ethnographic listening captures in-depth consumer behavior and cultural contexts through qualitative observation, providing rich insights into customer motivations and experiences. A/B testing quantitatively compares variations of marketing elements to identify the most effective option based on performance metrics and user responses. Explore the unique strengths of ethnographic listening and A/B testing to enhance your marketing strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between ethnographic listening and A/B testing is crucial for marketing as ethnographic listening provides deep qualitative insights into consumer behavior through observational research, while A/B testing offers quantitative data by comparing variable performance to optimize campaigns. Ethnographic listening uncovers emotional and cultural contexts that drive purchasing decisions. A/B testing identifies the most effective marketing elements with statistical rigor. Combining both approaches leads to more informed, customer-centric marketing strategies.
Comparison Table
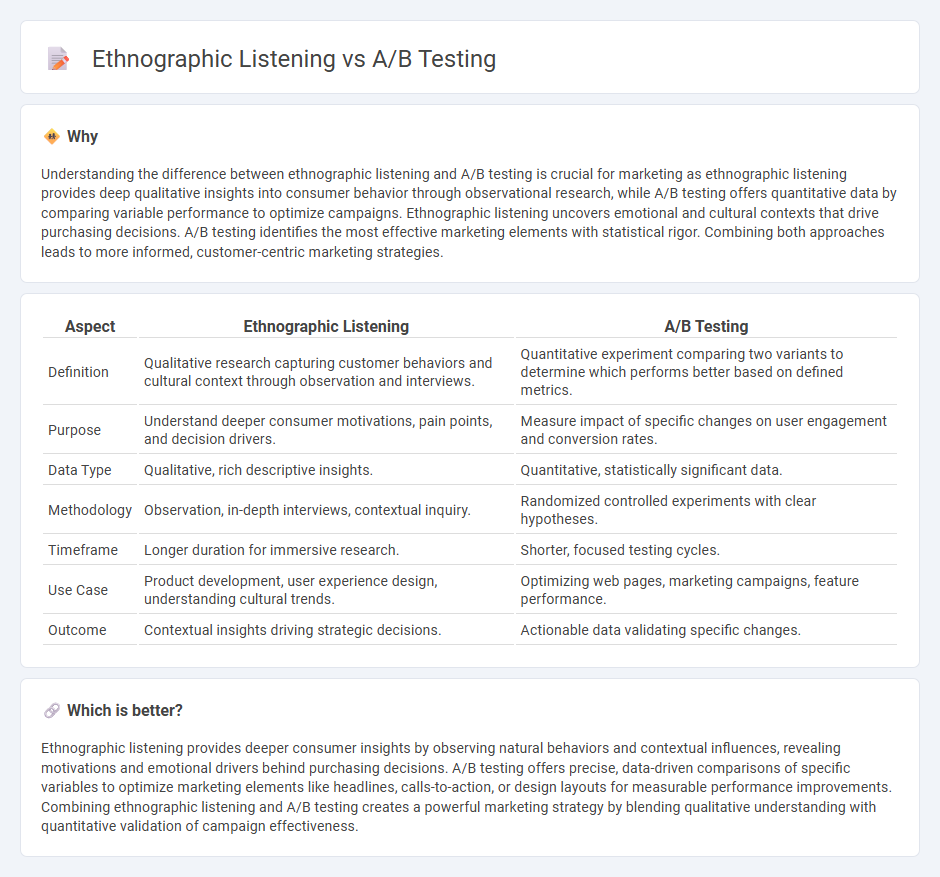
| Aspect | Ethnographic Listening | A/B Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Qualitative research capturing customer behaviors and cultural context through observation and interviews. | Quantitative experiment comparing two variants to determine which performs better based on defined metrics. |
| Purpose | Understand deeper consumer motivations, pain points, and decision drivers. | Measure impact of specific changes on user engagement and conversion rates. |
| Data Type | Qualitative, rich descriptive insights. | Quantitative, statistically significant data. |
| Methodology | Observation, in-depth interviews, contextual inquiry. | Randomized controlled experiments with clear hypotheses. |
| Timeframe | Longer duration for immersive research. | Shorter, focused testing cycles. |
| Use Case | Product development, user experience design, understanding cultural trends. | Optimizing web pages, marketing campaigns, feature performance. |
| Outcome | Contextual insights driving strategic decisions. | Actionable data validating specific changes. |
Which is better?
Ethnographic listening provides deeper consumer insights by observing natural behaviors and contextual influences, revealing motivations and emotional drivers behind purchasing decisions. A/B testing offers precise, data-driven comparisons of specific variables to optimize marketing elements like headlines, calls-to-action, or design layouts for measurable performance improvements. Combining ethnographic listening and A/B testing creates a powerful marketing strategy by blending qualitative understanding with quantitative validation of campaign effectiveness.
Connection
Ethnographic listening provides deep qualitative insights into consumer behaviors and cultural contexts, which inform the design of more relevant A/B tests. By integrating ethnographic data, marketers can create targeted hypotheses that increase the accuracy and effectiveness of A/B testing outcomes. This synergy enhances decision-making by combining rich user narratives with quantitative performance metrics.
Key Terms
Split Testing
Split testing, or A/B testing, compares two versions of a webpage or app to measure which performs better based on user interactions and conversion rates. This method relies on quantitative data to optimize design, content, and functionality by isolating variables and analyzing statistical outcomes. Explore more insights on how Split Testing can enhance user experience and drive effective decision-making.
Qualitative Observation
A/B testing provides quantitative data by comparing user responses to two different variants, enabling precise measurement of performance metrics such as click-through rates and conversions. Ethnographic listening emphasizes qualitative observation, capturing in-depth user behaviors and motivations through immersive engagement and contextual understanding. Explore how integrating these approaches can enhance your user experience analysis.
User Behavior
A/B testing provides quantitative insights by comparing user responses to different variations of a product or feature, highlighting which version performs better in achieving set goals. Ethnographic listening offers qualitative depth through observing and engaging with users in their natural environments, revealing underlying motivations and context behind behaviors. Explore deeper into how these methods can uniquely inform product development and user experience strategies.
Source and External Links
What is A/B testing? With examples - Optimizely - A/B testing is a method to compare two versions of a webpage or app by splitting user traffic randomly to determine which performs better using statistical analysis, turning optimization into data-informed decisions.
A/B testing - Wikipedia - A/B testing is a simple randomized controlled experiment comparing two variants to see which performs better, often used in marketing campaigns to measure user response to different calls to action.
A/B Testing 101 - NN/g - A/B testing is a quantitative UX research method that compares two or more design versions by splitting live traffic to determine which variation best supports business objectives, using statistical significance to decide implementation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com