Dark social refers to the untraceable sharing of content through private channels like messaging apps and email, which significantly complicates attribution modeling by obscuring the true source of traffic and conversions. Attribution modeling relies on tracking user interactions across multiple touchpoints to accurately assign credit to marketing efforts, but struggles to capture dark social activity due to its hidden nature. Explore how integrating dark social data can enhance attribution accuracy and improve marketing ROI.
Why it is important
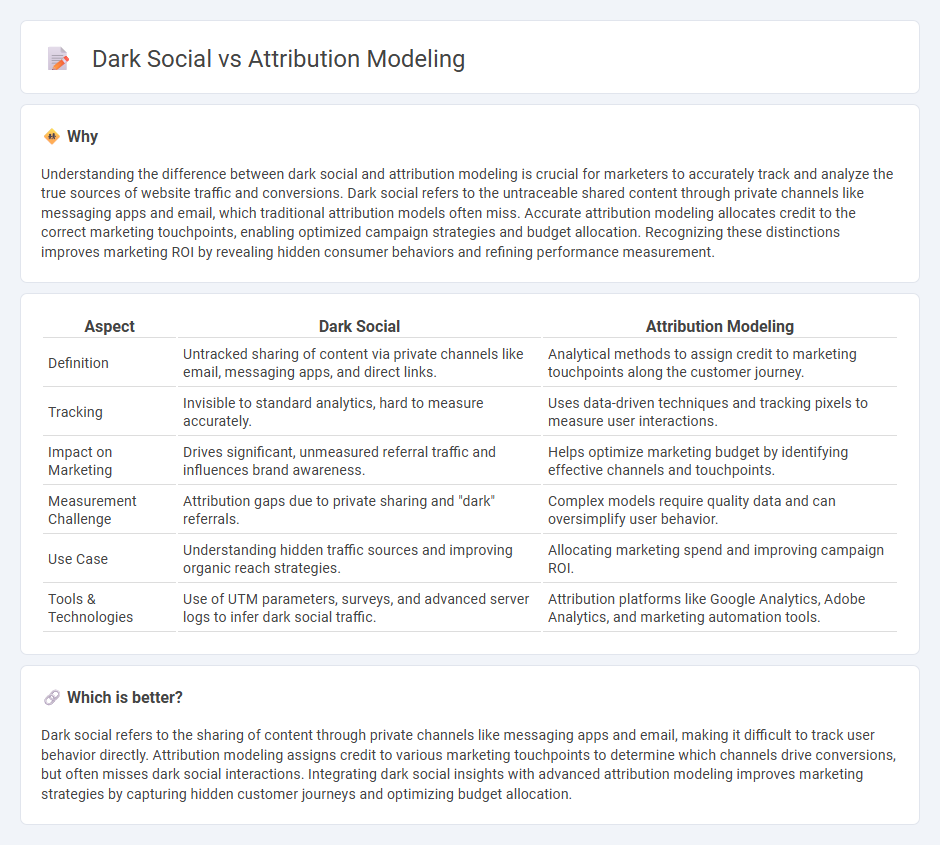
Understanding the difference between dark social and attribution modeling is crucial for marketers to accurately track and analyze the true sources of website traffic and conversions. Dark social refers to the untraceable shared content through private channels like messaging apps and email, which traditional attribution models often miss. Accurate attribution modeling allocates credit to the correct marketing touchpoints, enabling optimized campaign strategies and budget allocation. Recognizing these distinctions improves marketing ROI by revealing hidden consumer behaviors and refining performance measurement.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Social | Attribution Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Untracked sharing of content via private channels like email, messaging apps, and direct links. | Analytical methods to assign credit to marketing touchpoints along the customer journey. |
| Tracking | Invisible to standard analytics, hard to measure accurately. | Uses data-driven techniques and tracking pixels to measure user interactions. |
| Impact on Marketing | Drives significant, unmeasured referral traffic and influences brand awareness. | Helps optimize marketing budget by identifying effective channels and touchpoints. |
| Measurement Challenge | Attribution gaps due to private sharing and "dark" referrals. | Complex models require quality data and can oversimplify user behavior. |
| Use Case | Understanding hidden traffic sources and improving organic reach strategies. | Allocating marketing spend and improving campaign ROI. |
| Tools & Technologies | Use of UTM parameters, surveys, and advanced server logs to infer dark social traffic. | Attribution platforms like Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics, and marketing automation tools. |
Which is better?
Dark social refers to the sharing of content through private channels like messaging apps and email, making it difficult to track user behavior directly. Attribution modeling assigns credit to various marketing touchpoints to determine which channels drive conversions, but often misses dark social interactions. Integrating dark social insights with advanced attribution modeling improves marketing strategies by capturing hidden customer journeys and optimizing budget allocation.
Connection
Dark social refers to the sharing of content through private channels like messaging apps and email, which traditional analytics tools often fail to track accurately. Attribution modeling helps marketers assign credit to various touchpoints in the customer journey, but dark social complicates this process by obscuring key referral data. Integrating dark social insights into attribution models enhances the accuracy of marketing ROI measurement and improves campaign optimization strategies.
Key Terms
**Attribution Modeling:**
Attribution modeling analyzes the customer journey by assigning value to each touchpoint, helping marketers understand which channels or campaigns drive conversions effectively. Dark social refers to traffic from private sharing channels, such as messaging apps or email, that traditional analytics tools cannot easily track, posing challenges for accurate attribution. Explore how advanced attribution modeling techniques can help uncover the impact of dark social and refine marketing strategies.
Multi-touch Attribution
Multi-touch attribution assigns credit to multiple marketing touchpoints influencing a consumer's purchase decision, providing granular insights into channel performance across digital campaigns. Dark social refers to traffic from private channels like messaging apps and email, often invisible to traditional analytics, challenging accurate attribution. Explore advanced multi-touch attribution techniques to better capture dark social impact and enhance marketing ROI measurement.
Conversion Path
Attribution modeling analyzes conversion paths by assigning credit to marketing touchpoints, enabling marketers to understand which channels drive sales. Dark social, representing traffic from private sharing channels like messaging apps, often escapes traditional attribution models, causing underreported conversion sources. Explore how integrating dark social insights can refine your attribution strategy and accurately measure conversion paths.
Source and External Links
A Beginner's Guide to Attribution Model Frameworks - Amplitude - Attribution modeling is a framework that assigns credit to different marketing activities for conversions, helping businesses understand which channels and touchpoints drive sales, with models classified as single-touch or multi-touch (including linear, rule-based, and algorithmic) depending on the strategy and budget.
About attribution modeling - Campaign Manager 360 Help - Attribution modeling consists of rules that assign credit for sales and conversions to various touchpoints along conversion paths, such as the Last Interaction model that assigns credit to the final touchpoint or the First Interaction model that credits the initial touchpoint.
Attribution models: What they are, why they matter, when to use them - Multi-touch attribution models include variations such as linear (equal credit to all touchpoints), time decay (more credit to recent interactions), U-shaped (most credit to first and last touchpoints, 40% each), W-shaped (credit split among first, last, and qualified lead touchpoints), and Z-shaped (weighted credit to key sales funnel points).
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com